Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18480-18486
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18480
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18480
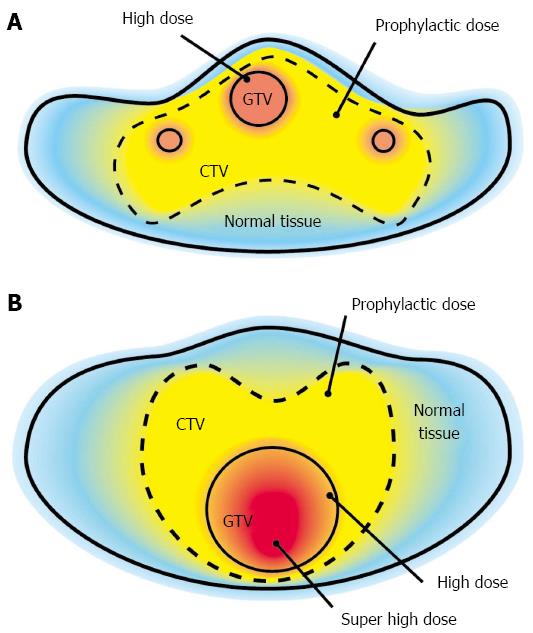
Figure 1 Simultaneous integrated boost irradiation.
A: The concept behind standard simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) irradiation. A prophylactic dose is delivered to clinical target volume, and a curative (higher) dose is delivered to gross tumor volume (GTV). Dose distribution within GTV is usually homogeneous; B: The concept of the modified SIB irradiation technique. It is almost the same as the standard SIB technique, but the modified SIB technique can deliver a much higher dose to the part of GTV without excessive irradiation of the surrounding healthy tissue by allowing for heterogeneity of dose distribution within GTV.
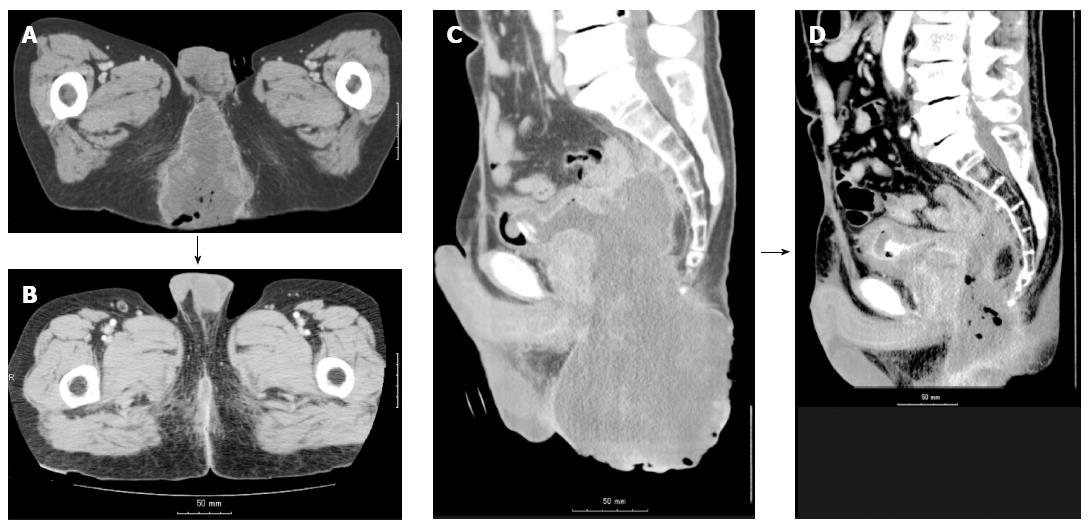
Figure 2 Computed tomography image.
A: An axial computed tomography (CT) image before radiotherapy. A massive tumor is seen in the perineum, and a part of the tumor is protruding. Both lower extremities are elevated because the patient could not stretch both legs. B: An axial CT image on day 120 from the start of the radiotherapy. The macroscopic tumor disappeared, and the patient could stretch both lower extremities; C: A sagittal CT image before the radiotherapy; D: A part of the bladder wall has been lost to invasion of the massive solid tumor.
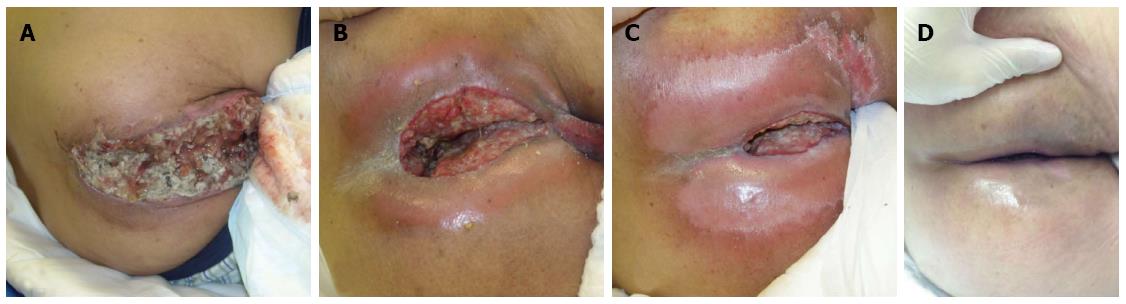
Figure 3 Macroscopic findings before radiotherapy.
A: Day 0. The tumor is exposed from the perineum with oozing of blood, offensive odor and sever pain; B: Day 28 from the start of radiotherapy. The tumor was shrinking due to the modified SIB technique. Leakage of urine from a bladder fistula was observed; C: Day 56. Further tumor shrinkage is observed, but a slight residual tumor is present. The defect in the healthy tissue was shrinking; D: Day 180. The macroscopic tumor as well as exposure of the mucosa also disappeared. The patient could walk normally.
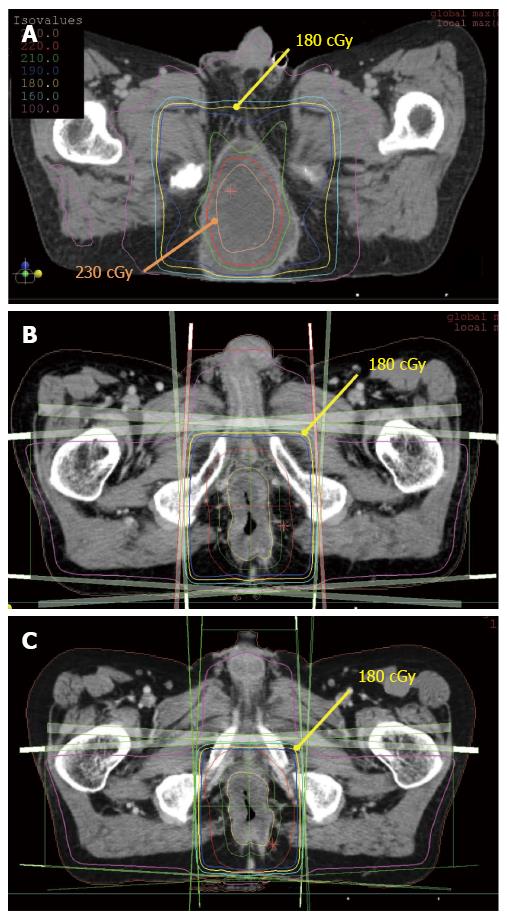
Figure 4 Radiotherapy planning.
A: The initial radiotherapy planning (RTP). RTP consists of eight static fields using the modified simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) technique. The central part of gross tumor volume (GTV) is irradiated with 230 cGy per fraction. A total dose of 36 Gy per 20 fractions was delivered to the whole pelvis, and a total dose of 46 Gy per 20 fractions was delivered to a part of GTV; B: The second RTP for this patient (Usual boost irradiation. Not the modified SIB technique); C: The third RTP for this patient (not the modified SIB technique).
- Citation: Nomiya T, Akamatsu H, Harada M, Ota I, Hagiwara Y, Ichikawa M, Miwa M, Kawashiro S, Hagiwara M, Chin M, Hashizume E, Nemoto K. Modified simultaneous integrated boost radiotherapy for an unresectable huge refractory pelvic tumor diagnosed as a rectal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18480-18486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18480.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18480