Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2013; 19(26): 4242-4251
Published online Jul 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4242
Published online Jul 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4242
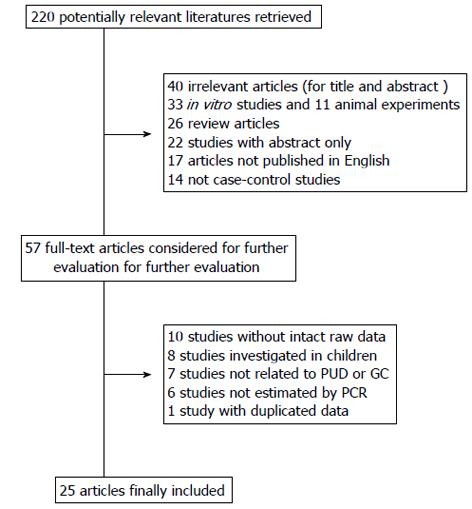
Figure 1 Flowchart of literature search and studies selection.
PUD: Peptic ulcer disease; GC: Gastric cancer; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
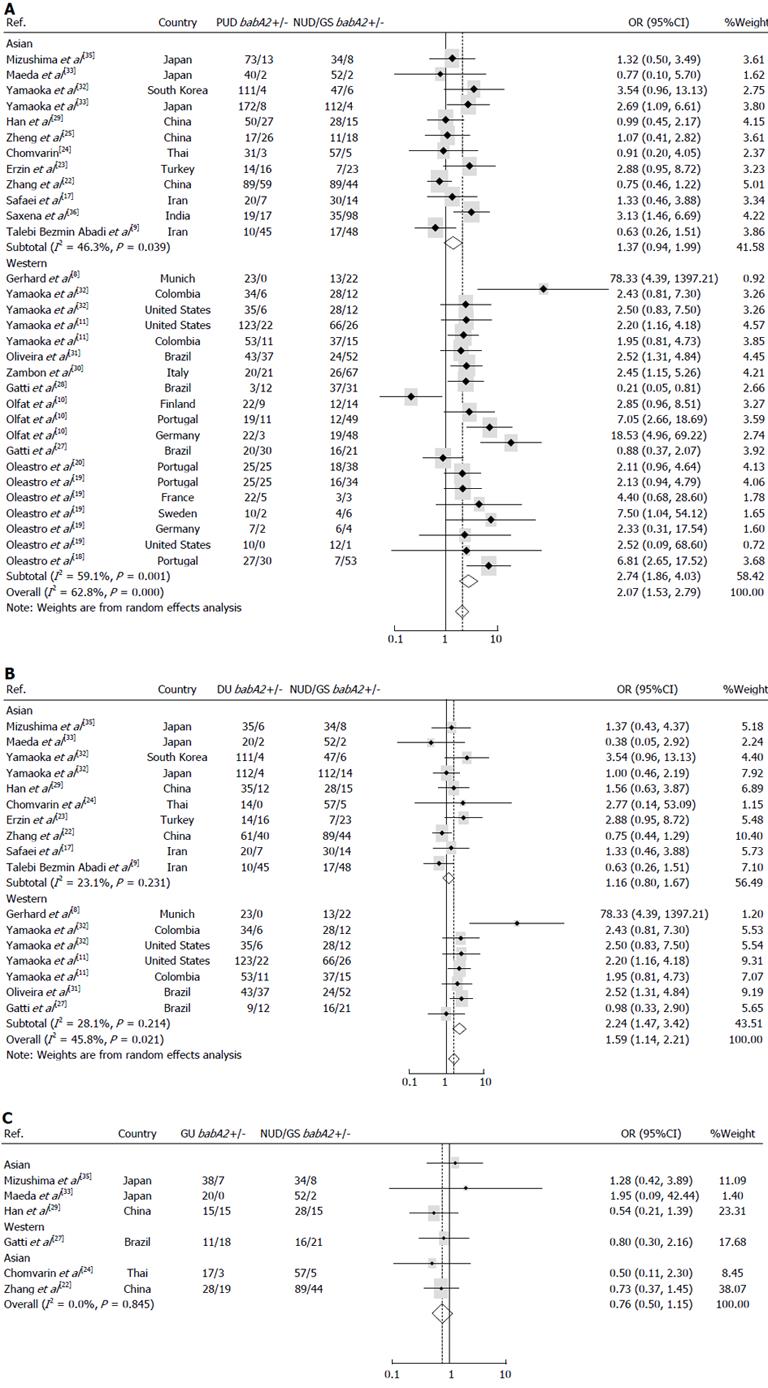
Figure 2 Results of the association between babA2 gene and peptic ulcer disease, duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer risk.
A: Association between babA2 and peptic ulcer disease (PUD); B: Association between babA2 and duodenal ulcer (DU); C: Association between babA2 and gastric ulcer (GU). ORs and 95%CIs were calculated by a random-effect (A, B) and fixed-effect (C) model. NUD: Nonulcer disease.
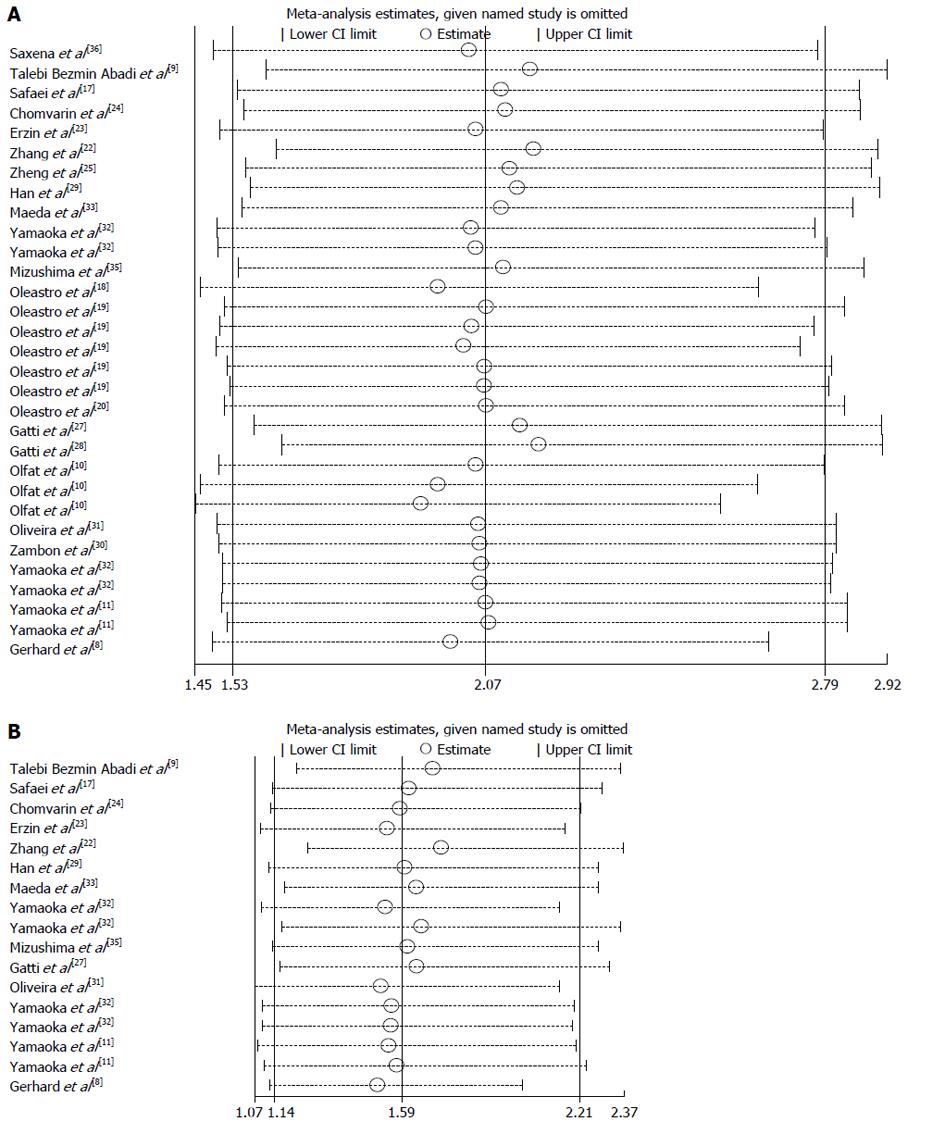
Figure 3 Influence of the summary OR coefficients on the association between babA2 genotype and peptic ulcer disease and duodenal ulcer risk.
A: babA2 genotype and peptic ulcer disease (PUD) risk; B: babA2 genotype and duodenal ulcer risk. Results were calculated by omitting each study (on the left) in turn. Bars, 95%CI. Meta-analysis random-effects estimates (exponential form) were used.
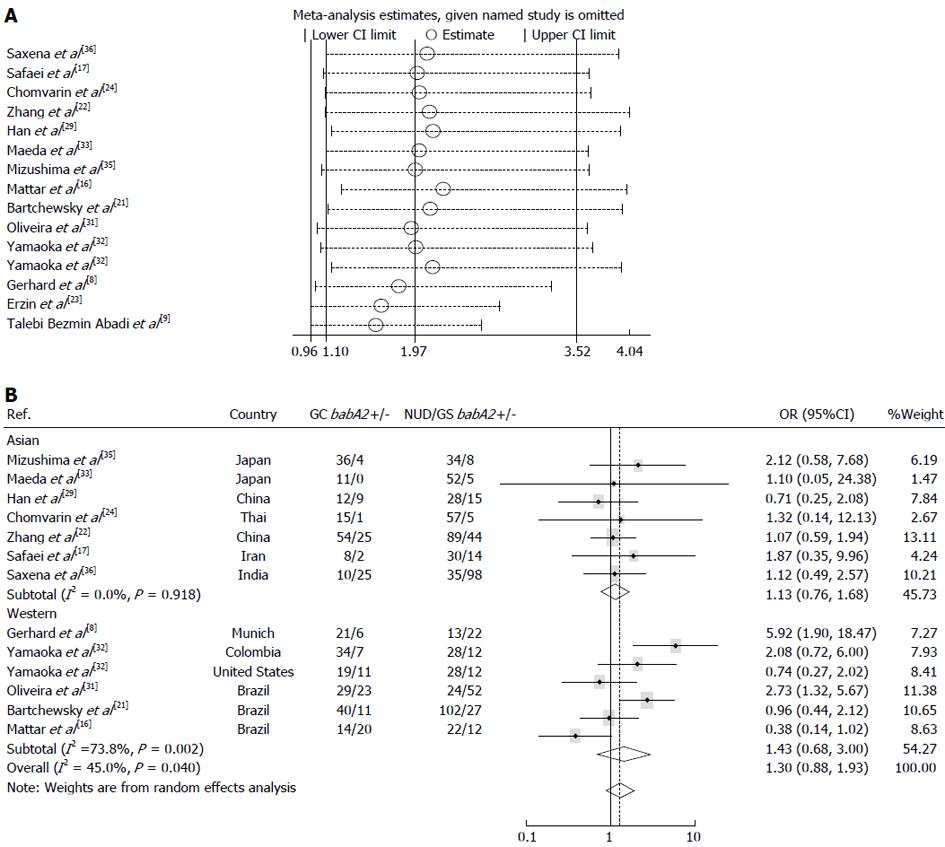
Figure 4 Influence of summary OR coefficients and results on the association between babA2 genotype and gastric cancer risk.
A: Influence analysis. Results were calculated by omitting each study (on the left) in turn. Bars, 95%CI. Meta-analysis random-effects estimates (exponential form) were used; B: Results. ORs and 95%CIs were calculated by a random-effect model.
-
Citation: Chen MY, He CY, Meng X, Yuan Y. Association of
Helicobacter pylori babA2 with peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(26): 4242-4251 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i26/4242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4242