Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17426-17433
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17426
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17426
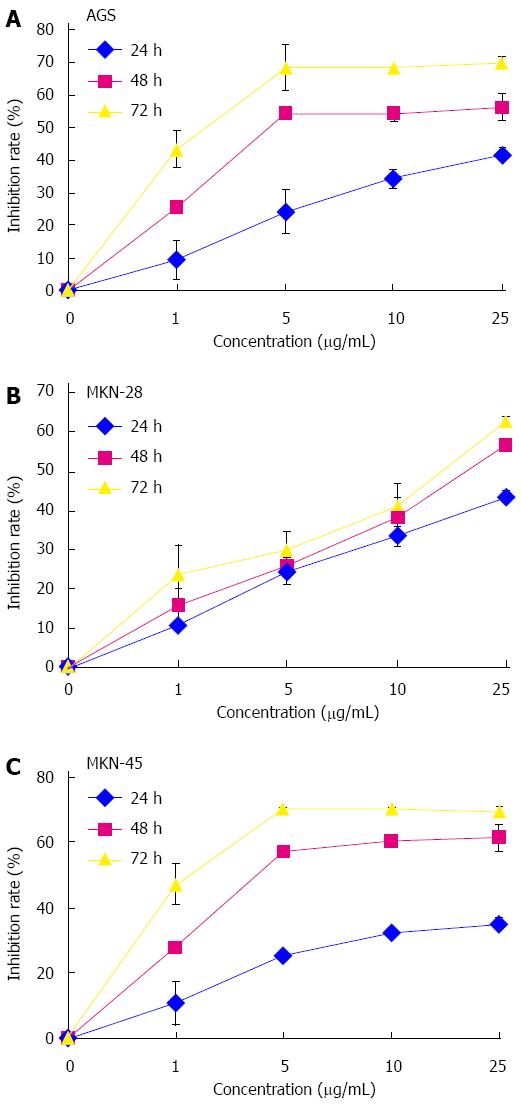
Figure 1 Cytotoxicities of lobaplatin in human gastric cancer cell lines.
Cells were exposed to various concentrations of the compound (0, 1, 5, 10 and 25 μg/mL) for 24, 48, and 72 h followed by analysis by CCK-8 assay. A: AGS; B: MKN-28; C: MKN-45. All of the assays were performed in triplicate.
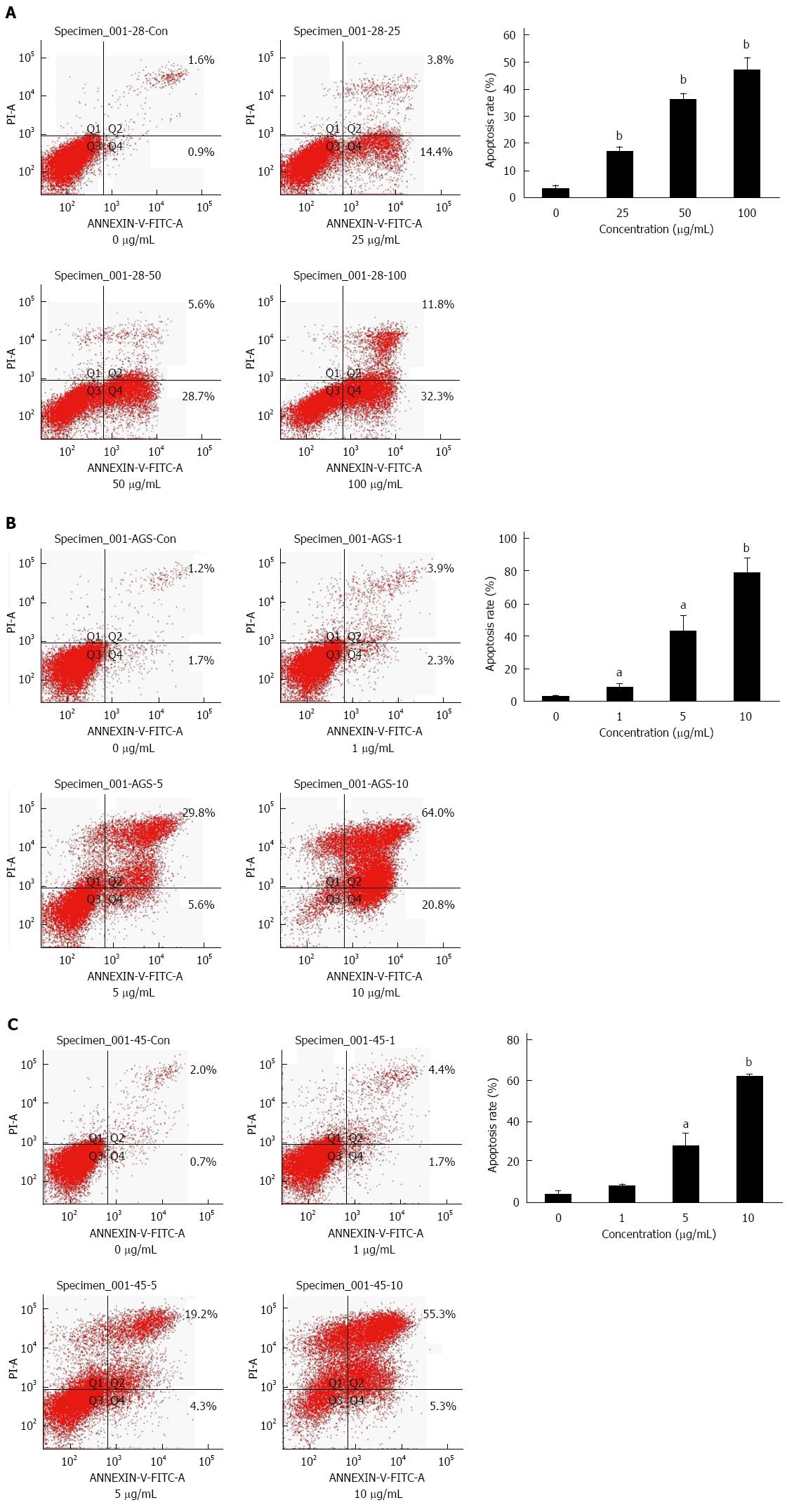
Figure 2 Induction of apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells by lobaplatin treatment.
MKN-28 (A), AGS (B), and MKN-45 (C) cells were exposed to various concentrations of lobaplatin (0, 1, 5 and 10 μg/mL or 0, 25, 50 and 100 μg/mL) for 24 h and their apoptosis ratios were analyzed using the Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit. All assays were performed in triplicate. aP < 0.05 vs control group; bP < 0.01 vs control group.
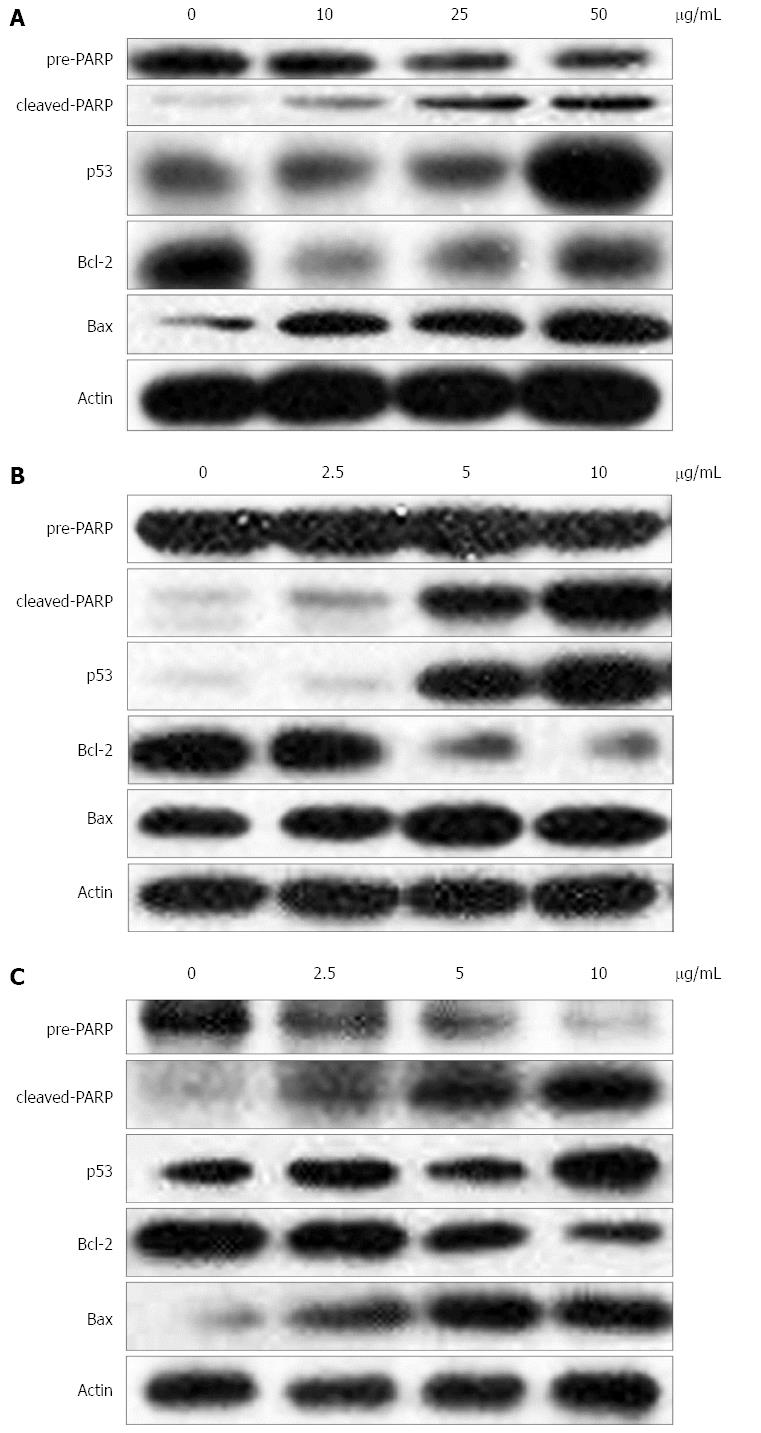
Figure 3 Cellular expression of apoptosis-related proteins was determined by Western blot after gastric cells were exposed to various concentrations (0, 5, 25 and 50 μg/mL) of lobaplatin for 24 h.
A: MKN-28; B: AGS; C: MKN-45.
- Citation: Yin CY, Lin XL, Tian L, Ye M, Yang XY, Xiao XY. Lobaplatin inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17426-17433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17426.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17426