Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 16381-16386
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16381
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16381
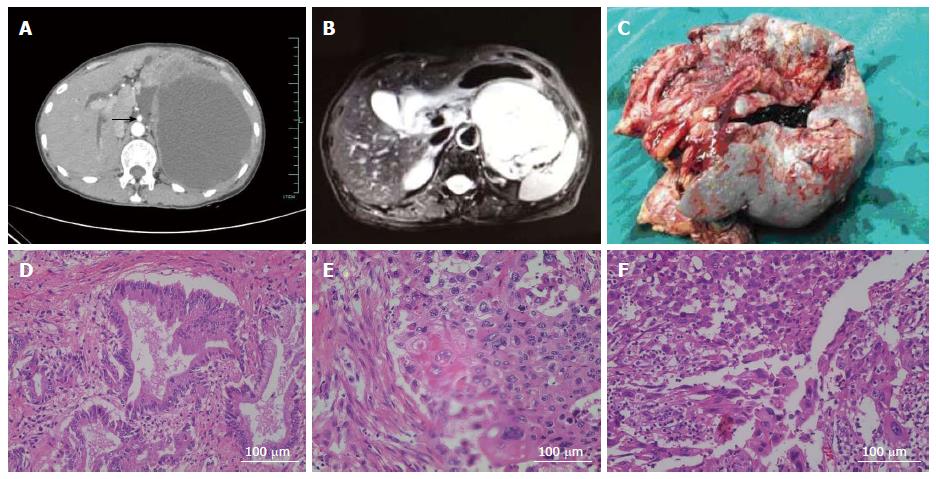
Figure 1 Imaging and pathological diagnosis of the neoplasm.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan of lesion, arrow: superior mesenteric artery; B: Magnetic resonance imaging scan of lesion; C: the resected specimen in operation; D-F: Pathological examination identified three different cellular components within the lesion, including adenocarcinoma (D), squamous carcinoma (E) and sarcomatoid change (F).
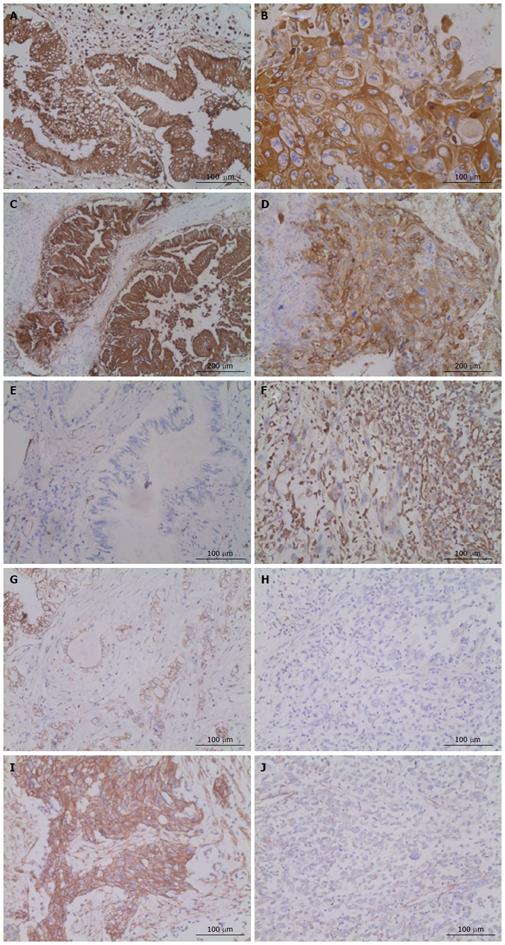
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry of different cellular components within the lesion.
A, B: cytokeratin 7 was examined in the lesion of adenocarcinoma (A) and squamous carcinoma (B); C, D: Carcinoma antigen 19-9 was examined in the lesion of adenocarcinoma (C) and squamous carcinoma (D); E, F: Vimentin was examined in the lesion of adenocarcinoma (E) and sarcomatoid change (F); G, H: E-cadherin was examined in the lesion of adenocarcinoma (G) and sarcomatoid change (H); I, J: p63 was examined in the lesion of squamous carcinoma (I) and sarcomatoid change (J).
- Citation: Lu BC, Wang C, Yu JH, Shen ZH, Yang JH. A huge adenosquamous carcinoma of the pancreas with sarcomatoid change: An unusual case report. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 16381-16386
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/16381.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16381