Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4126-4135
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4126
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4126
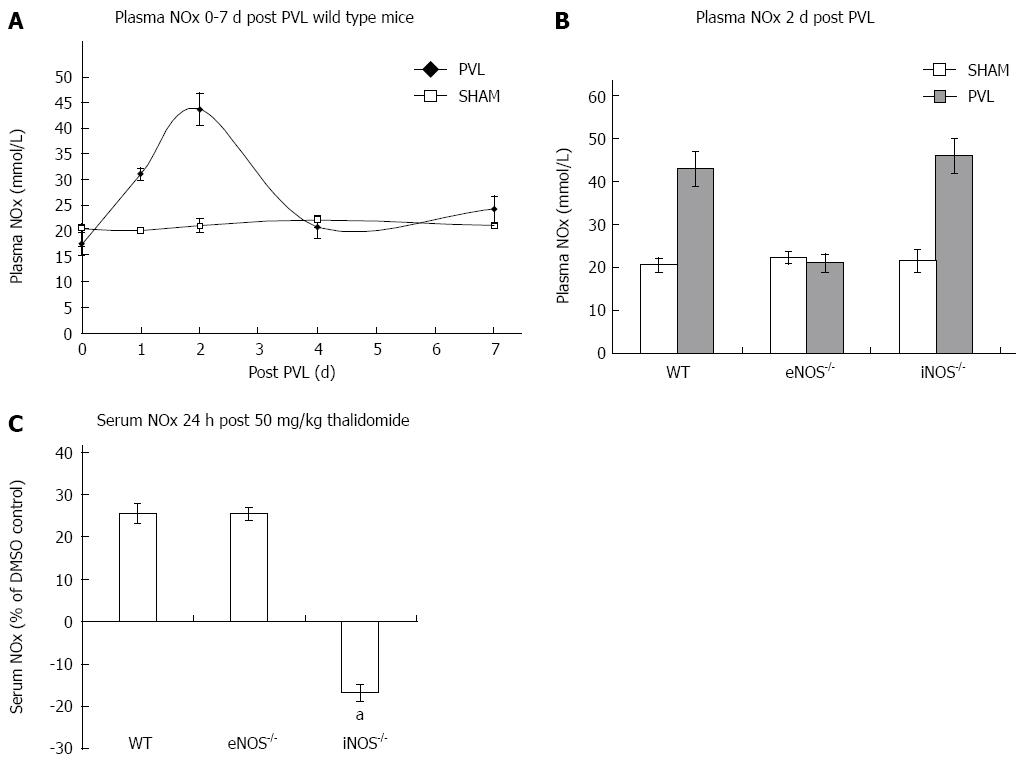
Figure 1 Portal vein ligation and thalidomide increases nitric oxide via endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthase respectively.
Plasma total nitrate (NOx) was measured daily for 7 d in wild type (WT), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-/- and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-/- mice following portal vein ligation (PVL) or sham surgery. A: Plasma NOx increased following PVL in wild type mice but not following sham surgery. Levels increased to a maximum 2 d after PVL, after which NOx returned to pre-surgical baseline; B: Plasma NOx increased 2 d following PVL in iNOS-/- but not eNOS mice. In eNOS-/- mice NO was not increased following PVL; C: Unadulterated 8 wk WT, eNOS-/- and iNOS-/- mice were given 50 mg/kg thalidomide or vehicle. Blood was collected by cardiac puncture and plasma was assayed for NOx. Plasma NOx was significantly increased by the administration of thalidomide in WT and eNOS-/- mice but was reduced in iNOS-/- mice. aP < 0.05 vs other groups.
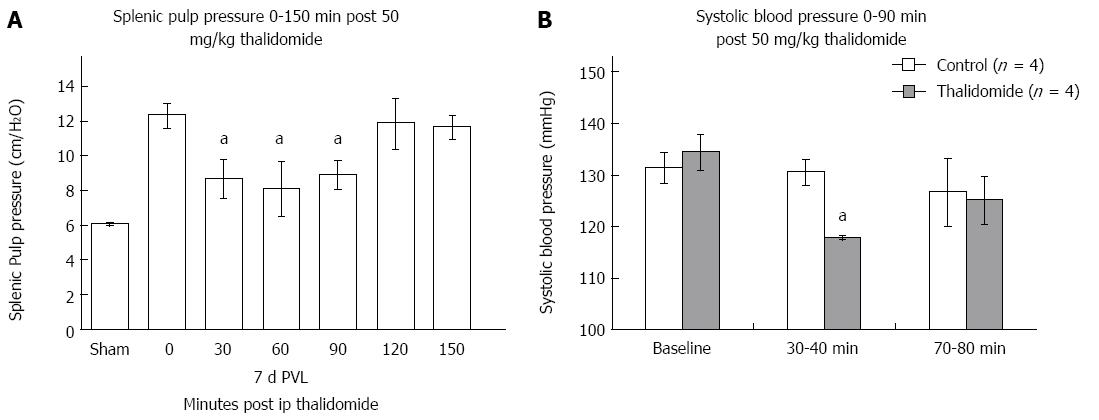
Figure 2 Thalidomide temporarily ameliorates splenic pulp pressure and mean systolic blood pressure in 7 d portal vein ligation mice.
A: 7 d wild type sham and portal vein ligation (PVL) mice were treated with 50 mg/kg thalidomide ip and splenic pulp pressure was measured 0-150 min following administration. Splenic pulp pressure was rapidly and temporarily decreased by thalidomide; after 2 h pressure returned back to pre-thalidomide levels; B: Systolic blood pressure was also measured in 7 d PVL wild type mice following the administration of 50 mg/kg thalidomide or vehicle control. In a similar manner to splenic pulp pressure the systolic blood pressure was temporarily decreased by thalidomide. aP < 0.05 vs control group.
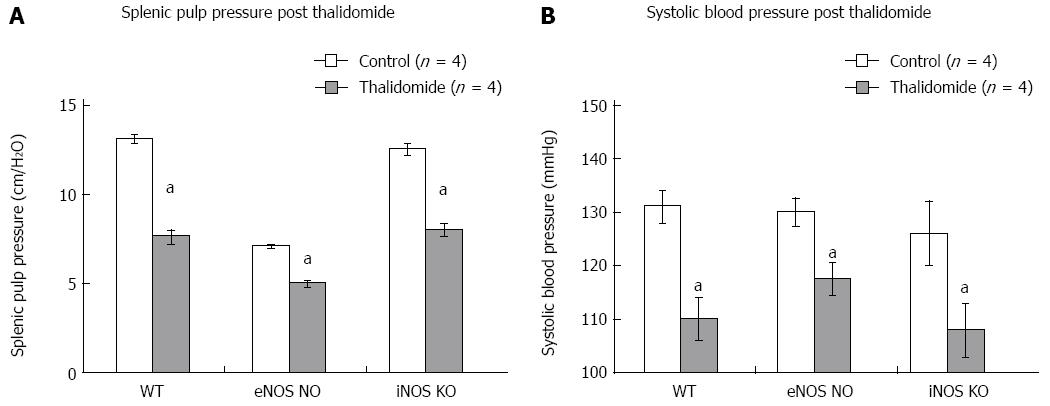
Figure 3 Thalidomide reduction of splenic pulp pressure and systolic blood pressure is endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthase independent.
7 d portal vein ligation wild type, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-/- and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-/- mice were treated with 50 mg/kg thalidomide or dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle control ip. Splenic pulp pressure (A) and systolic blood pressure (B) were measure 60 min after administration. Thalidomide reduced splenic pulp pressure and systolic pulp pressure in wild type, eNOS-/- and iNOS-/- mice (n = 4 mice per group, aP < 0.05 vs control group).
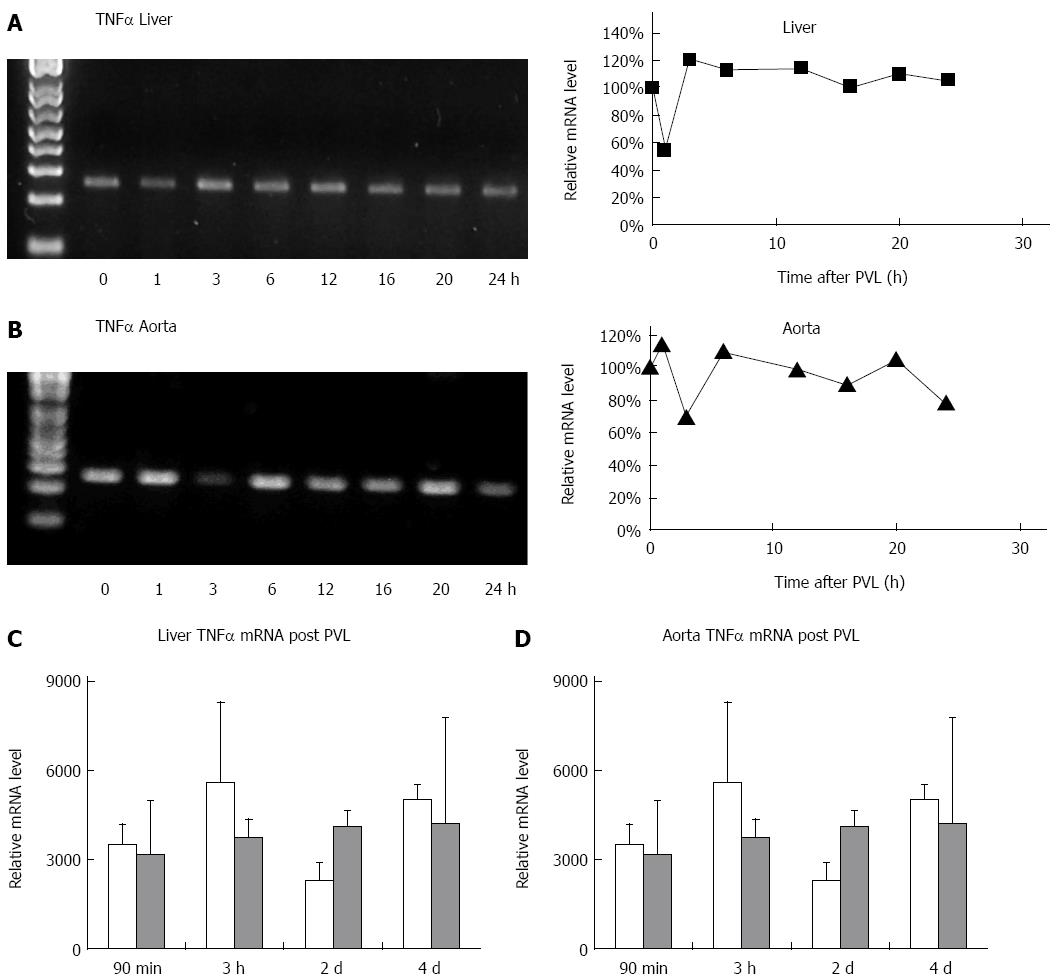
Figure 4 Portal vein ligation does not increase hepatic or aortic tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA expression.
Pre-hepatic portal hypertension was induced in wild type mice by partial ligation of the portal vein. 0-24 h post ligation livers (A) and thoracic aortas (B) were harvested and quantified for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) mRNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. TNFα was not changed within livers and aorta following portal vein ligation (PVL). Figures are representative of three experiments. Hepatic (C) and aortic (D) TNFα expression was unchanged 0-4 d post PVL. Line graphs represent mean ± SE. n = 5 mice.
-
Citation: Theodorakis NG, Wang YN, Korshunov VA, Maluccio MA, Skill NJ. Thalidomide ameliorates portal hypertension
via nitric oxide synthase independent reduced systolic blood pressure. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4126-4135 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4126.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4126