Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 4053-4059
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4053
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4053
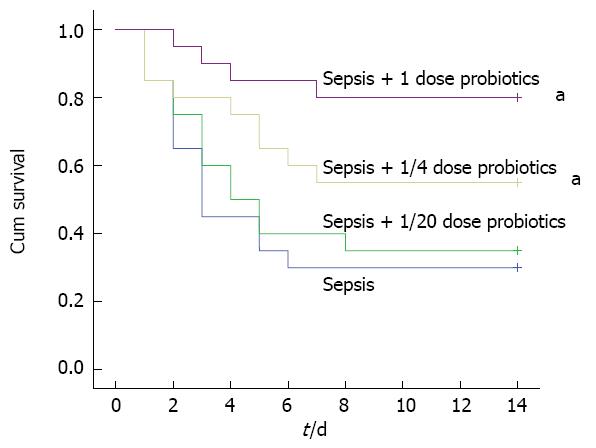
Figure 1 Survival in experimental sepsis.
Survival was analysed in Wistar rats subjected to cecal ligation and puncture. Probiotics (1, 1/4 or 1/20 doses) or vehicle treatment started 6 h later and thereafter administered once a day for 3 d. All animals were observed for two weeks to compare their survival rates (n = 20; aP < 0.05 vs septic model group).
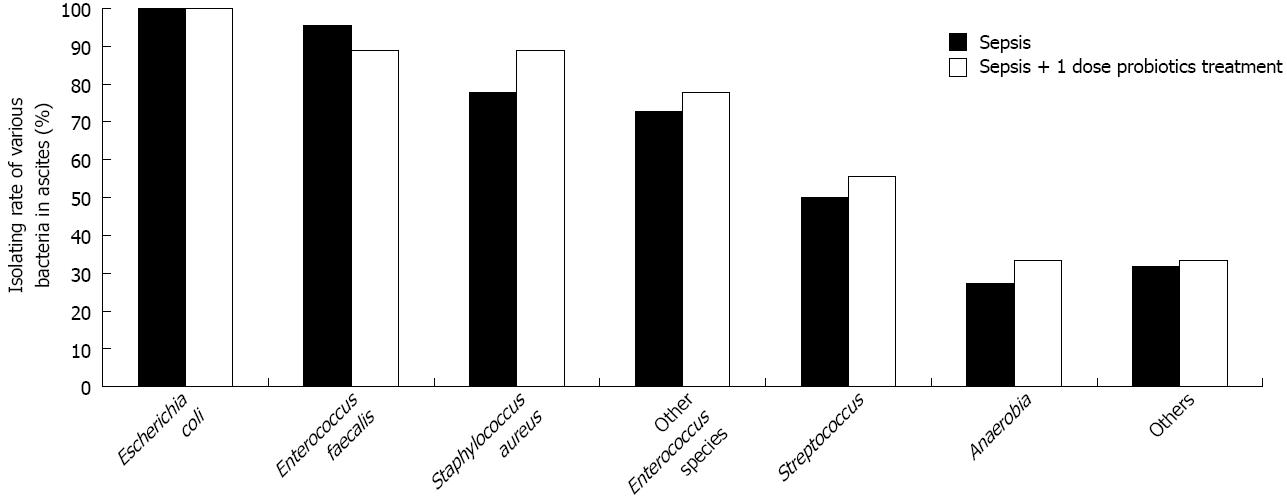
Figure 2 Comparison of isolating rate of various bacteria in ascites between sepsis and probiotics treated group.
Probiotics (1 dose) or vehicle treatment started 6 h later and thereafter administered once a day for 3 d. Samples of ascites were harvested for both anaerobic and aerobic culture. There was no statistical significance in isolating rates between two groups for all bacterial species (P > 0.05). In addition, “other Entertrococcus species” include Enterococcus avium, Enterococcus gallinarum, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus malodoratus. “Anaerobia” include Lactobacillus reuteri, Veillonella cricetiratti, Desulfovibrio fructosivorans, Clostridium oroticum, Lactobacillus bifermentans, Prevotella dentioola, Bacterorides ovatus and Prevotella nigrescens. “Others” include Micrococcus luteus, Morganella morganii ss morganii and Acinetobacter radioresistens.
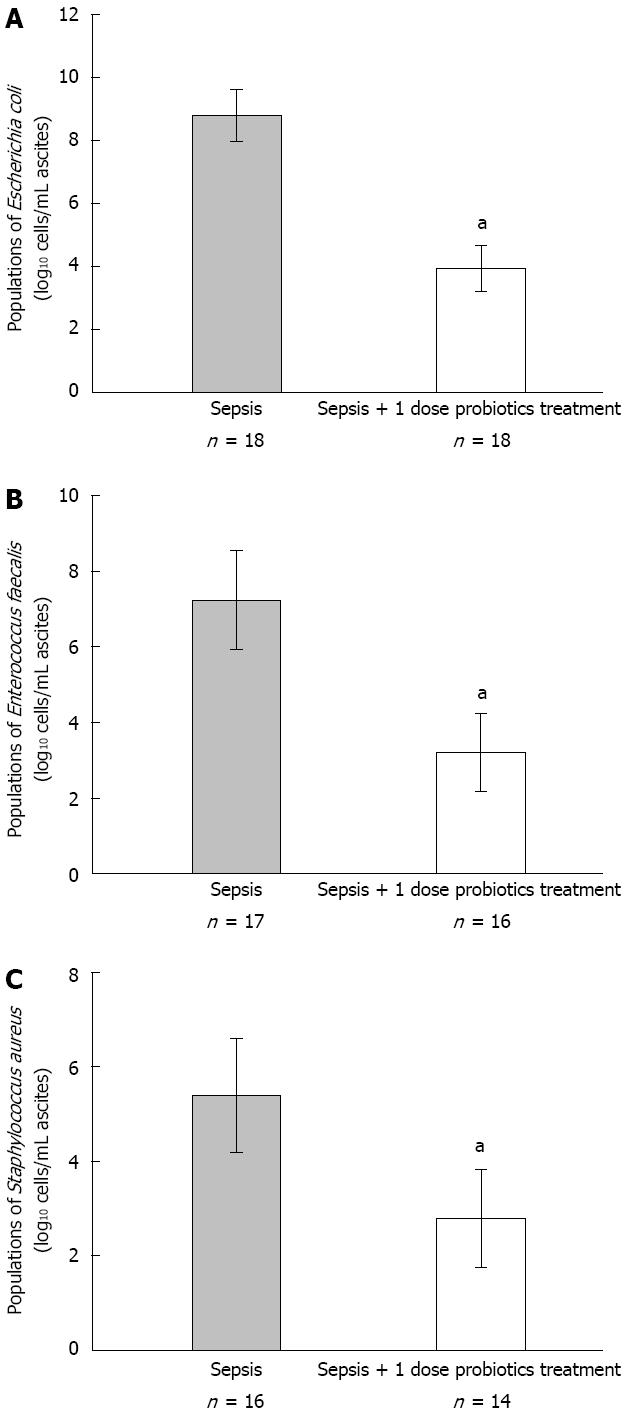
Figure 3 Comparison of predominant bacterial populations in ascites between sepsis and probiotics treated groups.
Probiotics (1 dose) or vehicle treatment started 6 h later and thereafter administered once a day for 3 d. Bacterial genomic DNA was extracted and analysed by quantitative real-time PCR as described previously. The population of Escherichia coli (A), Enterococcus faecalis (B) and Staphylococcus aureus (C) were compared between two groups (aP < 0.05 vs septic model group).
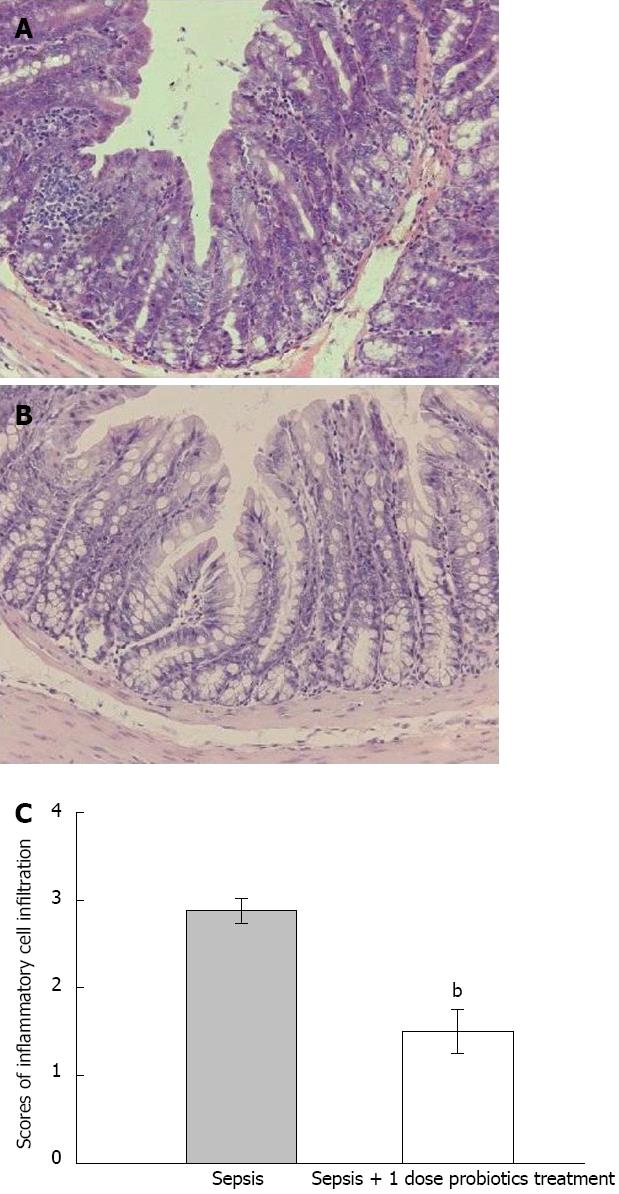
Figure 4 Colonic mucosal inflammation of experimental sepsis.
Probiotics (1 dose) or vehicle treatment started 6 h later and thereafter administered once a day for 3 d. We harvested colonic tissues after a 72 h period of cecal ligation and puncture. The sections of colonic tissues were stained by haematoxylin-eosin (× 400). Four fields of each sample were assessed. More neutrophils and mononuclear cells infiltrated into the intestinal mucosa in septic model group (A) than probiotics treatment group (B). We also compared scores of inflammatory cell infiltration between two groups (C) (bP < 0.01 vs septic model group).
- Citation: Liu DQ, Gao QY, Liu HB, Li DH, Wu SW. Probiotics improve survival of septic rats by suppressing conditioned pathogens in ascites. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 4053-4059
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/4053.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4053