Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4413-4418
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4413
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4413
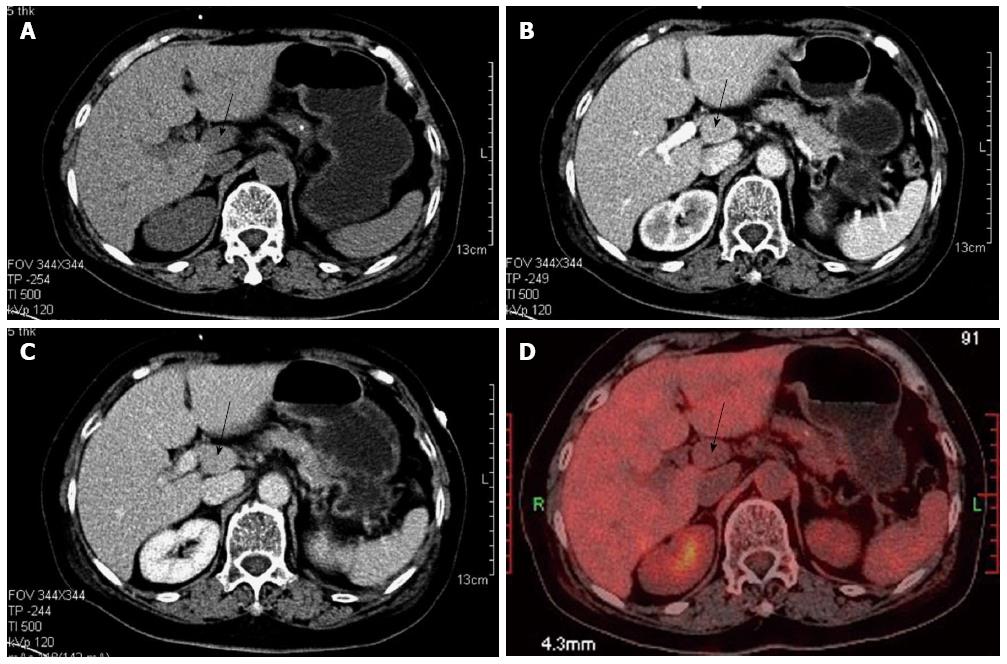
Figure 1 Radiologic findings.
A: Plain scanning-phase computed tomography (CT); B: Arterial enhancement-phase CT; C: Equilibrium-phase CT showing the tumor (black arrow) in the retroperitoneum; D: Positron emission tomography showing the tumor in the retroperitoneum with no 18fluorodeoxyglucose activity.
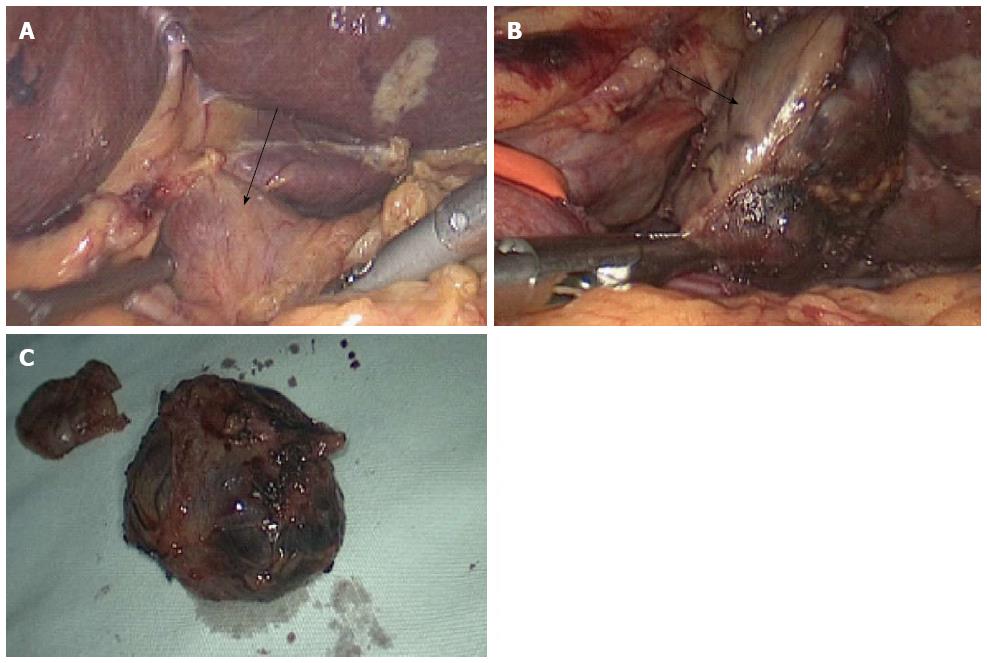
Figure 2 Tumor imaging during surgery.
A: An isolated, pink, slightly hard tumor was clearly identified under and left of the hepatoduodenal ligament (black arrow); B: Resection of the tumor was successfully performed using a harmonic scalpel with a laparoscopic approach (black arrow); C: Tumor specimen.
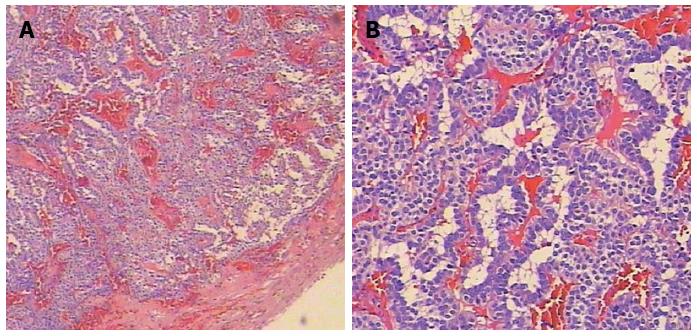
Figure 3 Pathologic results.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining showing the tumor capsule and submucosal infiltration (A: Magnification × 40; B: Magnification × 100).
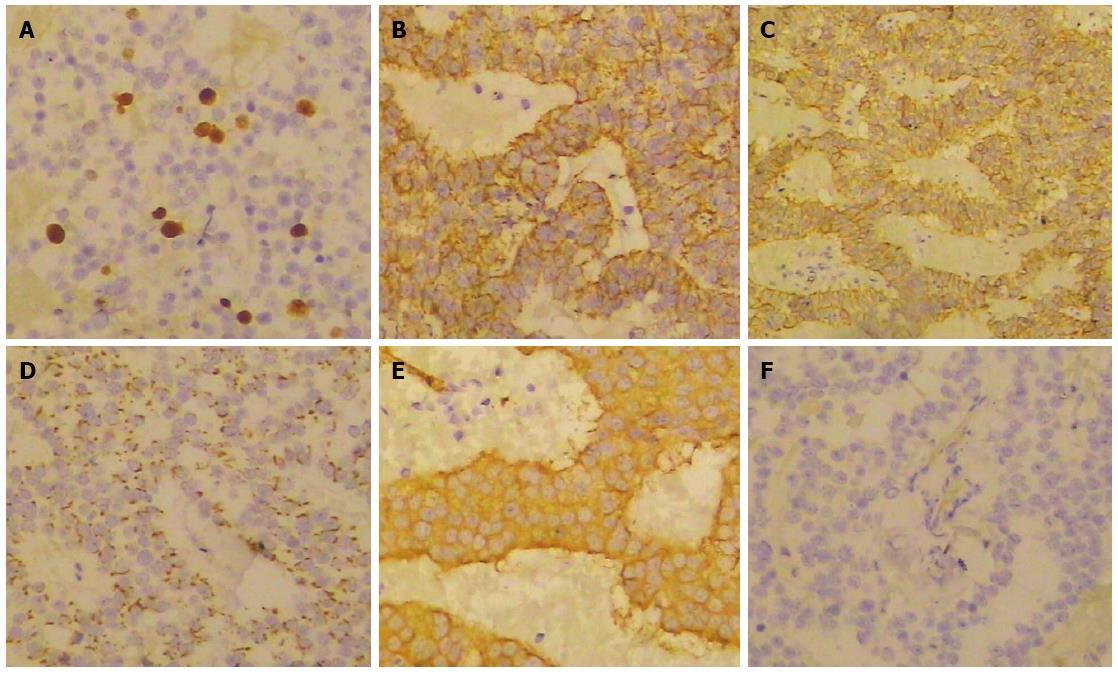
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical findings.
Tumor cells were immunoreactive for Ki67 (A), Insulin (B), CD56 (C), Chromogranin A (D), Synaptophysin (E), but negative for Serotonin (F).
- Citation: Liu J, Zhang CW, Hong DF, Wu J, Yang HG, Chen Y, Zhao DJ, Zhang YH. Laparoscope resection of retroperitoneal ectopic insulinoma: A rare case. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4413-4418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4413.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4413