Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2014; 20(38): 13966-13972
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13966
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13966
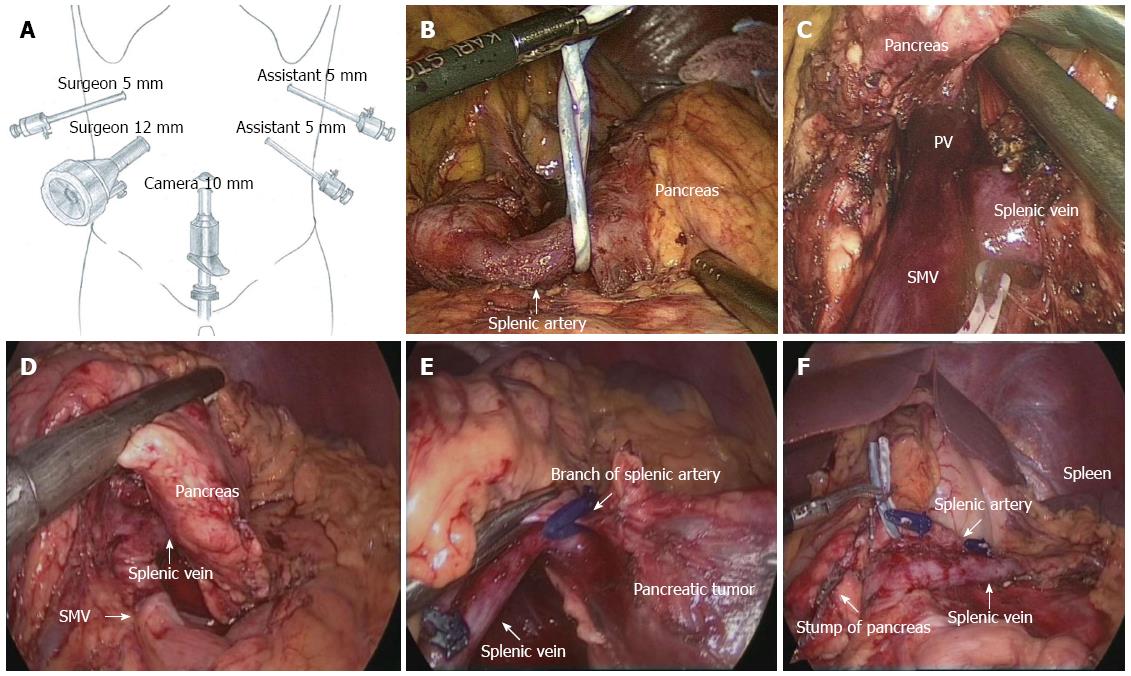
Figure 1 Surgical procedure of laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy (Kimura’s technique).
A: Trocar placement for LSPDP; B: The splenic artery was temporarily tied with a rubber band at its root in LSPDP; C: Mobilizing the inferior border of the pancreas and revealing the splenic vein; D: Transection of the pancreas with an endoscopic stapler; E: Branches of the splenic artery underwent ligation using a harmonic scalpel; F: Check the proximal pancreatic stump and splenic vessels after LSPDP. LSPDP: Laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy; PV: Portal vein; SMV: Superior mesenteric vein.
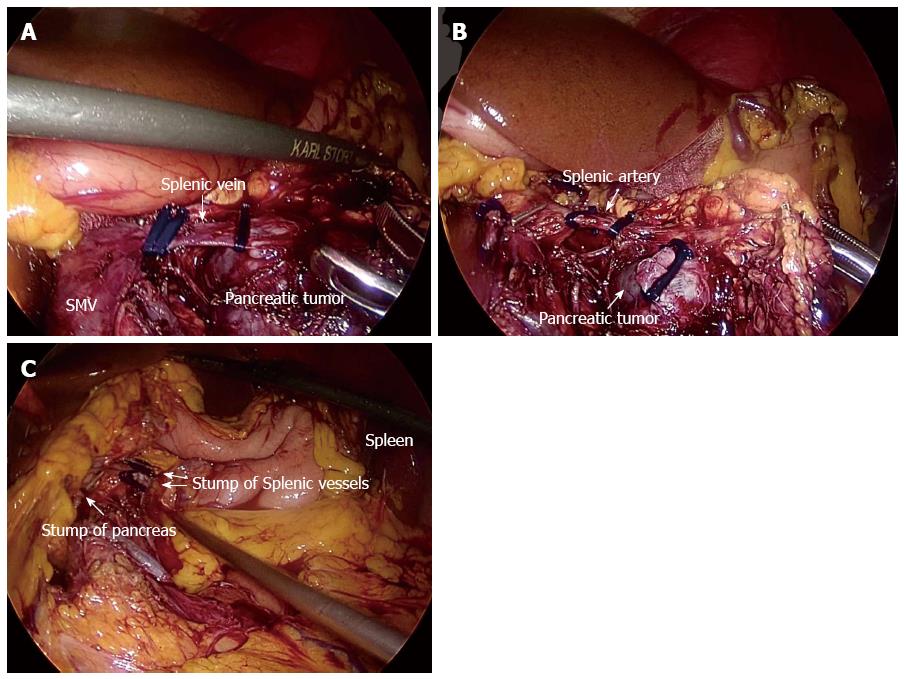
Figure 2 Surgical procedure of laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy (Warshaw’s technique).
A: Dissect the splenic vein at its root, which was surrounded by the pancreatic mass; B: Dissect the splenic artery; C: Check the proximal pancreatic stump and spleen after LSPDP with ligation of splenic vessels. LSPDP: Laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy; SMV: Superior mesenteric vein.
- Citation: Yan JF, Xu XW, Jin WW, Huang CJ, Chen K, Zhang RC, Harsha A, Mou YP. Laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic neoplasms: A retrospective study. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(38): 13966-13972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i38/13966.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13966