Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2013; 19(2): 227-234
Published online Jan 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.227
Published online Jan 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.227
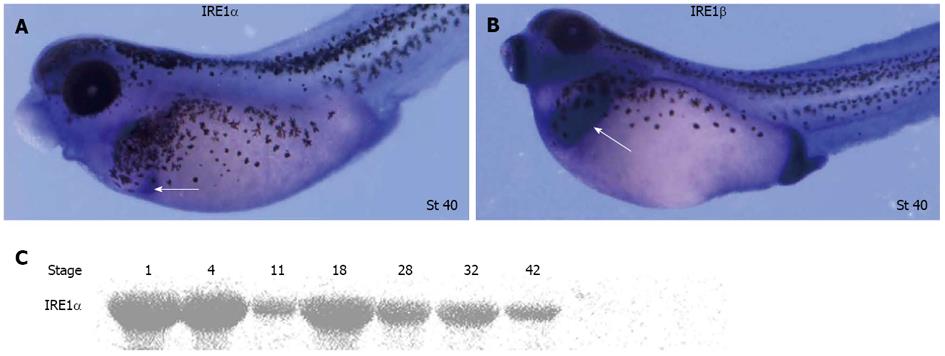
Figure 1 Expression pattern of xIRE1 in Xenopus lavies during development.
A, B: Whole-mount in situ hybridizations revealed relatively high expression of inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE) 1α in pancreas (white arrow in A) and relatively high expression of IRE1β in liver (white arrow in B); C: Western blotting revealed temporal expression of IRE1α during Xenopus embryogenesis.
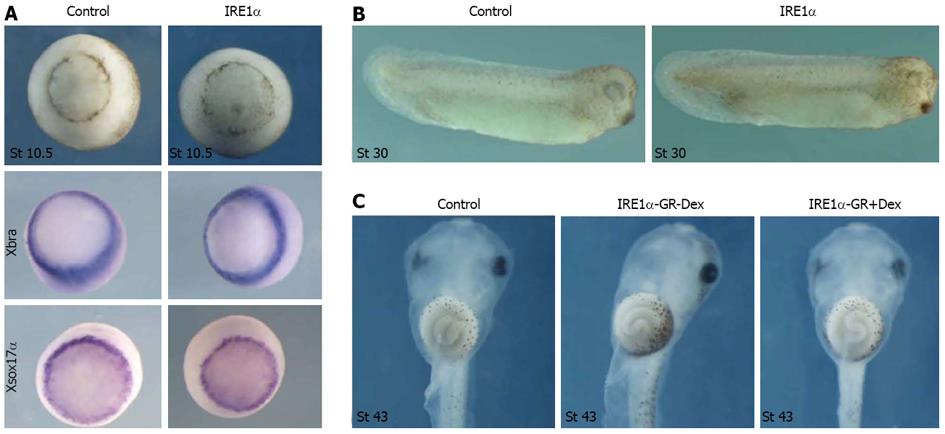
Figure 2 Overexpression of inositol-requiring enzyme 1α affected neither mesoderm and endoderm formation nor gut development.
A: Overexpression of inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE) 1α did not change the phenotype and the expression of Xbra and Xsox17α at stage 10.5; B: IRE1α mRNA injected embryos at tailbud stage were nearly normal; C: Embryos injected with IRE1α-GR mRNA did not display any defect until tadpole stage.
Figure 3 Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α morpholino oligonucleotide blocks inositol-requiring enzyme 1α translation in an in vitro transcription/translation assay.
In this assay, xIRE1α was effectively transcribed/translated from a pCS2+xIRE1α construct. However, translation was dramatically decreased by addition of IRE1α morpholino oligonucleotide (MO). IRE: Inositol-requiring enzyme.
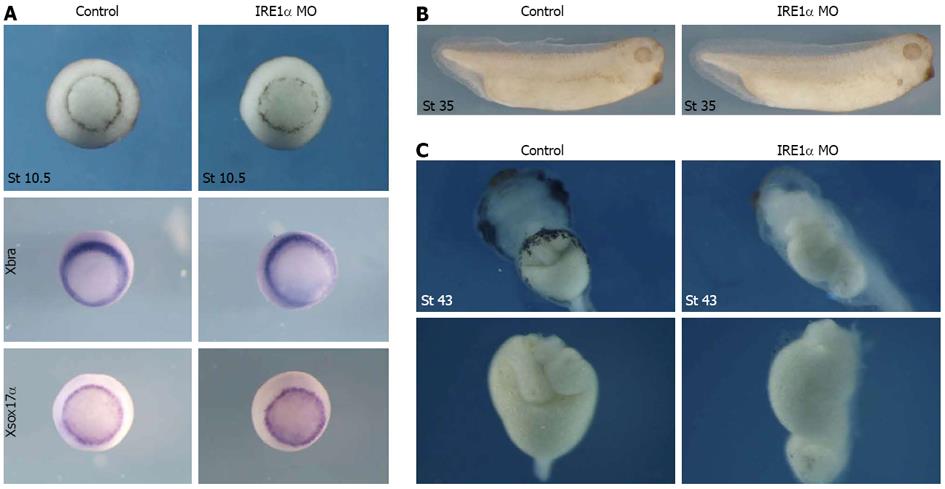
Figure 4 Xenopus inositol-requiring enzyme 1α is required for gut development.
A: Knockdown of x IRE1α did not change the phenotype and the expression of Xbra and Xsox17α at stage 10.5; B: The inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE) 1α morpholino oligonucleotide (MO)-injected embryos were morphologically normal before the tailbud stages; C: IRE1α knockdown upon injection of 50 ng of MO resulted in a gut defective phenotype. Surgically-resected guts from embryos were shown in C under panel. Coiled structure of gut was not detected in IRE1α MO-injected embryos at stage 43. MO injection was repeated 5 times in a total of 278 embryos.
Figure 5 Rescue of xIRE1α knockdown with IRE1α-GR mRNA.
Gut defective phenotype caused by 50 ng of morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) could be rescued by co-injection of 1 ng of inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE) 1α-GR mRNA. Co-injection was done 3 times in a total of 258 embryos.
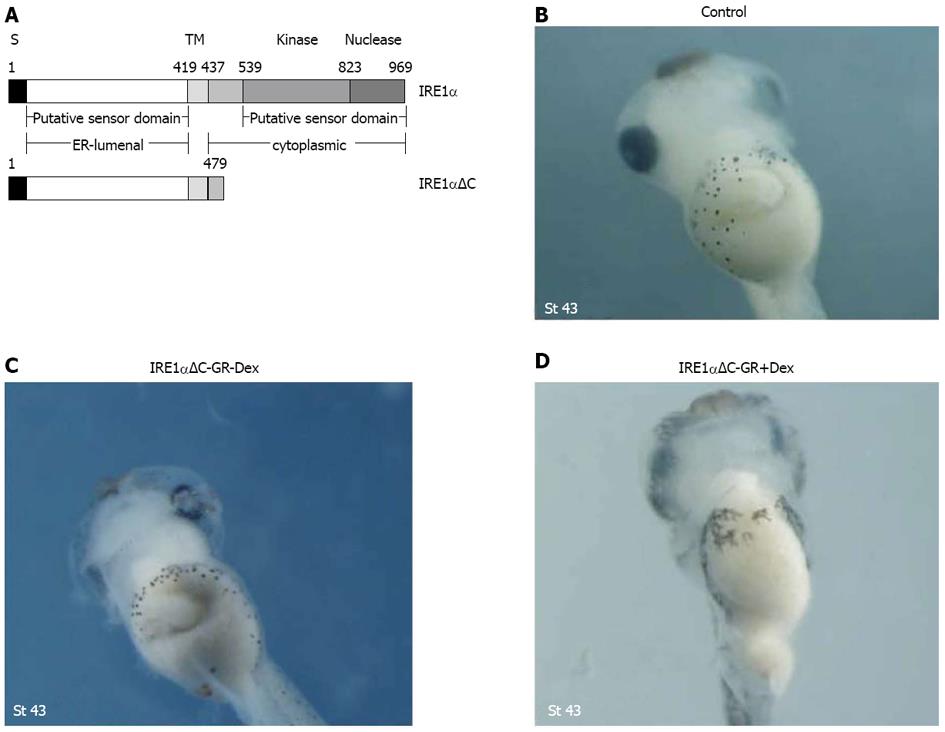
Figure 6 Injection of IRE1αΔC-GR mRNA caused morphological alterations with gut malformation.
A: Diagram depicting the construction of deletion mutants. S and TM denote the signal peptide and the transmembrane domain; B-D: Gut defects were also observed with a dominant-negative mutant, IRE1αΔC, lacking the cytoplasmic kinase and RNase domains.
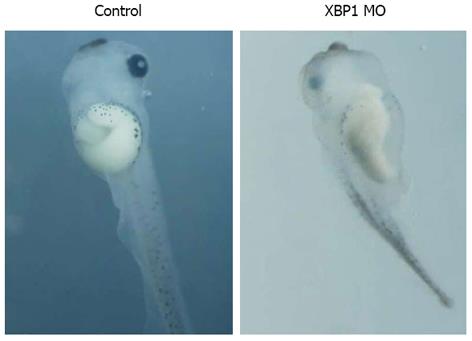
Figure 7 XBP1 knockdown affected gut development.
Injection of XBP1(C) morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) caused similar phenotype with gut-coiling defect at stage 43.
-
Citation: Guo J, Li XX, Feng JJ, Yin CY, Wang XJ, Wang N, Yuan L. Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α is required for gut development in
Xenopus lavies embryos. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(2): 227-234 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i2/227.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.227