Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2013; 19(44): 8078-8084
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8078
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8078
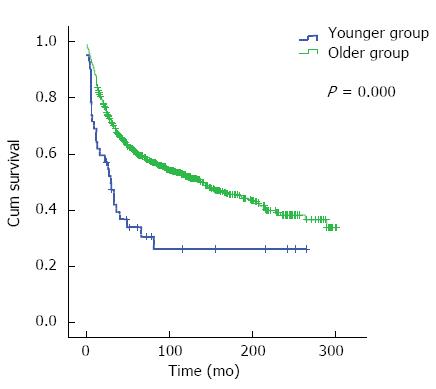
Figure 1 Overall survival of patients in the younger group (≤ 30 years) and older group (> 30 years).
The younger group had worse prognosis than the older group (P = 0.000).
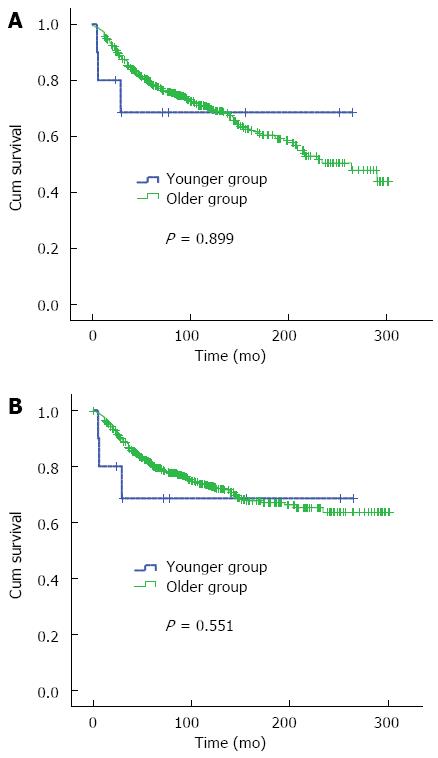
Figure 2 Overall survival of younger patients (≤ 30 years) and older patients (> 30 years) in stage I and II tumor subgroup.
A: Overall survival was totally similar between the two groups (P = 0.899); B: Cancer-related survival was similar between the two groups (P = 0.551).
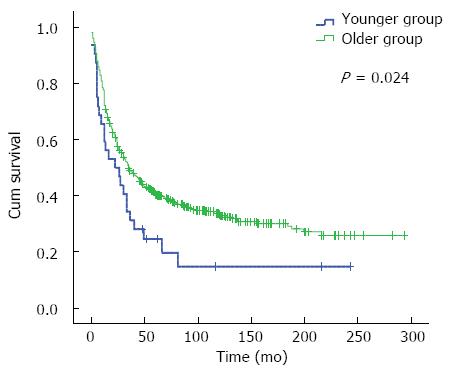
Figure 3 Overall survival of younger patients (≤ 30 years) and older patients (> 30 years) in stage III and IV tumor subgroup.
The younger group had worse prognosis than the older group (P = 0.024).
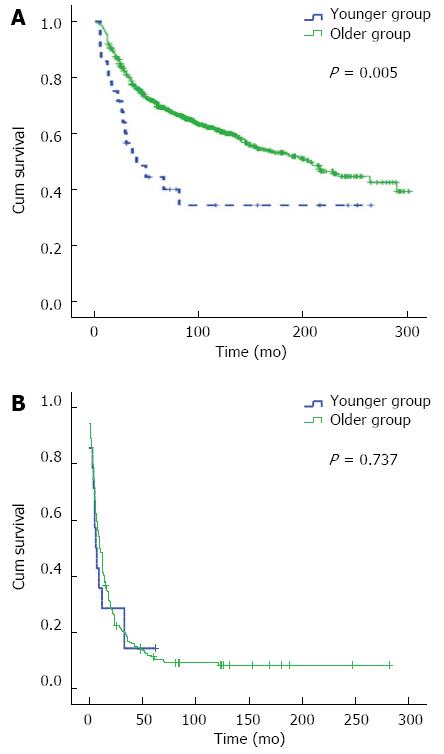
Figure 4 Overall survival of younger patients (≤ 30 years) and older patients (> 30 years) based on approach of surgery.
A: The younger group had worse prognosis than the older group (P = 0.005) undergoing radical surgery; B: There was no difference between the two groups (P = 0.737) treated by non-radical surgery.
- Citation: Fu JF, Huang YQ, Yang J, Yi CH, Chen HL, Zheng S. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of young patients with colorectal cancer in Eastern China. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(44): 8078-8084
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i44/8078.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8078