Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2014; 20(41): 15037-15048
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15037
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15037
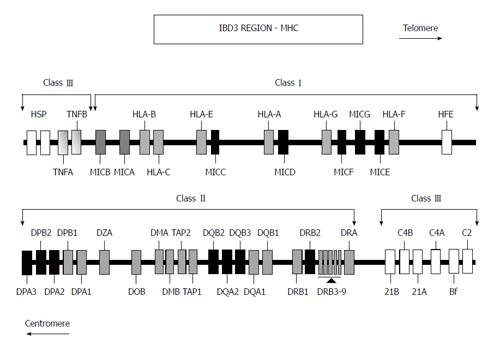
Figure 1 Localization of the MIC genes in the major histocompatibility complex class I region on the short arm of human chromosome six.
Classical human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I locus (HLA-A, -B and -C), non-classical MHC (HLA-E, -F and -G) (grey boxes), and TNF-α and HFE (white box) are shown. Pseudogenes are painted in black boxes.
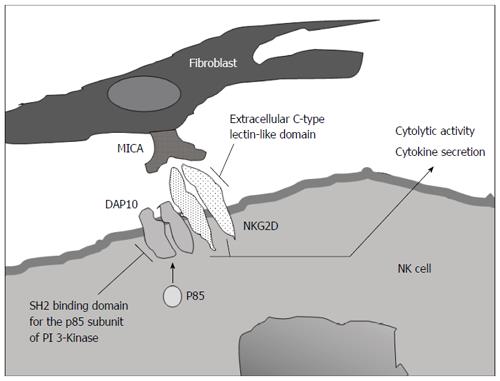
Figure 2 NKG2D signalling requires association with the DAP10 adapter protein.
Engagement of NKG2D on NK cells [e.g., via binding of the ligand MHC class I chain-related molecule A (MICA)] can trigger cytolytic activity. It can also elicit cytokine production (e.g., MIP-1β, TNF-α and IFN-γ)[7].
-
Citation: Muro M, López-Hernández R, Mrowiec A. Immunogenetic biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases: Role of the
IBD3 region. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(41): 15037-15048 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i41/15037.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15037