Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 3719-3737
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719
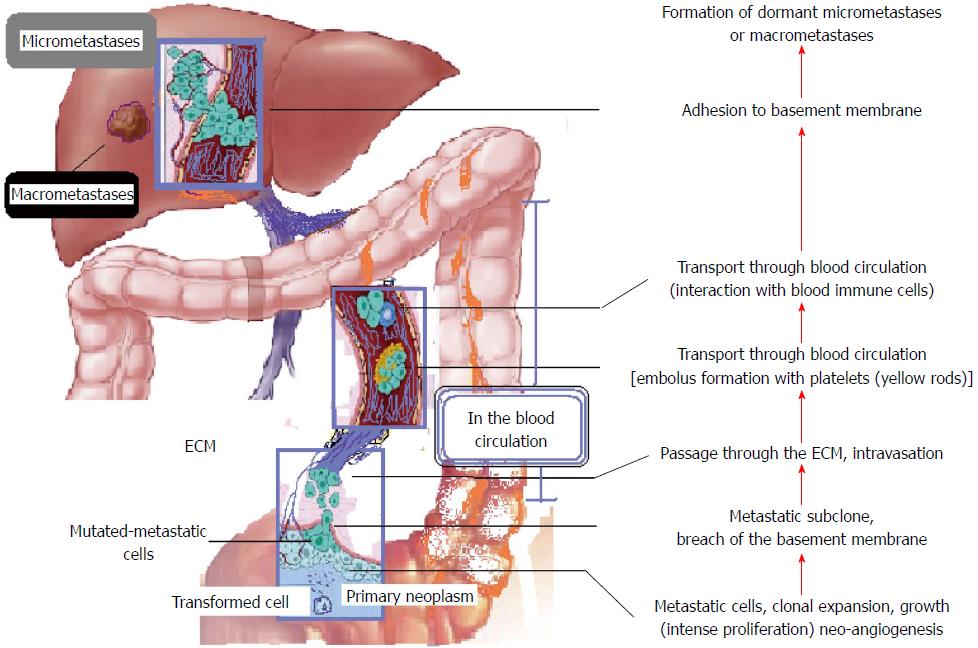
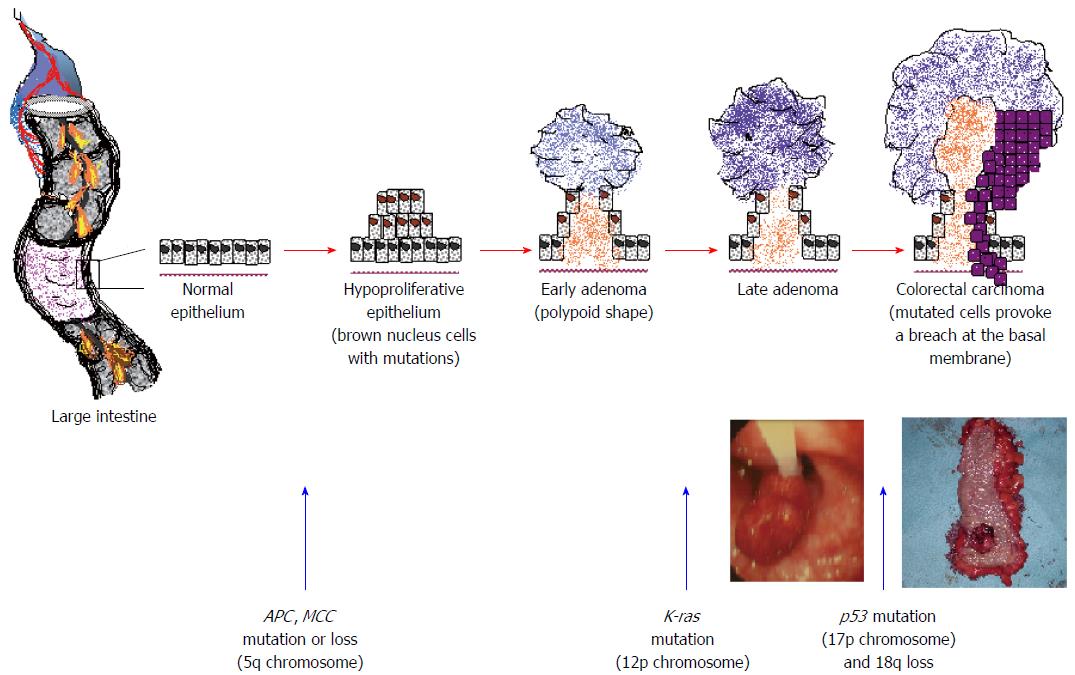
Figure 1 The invasion-metastasis cascade[1,178].
Successive interrelated stages/steps until foreign tissue colonisation and the formation of macrometastases. The paradigm of colorectal liver metastasis, from the large intestine through the superior and inferior mesenteric veins and the portal vein to the liver. ECM: Extra cellular matrix.
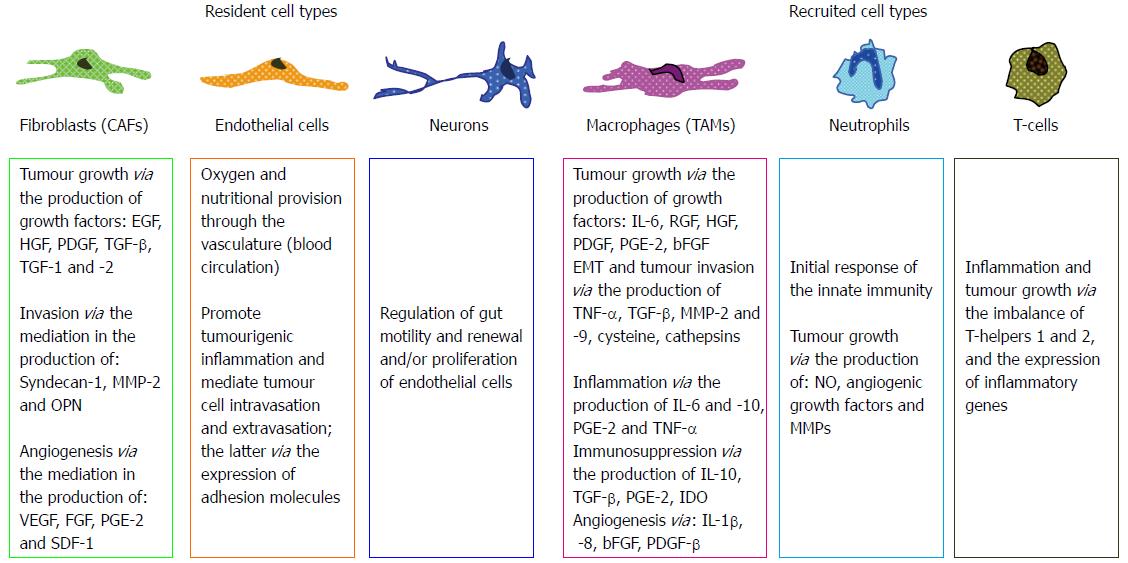
Figure 3 Various cellular types[22,23,112].
Various cellular types (resident: fibroblasts, endothelial cells and neurons, or recruited: macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes) which mediate cancer progression and growth in the colorectal microenvironment. bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; CAF: Cancer associated fibroblasts; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EMT: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IGF: Insulin growth factor; IL-10: Interleukin 10; MMP: Matrix metalloprotease; NO: Nitric oxide; OPN: Osteopontin; PDGF-β: Platelet-derived growth factor-beta; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
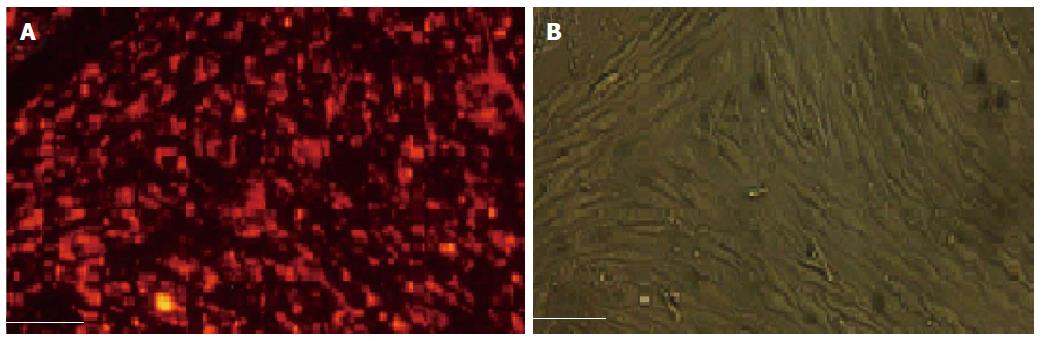
Figure 4 Sinusoidal endothelial cells.
Fluorescence labeled (AcLDL) (A) and light microscopy (B). The cells have a cobblestone architecture on the sixth day in culture (authors’ archive). Magnification × 200. Scale bars = 100 μm. AcLDL: Acetylated low density lipoprotein.
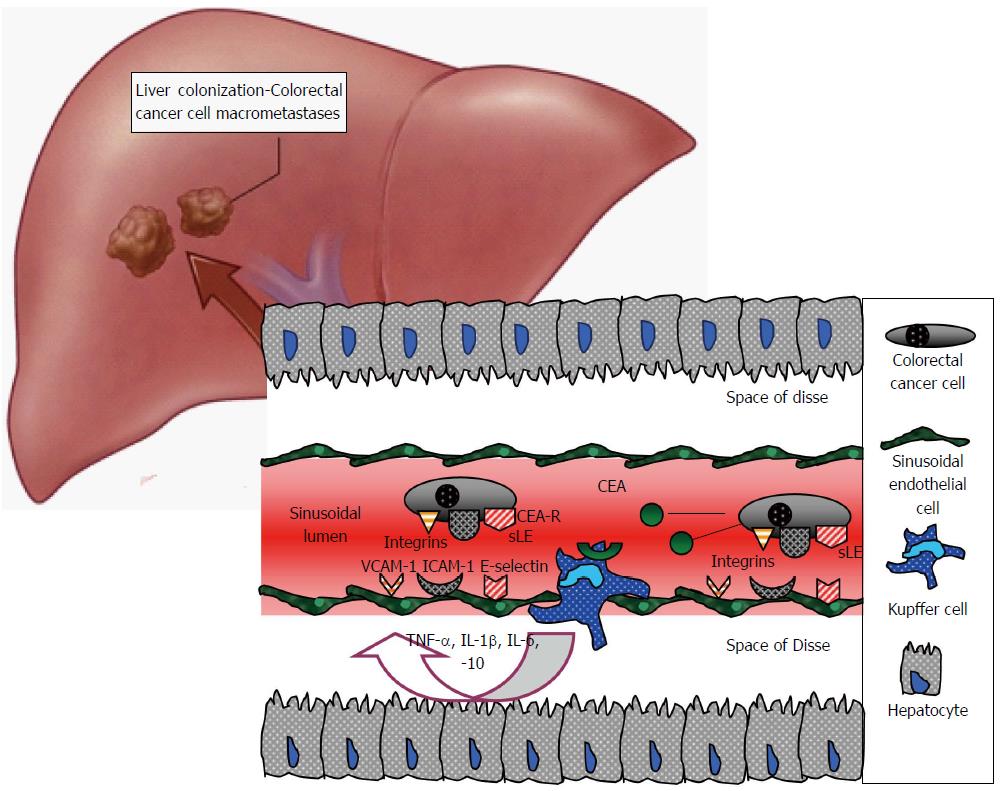
Figure 5 The role of Kupffer cells in colorectal cell adhesion-arrest within the sinusoids during haematogenous liver metastases.
Kupffer cells are activated through carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), release multiple chemokines and stimulate sinusoidal endothelial cells to express adhesion molecules, inducing colorectal cancer cell arrest. CEA-R: CEA receptor; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL: Interleukin; sLE: Sialyl Lewis antigen; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
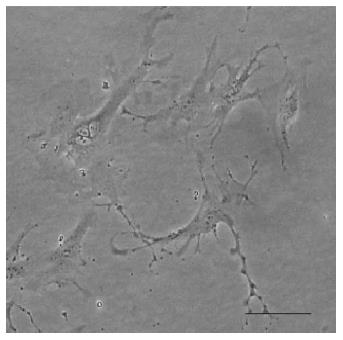
Figure 6 Hepatic stellate cells with their cytoplasmic processes, after 4 d in culture (authors’ archive).
Light microscopy (magnification × 200). Scale bar = 100 μm.
- Citation: Paschos KA, Majeed AW, Bird NC. Natural history of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer - pathobiological pathways with clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 3719-3737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/3719.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719