Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2013; 19(22): 3487-3493
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3487
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3487
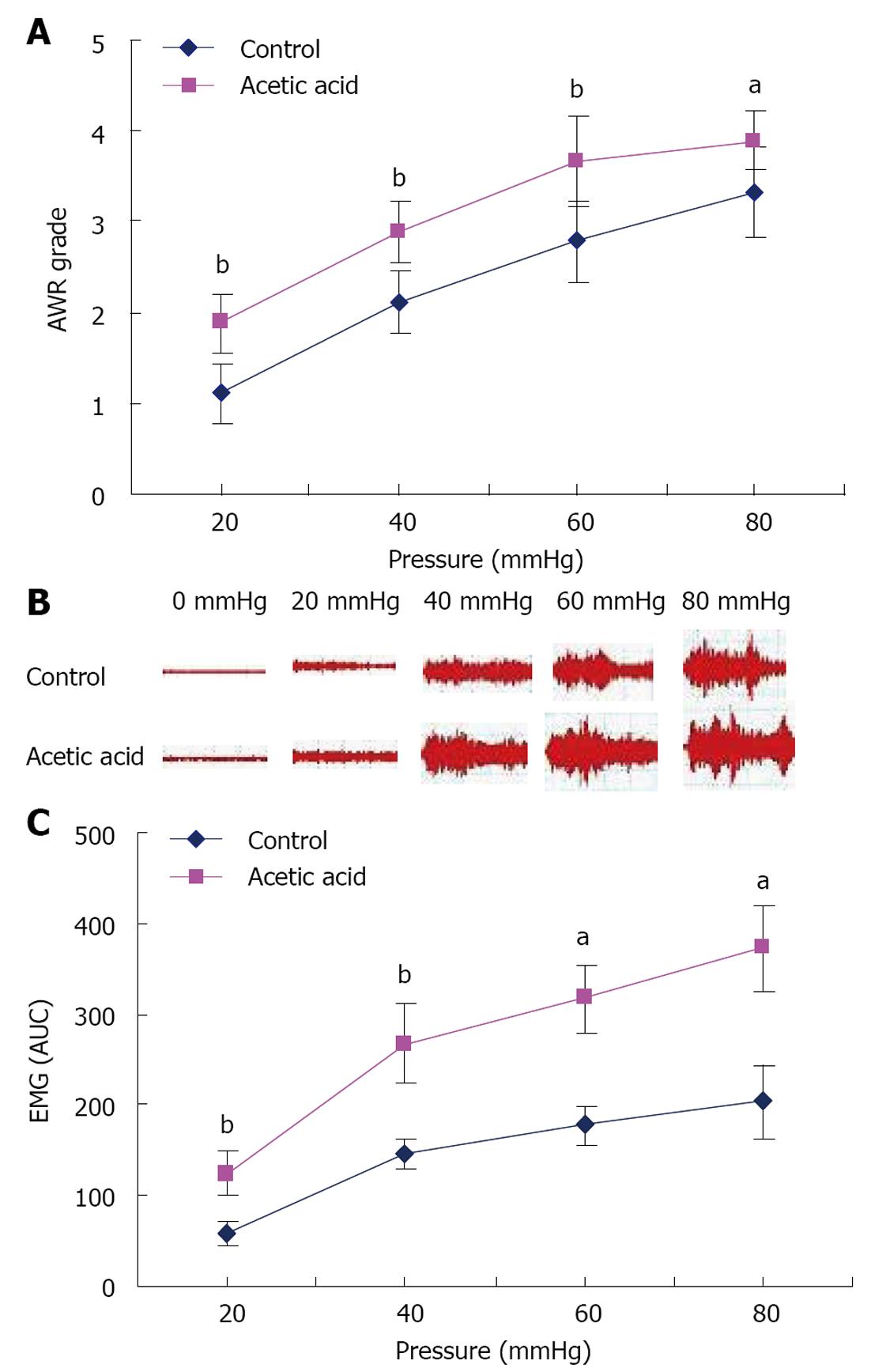
Figure 1 Evaluation of visceral sensitivity in neonatal acetic acid-treated rats when adults.
A: Abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores were used as an index in response to distension pressure. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group, n = 9; B: Typical electromyographic (EMG) activity in the external oblique muscle in response to graded colorectal distension; C: Area under the curve (AUC) of EMG activity in the external oblique muscle in response to graded colorectal distension. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group, n = 9.
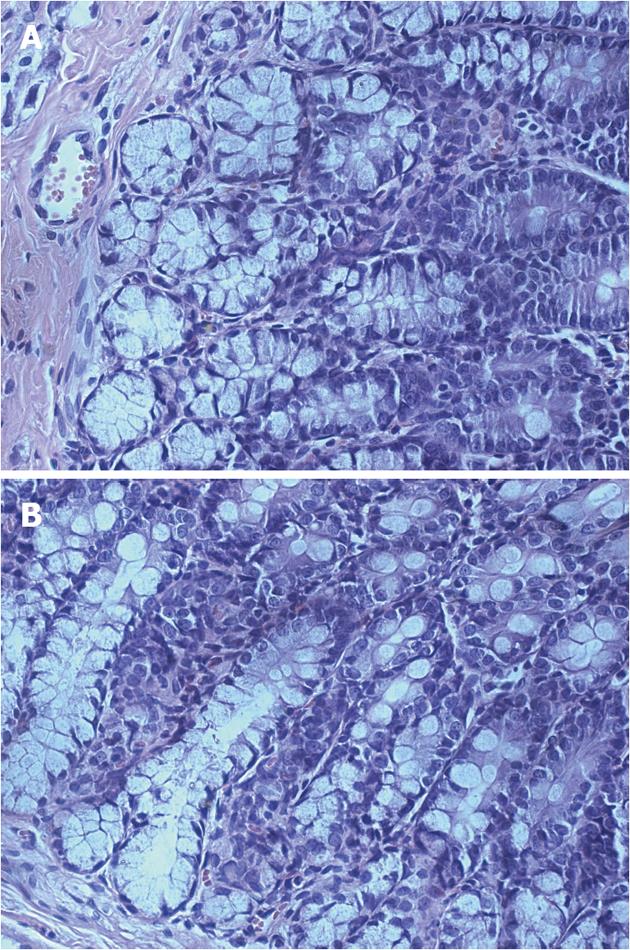
Figure 2 Photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections from colons of control adult rats (A) and neonatal acetic acid-treated adult rats (B).
No significant inflammation or abnormalities in structure were observed in neonatal acetic acid-treated rats.
Figure 3 Myeloperoxidase activity in rat colon (A) and nesfatin-1 levels in rat serum (B).
A: There was no difference in myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in neonatal acetic acid-treated rats compared with control rats; B: The average serum nesfatin-1 level was statistically higher in neonatal acetic acid-treated rats than in controls (n = 12).
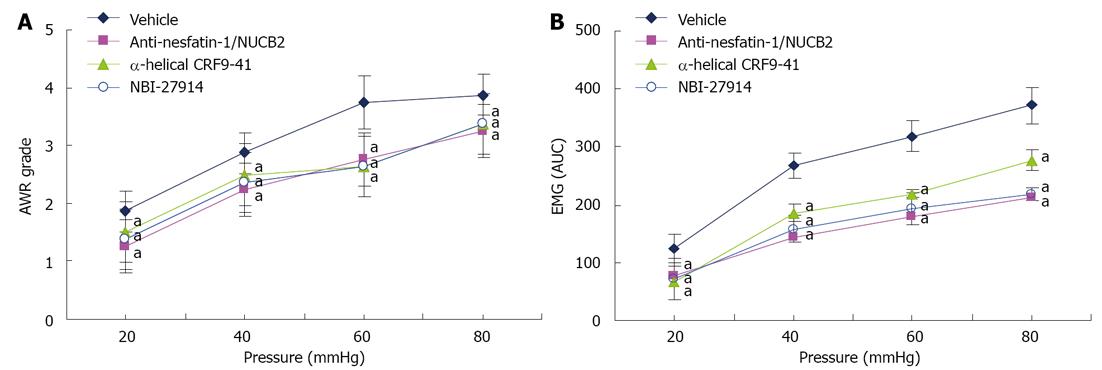
Figure 4 Effect of anti-nesfatin-1/nucleobindin-2, α-helical corticotropin releasing factor 9-41 and NBI-27914 treatment on visceral sensitivity in model rats.
A: Abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores were used as an index in response to distension pressure. Model rats receiving intracerebroventricular injection of anti-nesfatin-1/nucleobindin-2 (NUCB2), α-helical corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) 9-41 and NBI-27914 showed decreased mean AWR scores compared with model rats receiving vehicle injection, at 20, 40, 60 and 80 mmHg, aP < 0.05 vs vehicle group, n = 8; B: Electromyographic (EMG) activity in the external oblique muscle in response to graded colorectal distension. Compared with vehicle administration, EMG activity in model rats administered intracerebroventricularly with anti-nesfatin-1/NUCB2, α-helical CRF9-41 or NBI-27914 was significantly decreased at 20, 40, 60 and 80 mmHg compared with model rats receiving vehicle injection, aP < 0.05 vs vehicle group, n = 8.
- Citation: Jia FY, Li XL, Li TN, Wu J, Xie BY, Lin L. Role of nesfatin-1 in a rat model of visceral hypersensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(22): 3487-3493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i22/3487.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3487