Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 4094-4098
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4094
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4094
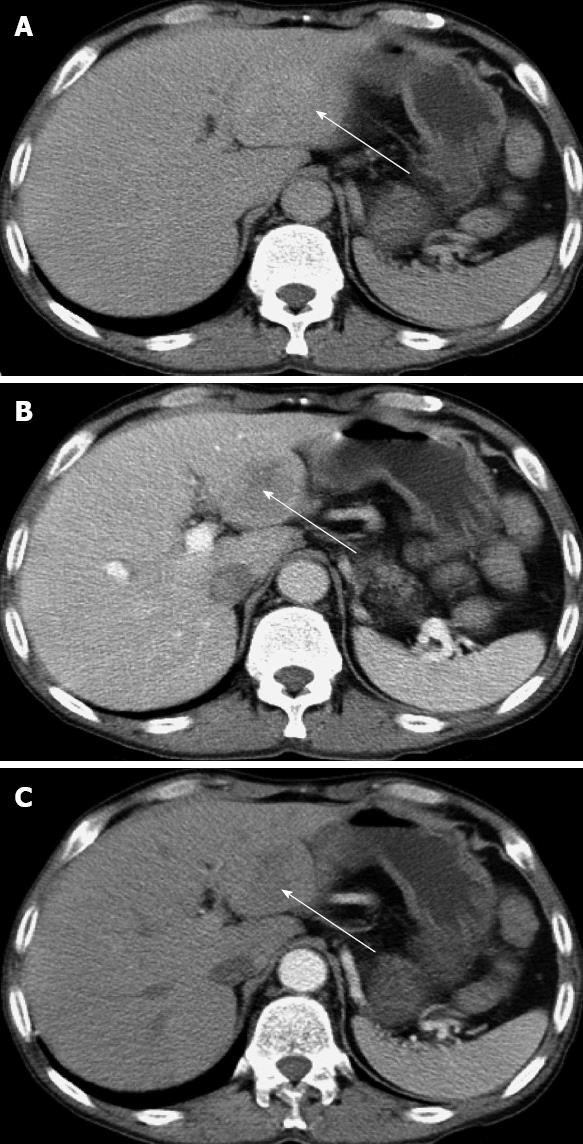
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography scan shows a mass in segment III of the liver.
A: Hepatic equilibrium phase; B: Portal venous phase; C: Hepatic arterial phase. The arrows indicate the tumor in the liver.
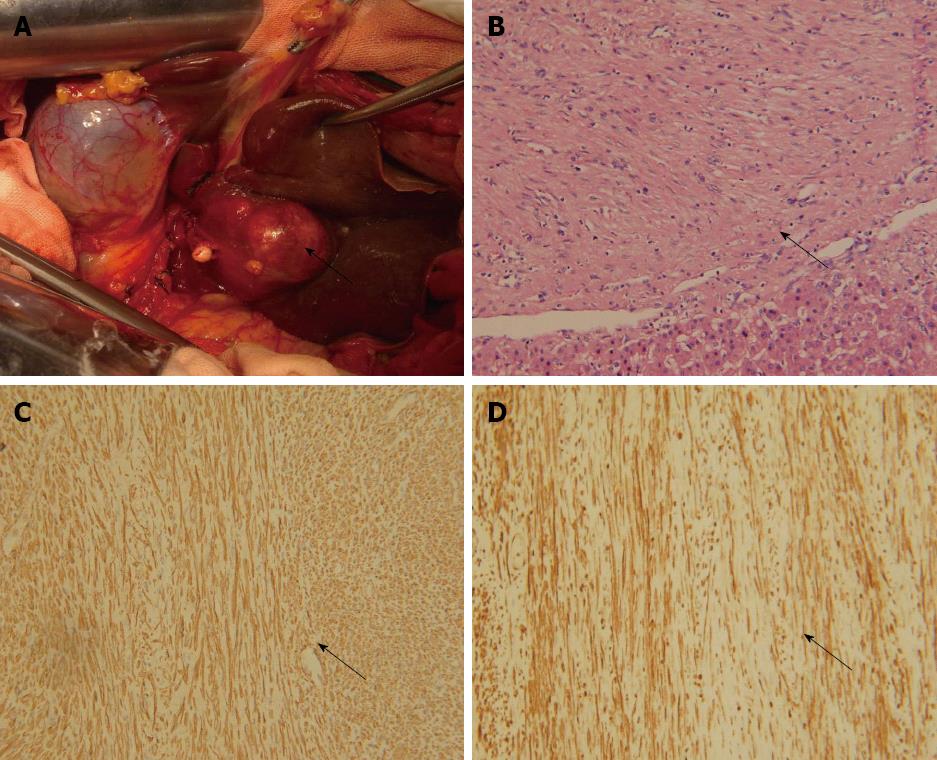
Figure 2 Pathological characteristics of the primary liver leiomyoma.
A: Tumor (arrow) located in segment III of the liver; B: Tumor (arrow) and normal liver tissue, hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 200; C: α-smooth muscle actin staining (arrow) of tumor tissues, immunohistochemical staining, × 200; D: Desmin staining (arrow) of tumor tissues, immunohistochemical staining, × 200.
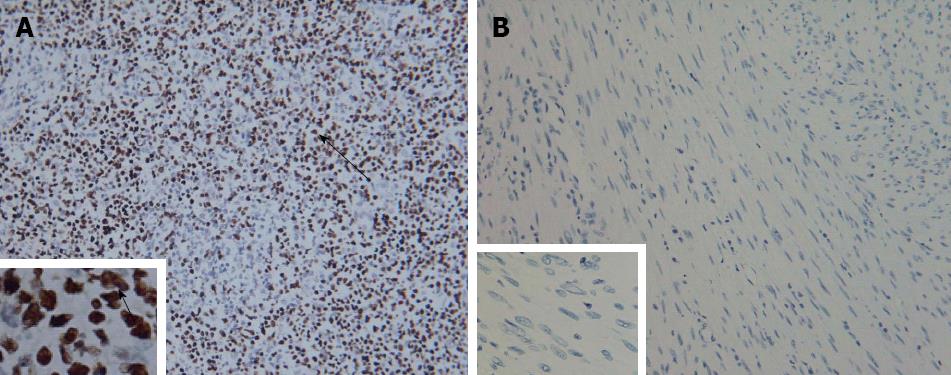
Figure 3 Tumor cells stained negative by in situ hybridization with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA.
A: Positive control staining × 200, × 1000; B: Tumor cell staining × 200, × 1000. Arrows indicate positive staining of the nuclei.
- Citation: Luo XZ, Ming CS, Chen XP, Gong NQ. Epstein-Barr virus negative primary hepatic leiomyoma: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 4094-4098
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/4094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4094