Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2014; 20(28): 9392-9404
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9392
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9392
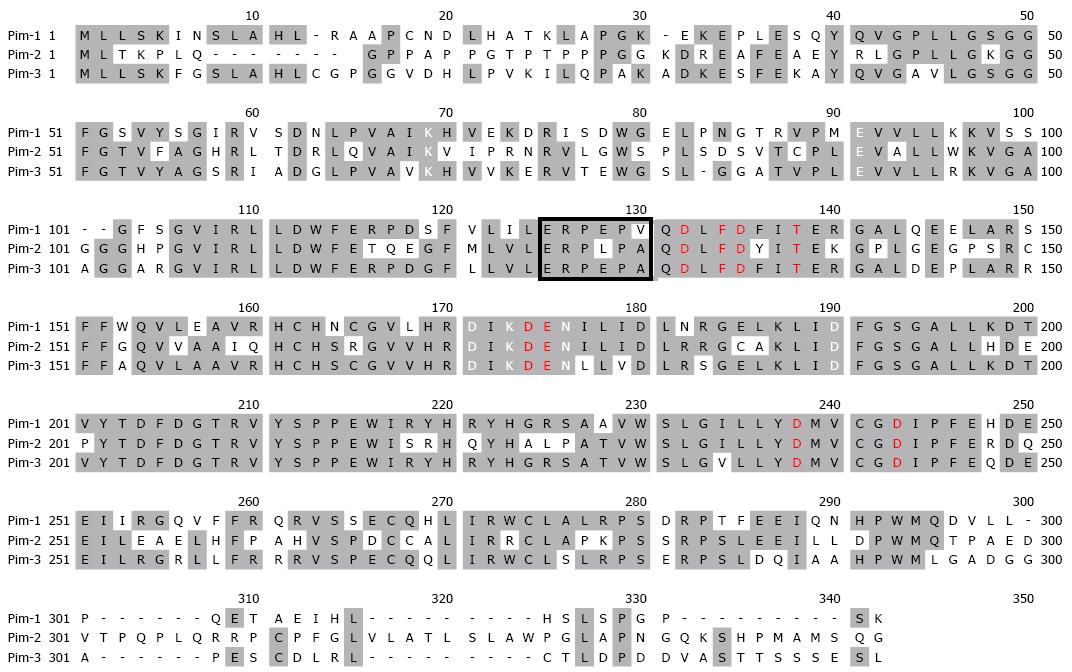
Figure 1 Amino acid alignment of human Pim family proteins[13].
The amino acid sequences of human Pim family kinases are aligned and common residues shared with Pim-3 are highlighted. The box indicates the hinge region. Residues marked with white and red are important for adenosine triphosphate binding and substrate selectivity, respectively.
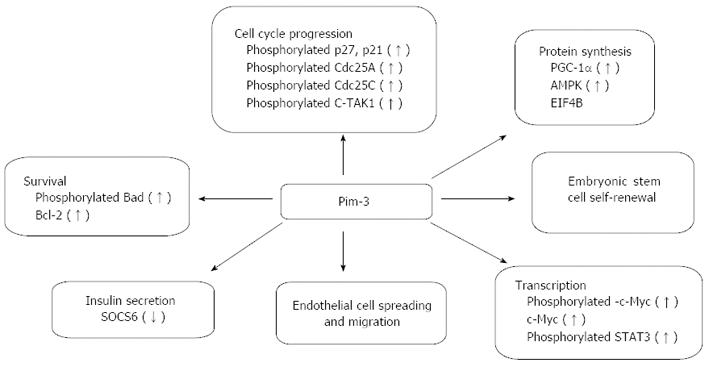
Figure 2 Presumed biological functions of Pim-3.
Pim-3 can interact with various target molecules, and thereby regulates various biological pathways including apoptosis, cell cycle, protein synthesis, and transcription.
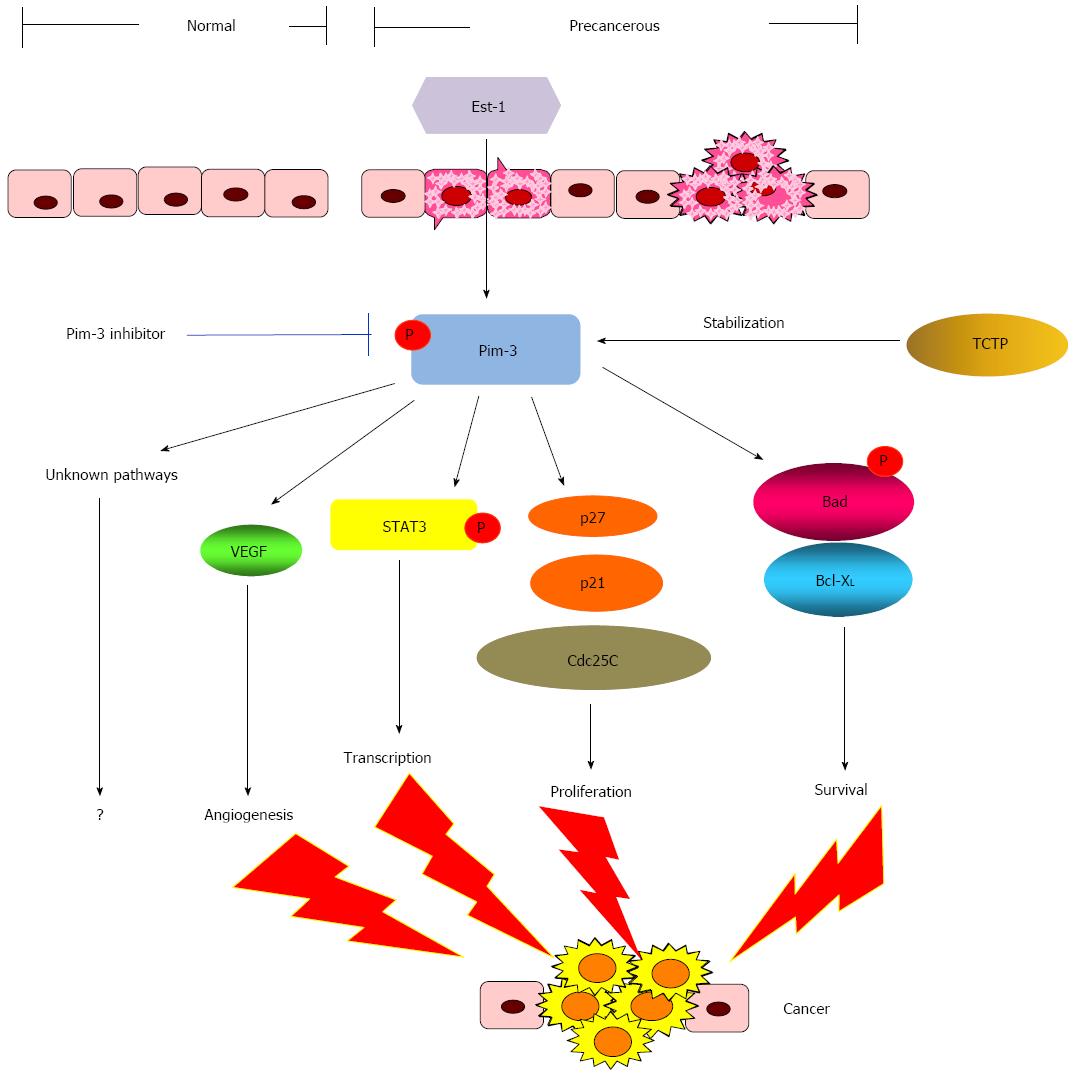
Figure 3 Presumed roles of Pim-3 in pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Pim-3 expression is regulated at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels by transcription factors (such as Ets-1) and post-translational controllers (such as translationally controlled tumor protein), respectively. Pim-3 kinase activation contributes to pancreatic carcinogenesis by inducing cell survival, cell cycle progression, gene transcription, protein synthesis in tumor cells, and angiogenesis.
- Citation: Li YY, Mukaida N. Pathophysiological roles of Pim-3 kinase in pancreatic cancer development and progression. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(28): 9392-9404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i28/9392.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9392