Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17737-17745
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17737
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17737
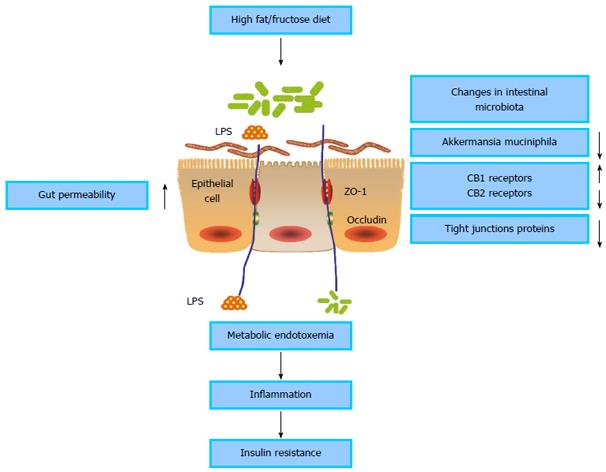
Figure 1 Influence of the intestinal microbiota in promoting gut permeability and insulin resistance.
Changes in the intestinal microbiota reduce tight junction proteins of gut epithelial cells and increase gut permeability, thus promoting metabolic endotoxemia and insulin resistance. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
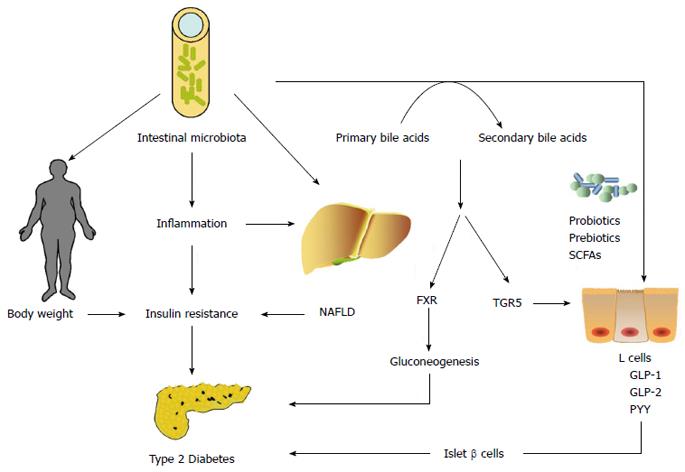
Figure 2 Role of the intestinal microbiota in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
The intestinal microbiota may play an important role in the onset of type 2 diabetes by influencing body weight, bile acid metabolism, proinflammatory activity, NAFLD and insulin resistance, and modulating gut hormones. NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; GLP: Glucagon-like peptide; PYY: Peptide YY.
- Citation: Han JL, Lin HL. Intestinal microbiota and type 2 diabetes: From mechanism insights to therapeutic perspective. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17737-17745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17737.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17737