Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2013; 19(17): 2676-2682
Published online May 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i17.2676
Published online May 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i17.2676
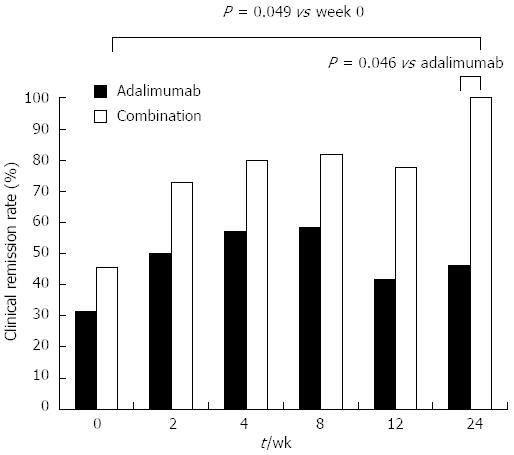
Figure 1 Clinical remission rate.
Combinational therapy with adalimumab and azathioprine significantly increased the clinical remission rate vs nonconcomitant use at week 24.
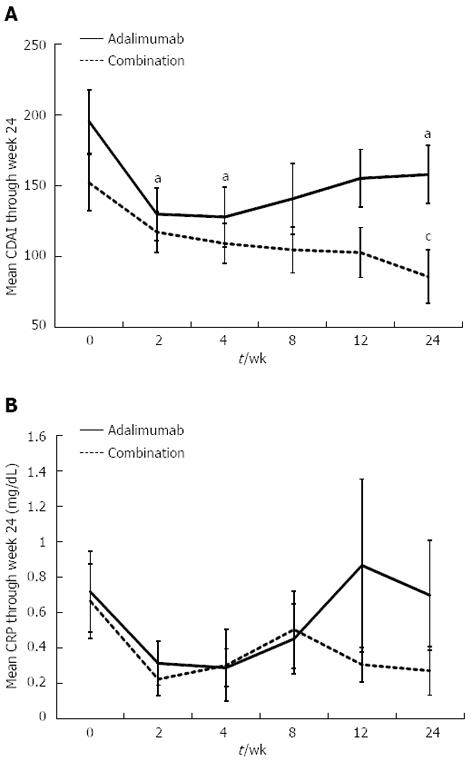
Figure 2 Mean Crohn’s disease activity index and C-reactive protein through week 24.
A: Combinational therapy with adalimumab (ADA) and azathioprine (AZA) significantly reduced the Crohn’s disease activity index (CDAI), compared with nonconcomitant use at week 24. aP < 0.05 vs week 0; cP < 0.05 vs adalimumab; B: The concomitant use of AZA tended to maintain low C-reactive protein (CRP) levels for 24 wk (CRP levels at weeks 0 and 24 were 0.66 ± 0.73 and 0.27 ± 0.44, respectively, P = 0.09).
- Citation: Ishida K, Inoue T, Fujiwara K, Sakanaka T, Narabayashi K, Nouda S, Okada T, Kakimoto K, Kuramoto T, Kawakami K, Abe Y, Takeuchi T, Murano M, Tokioka S, Umegaki E, Higuchi K. Clinical effects of adalimumab treatment with concomitant azathioprine in Japanese Crohn’s disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(17): 2676-2682
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i17/2676.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i17.2676