Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2014; 20(36): 12767-12780
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767
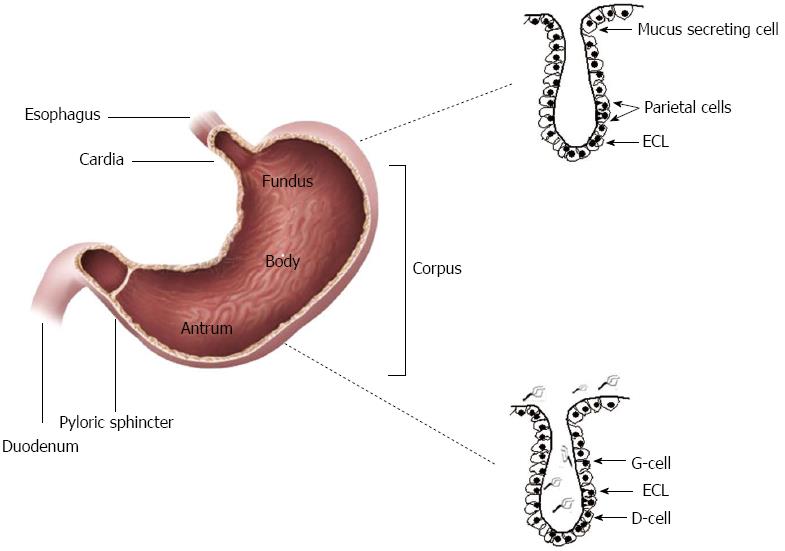
Figure 1 Helicobacter pylori colonization the antrum of the stomach.
The gastric epithelium consists of a single layer of cells that invaginate in order to form cardiac, oxyntic or/and pyloric gland. Cardiac glands are located closest to the esophagus, while the oxyntic glands located in the fundus and corpus of the stomach and contain chief cells, parietal cells and enterochromaffine-like cells (ECL). Pyloric glands which located in the antrum contain G and D cells. H. pylori colonization is only limited to the antrum of the stomach.
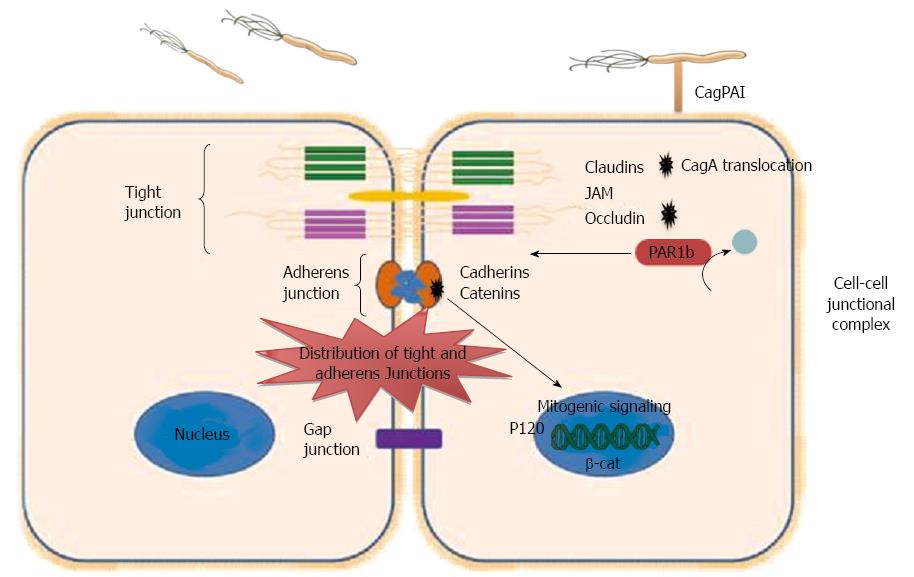
Figure 2 Dysregulation of epithelial junction by Helicobacter pylori.
Intercellular junctions include tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap. Tight junction consists of important Integral membrane proteins, such as occludin, claudins, and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs), while adheren junction consists of Catenins and Cadherins. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) interact with cell-cell junctions and disrupt the polarity of polarized epithelial cells. Translocated CagA binds to PAR1b and inhibits its activity and blocks its phosphorylation by atypical protein kinase C, eventually causing junctional and polarity defects. CagA interacts with E-cadherin leads to the release of E-cadherin from the E-cadherin/β-catenin adherent complex, results in buildup of β-catenin at the cytoplasm and nuclear translocation of β-catenin and p120, and activation of β-catenin-mediated signaling that induces transformation of gastric epithelial cells. CagPAI: Cag pathogenicity island.
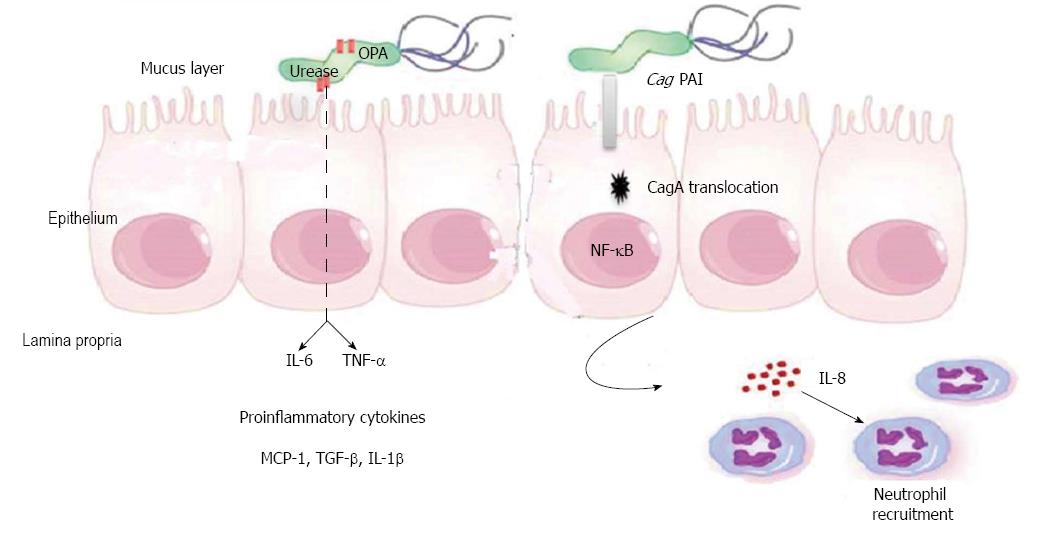
Figure 3 Cytokines production by gastric epithelial cell during Helicobacter pylori Infection.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) leads to production of proinflammatory cytokines by gastric epithelial cells (GECs). Interactions between the translocated cagA and gastric epithelial cells lead to activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, alteration in gene transcription in the GECs, and secretion of IL-8 by GECs, which leads to recruitment of neutrophils. H. pylori urease induces the production of IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by GECs. Other cytokines secreted by GECs during H. pylori infection such as, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-1α, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), migration inhibitory factor and tumor growth factor (TGF)-α.
-
Citation: Alzahrani S, Lina TT, Gonzalez J, Pinchuk IV, Beswick EJ, Reyes VE. Effect of
Helicobacter pylori on gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(36): 12767-12780 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i36/12767.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767