Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2013; 19(8): 1158-1165
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1158
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1158
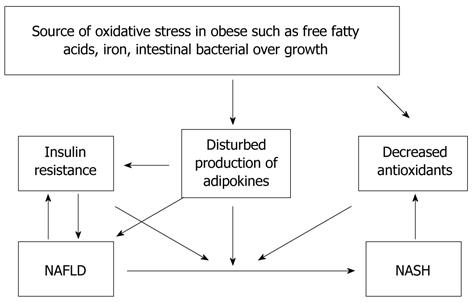
Figure 1 Oxidative stress is one of the most popular proposed mechanisms of hepatocellular injury and possible source of the oxidant stress as follows: increased free fatty acids supply, iron, intestinal bacterial over growth.
NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
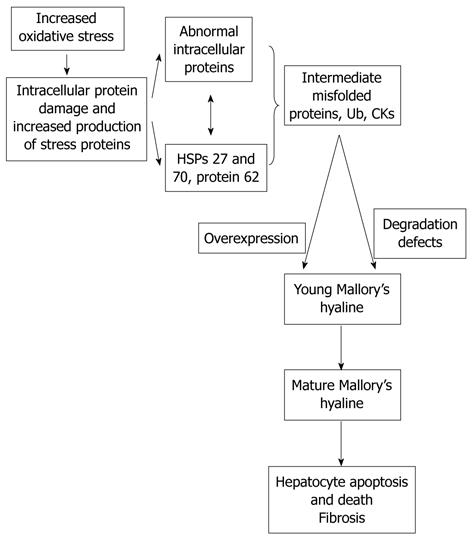
Figure 2 Logical and attractive hypothesis is that oxidative stress in TG-loaded hepatocytes is the cause of sustained injury with consequent NASH, fibrosis and cirrhosis.
HSP: Heat shock proteins.
- Citation: Basaranoglu M, Basaranoglu G, Sentürk H. From fatty liver to fibrosis: A tale of “second hit”. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(8): 1158-1165
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i8/1158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1158