Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2012; 18(24): 3035-3049
Published online Jun 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3035
Published online Jun 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3035
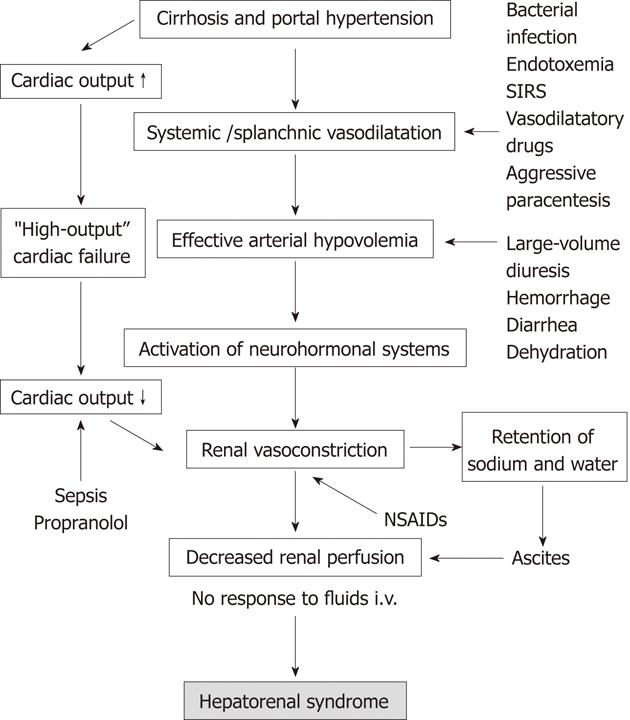
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of hepatorenal syndrome with possible triggering factors.
SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome; NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
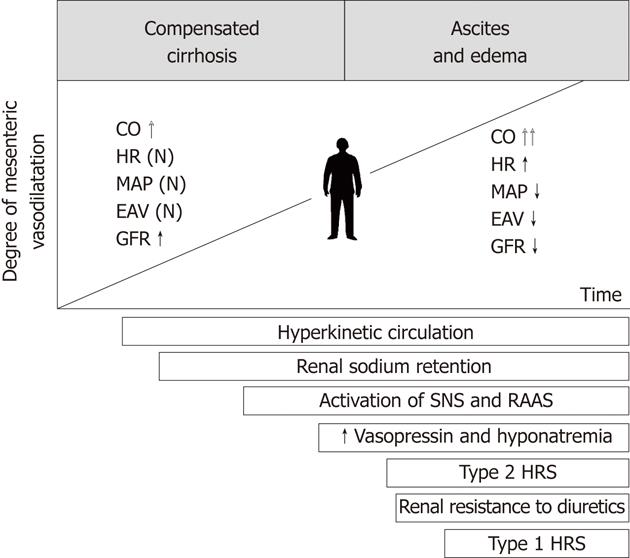
Figure 2 Hemodynamic and neurohormonal consequences of progressive vasodilatation in splanchnic vascular territory.
CO: Cardiac output; EAV: Effective arterial volemia; HR: Heart rate; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; HRS: Hepatorenal syndrome.
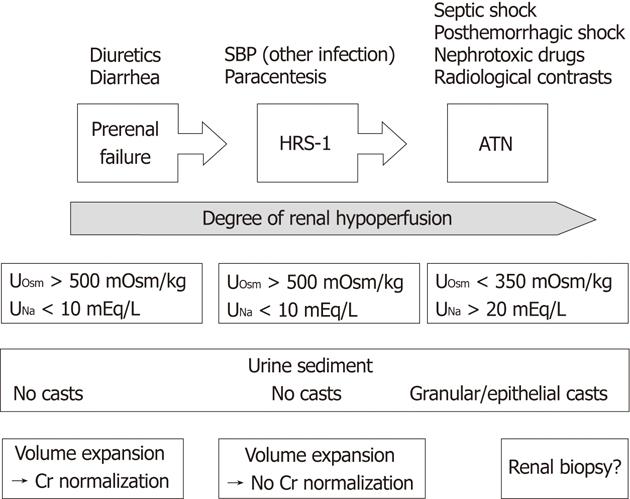
Figure 3 Differential diagnosis of three forms of acute kidney injury in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; Cr: Creatinine; HRS-1: Type 1 hepatorenal syndrome; ATN: Acute tubular necrosis; UOsm: Urine osmolality; UNa: Urinary sodium.
- Citation: Hartleb M, Gutkowski K. Kidneys in chronic liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(24): 3035-3049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i24/3035.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3035