Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2014; 20(18): 5411-5419
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5411
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5411
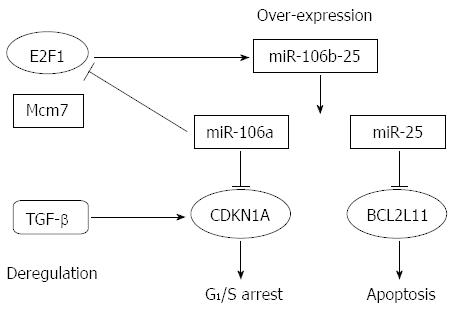
Figure 1 Functions of microRNA-106b-25.
By interfering with the expression of CDKN1 (p2lWaf1/Cip1) and BCL2L11 (Bim), the interaction of miR-106b-25 with E2F1 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) affects the cell cycle and apoptosis. miR: microRNA.
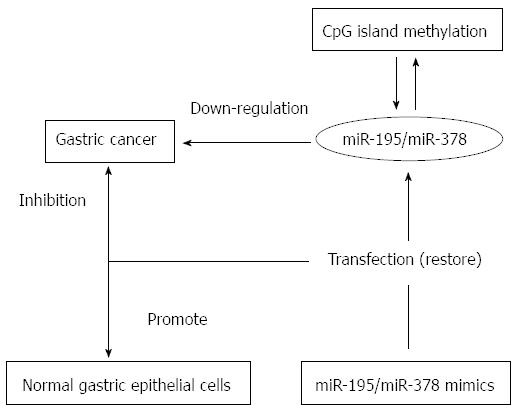
Figure 2 Roles of microRNA-195/microRNA-378 in gastric cancer.
Due to promoter methylation, miR-195 and miR-378 are down-regulated in gastric cancer compared with non-tumor tissue. miR-195 and miR-378 mimics inhibited tumor cell growth and promoted the growth of normal gastric epithelial cells. miR: microRNA.
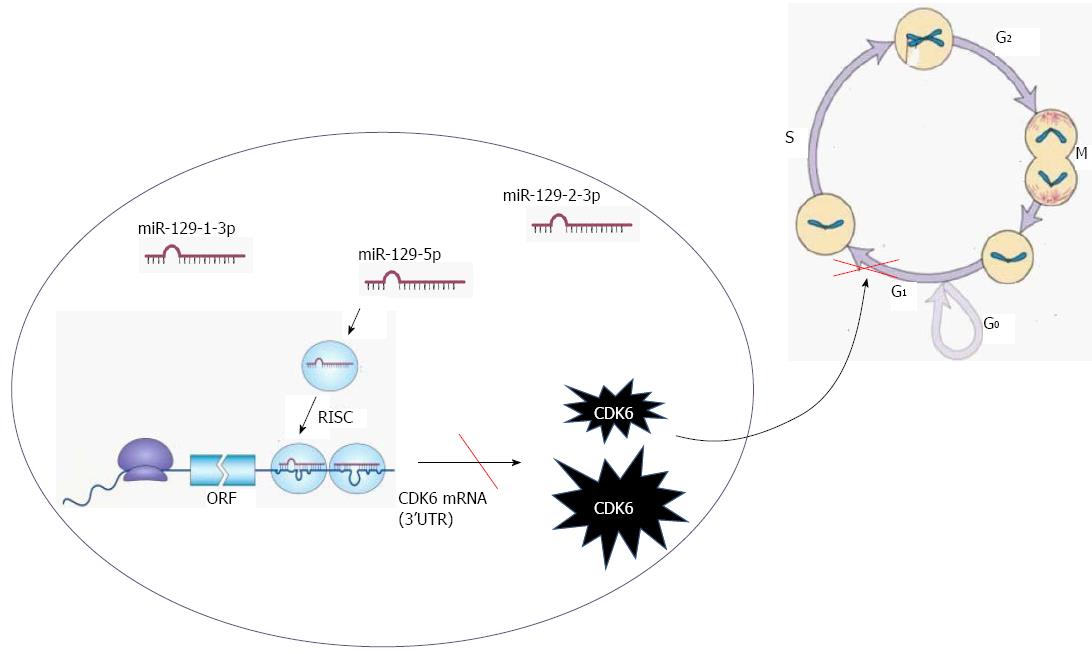
Figure 3 Molecular mechanisms of the microRNA-129 family in regulating the cell cycle in gastric cancer.
Cyclin dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) is a target of three members of the miR-129 family. Thus, increased miR-129 in gastric cancer cells might decrease CDK6 levels, affecting G1-S transition. miR: microRNA.
- Citation: Li PF, Chen SC, Xia T, Jiang XM, Shao YF, Xiao BX, Guo JM. Non-coding RNAs and gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(18): 5411-5419
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i18/5411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5411