Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2013; 19(1): 137-140
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.137
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.137
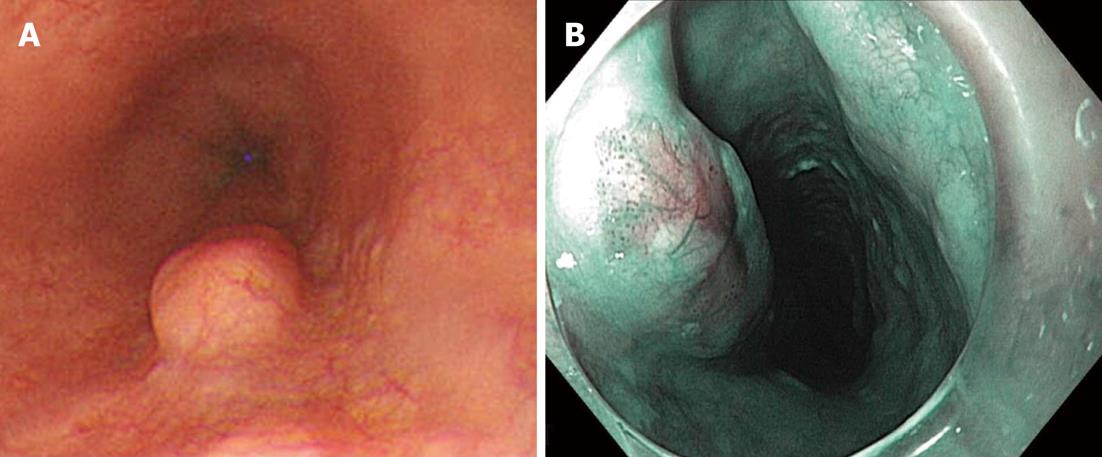
Figure 1 Endoscopic findings.
A: Endoscopic findings demonstrate a subepithelial tumor with intact overlying mucosa; B: Chromoendoscopy with narrow band imaging showed scattered brown dots, and dilated and tortuous vessels on the top of the lesion.
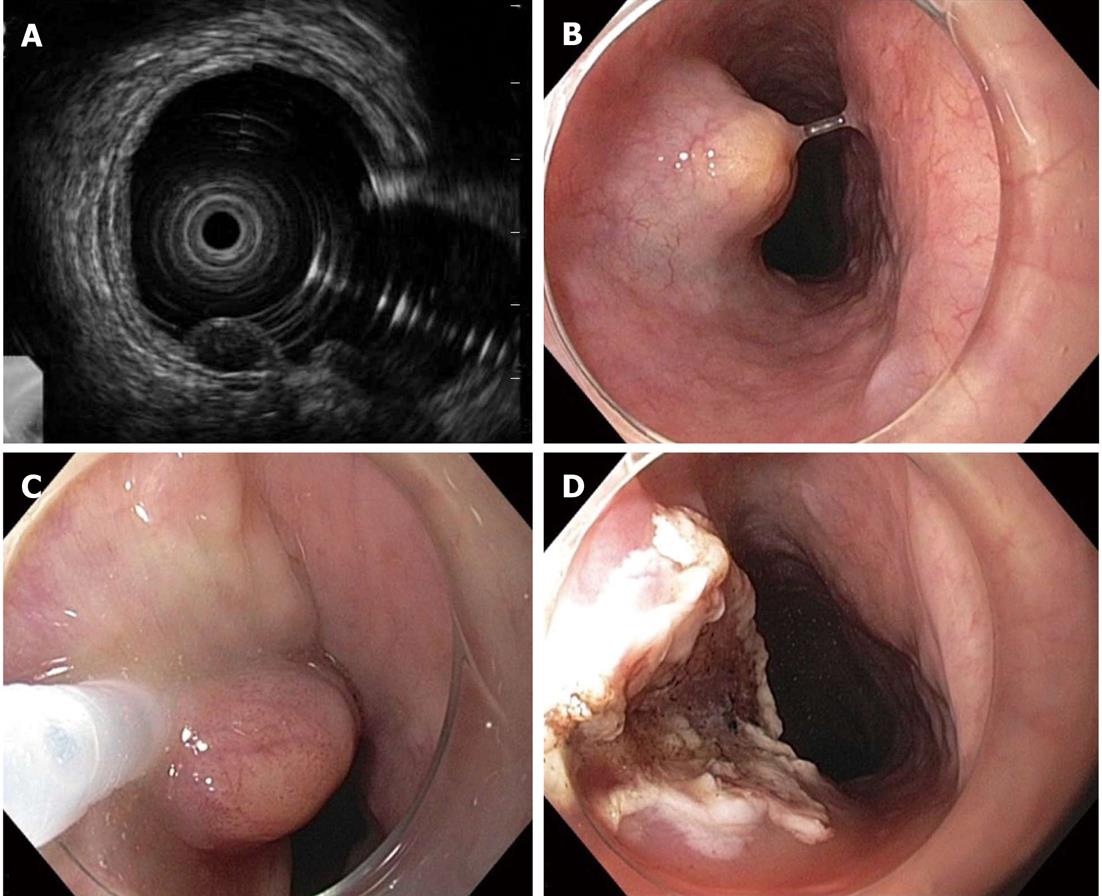
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound findings and procedures for endoscopic mucosal resection.
A: High frequency ultrasonic endoscopic findings showed a clear homogenous hypoechoic mass derived from the second layer of the esophagus; B: After making a submucosal bleb; C: The subepithelial lesion was captured using a snare; D: No immediate complications occurred after endoscopic mucosal resection.
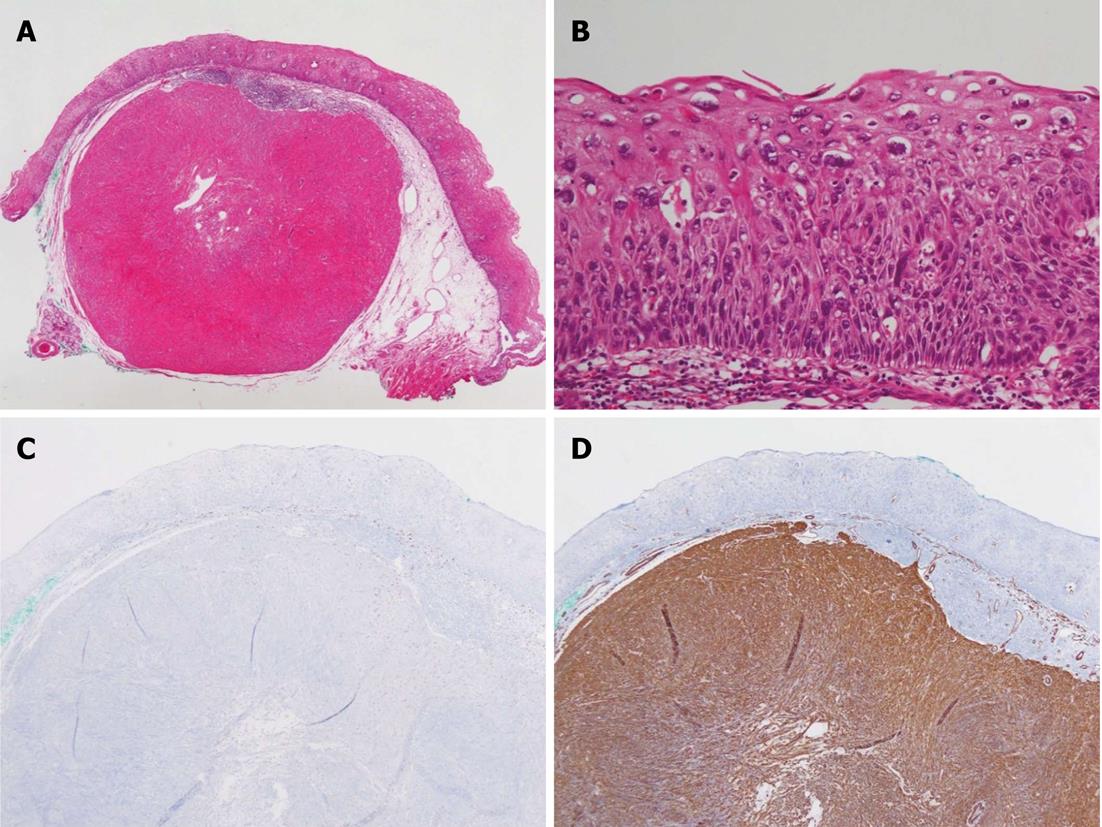
Figure 3 Histopathologic findings.
A: Esophageal leiomyoma arising from the muscularis mucosa (HE, 20 ×); B: Atypical cells in all three areas of the epithelium, but not full thickness, showed severe dysplasia (HE, 200 ×); C: The esophageal leiomyoma was negative for CD117 (C-Kit); D: The esophageal leiomyoma showed strong and diffuse positive staining for smooth muscle actin (200 ×).
- Citation: Ahn SY, Jeon SW. Endoscopic resection of co-existing severe dysplasia and a small esophageal leiomyoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(1): 137-140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i1/137.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.137