Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2013; 19(40): 6894-6901
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6894
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6894
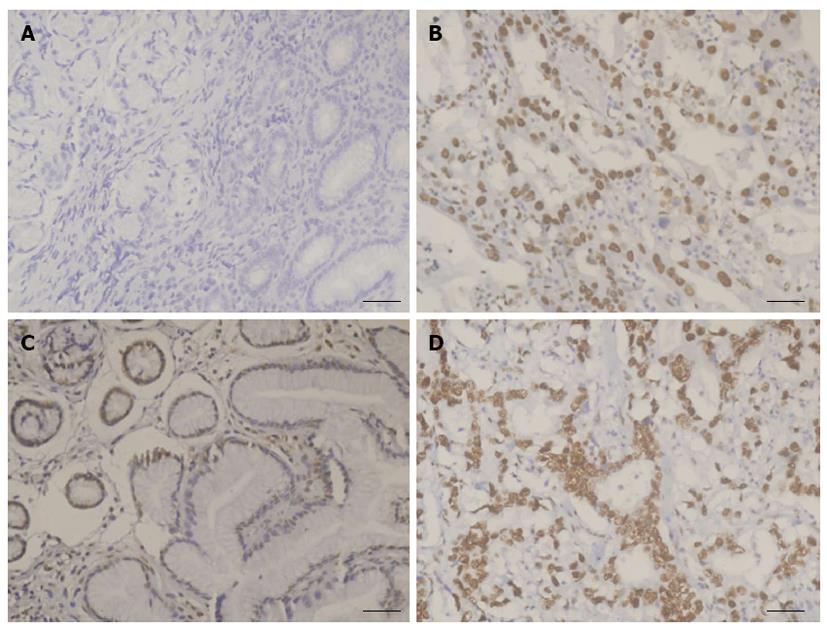
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry assay of DNA-dependent protein kinase and Ku 70/80 protein expression.
Immunostaining showing that the expression of DNA-dependent protein kinase was significantly upregulated in gastric cancer (B) compared to normal gastric mucosa (A). Ku 70/80 expression was significantly increased in gastric cancer (D) compared to normal gastric mucosa (C). Scale bar = 40 μm.
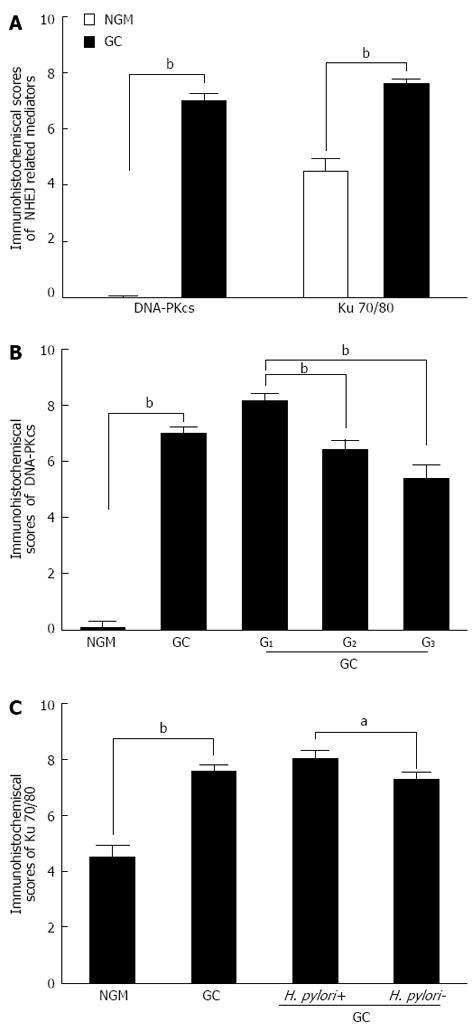
Figure 2 Comparison of the average expression levels of DNA-dependent protein kinase and Ku 70/80 in gastric carcinoma and normal gastric mucosa tissues.
A: Immunohistochemistry scores of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs) and Ku 70/80 in 146 cases of gastric carcinoma (GC) tissues compared with matched normal gastric mucosa; B: Comparison of the average expression level of DNA-PKcs between different differentiation degrees from well-differentiated (G1), moderately differentiated (G2) to poorly differentiated (G3) tumor tissues; C: Relative expression of Ku 70/80 in H. pylori-positive (H. pylori+) and -negative (H. pylori-) GC tissues. The data are shown as the mean values of each group, and the error bars represent SD. Statistical analysis was performed using the Kruskal-Wallis H test and Mann-Whitney U test. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 between groups. NGM: Normal gastric mucosa.
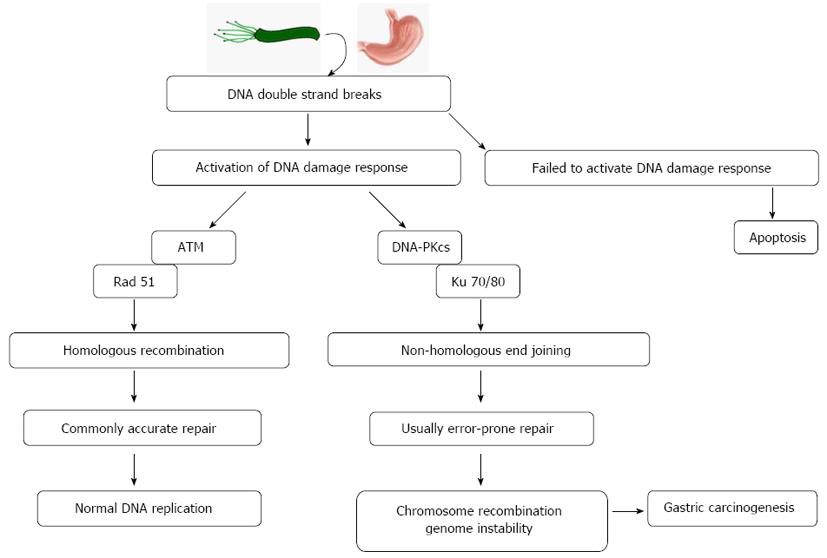
Figure 3 A model depicting the effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on the DNA-dependent protein kinase and Ku 70/80-mediated non-homologous end joining repair pathway in gastric epithelial cells that might ultimately promote carcinogenesis.
ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated; DNA-PKcs: DNA-dependent protein kinase.
- Citation: Li W, Xie C, Yang Z, Chen J, Lu NH. Abnormal DNA-PKcs and Ku 70/80 expression may promote malignant pathological processes in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(40): 6894-6901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i40/6894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6894