Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2979-2987
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2979
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2979
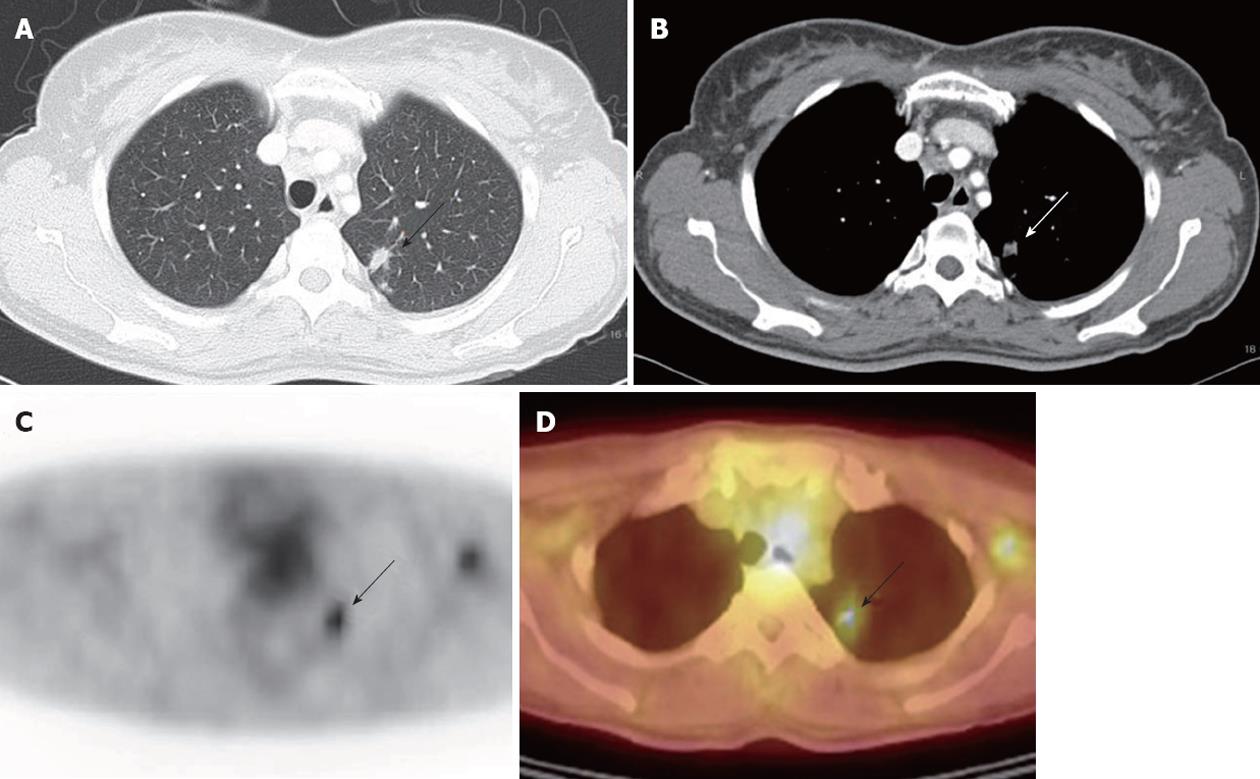
Figure 1 A 51 year-old-female with hepatocellular carcinoma was suspicious of lung metastasis (arrows) in both chest computed tomography and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan which turned out to be nontuberculosis mycobacterium infection on percutaneous transthoracic needle aspiration.
A: High-resolution computed tomography (CT); B: Contrast-enhanced CT; C: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET); D: PET/CT scan.
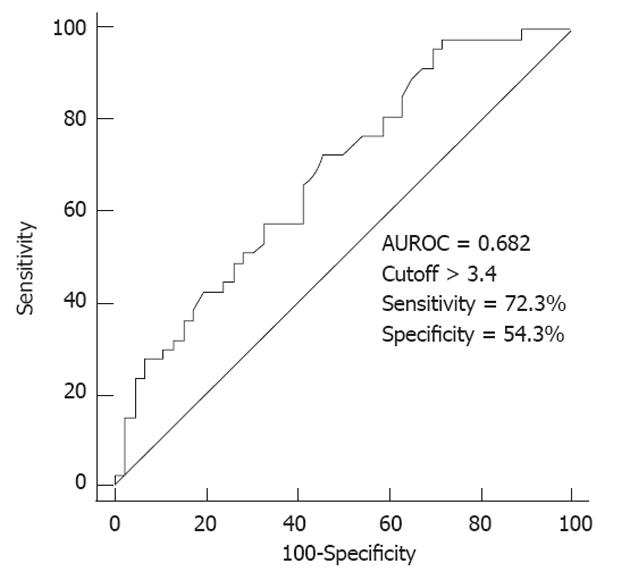
Figure 2 The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve to estimate the optimal cutoff of average standardized uptake value to predict extrahepatic metastasis.
AUROC: Area under receiver operating characteristic.
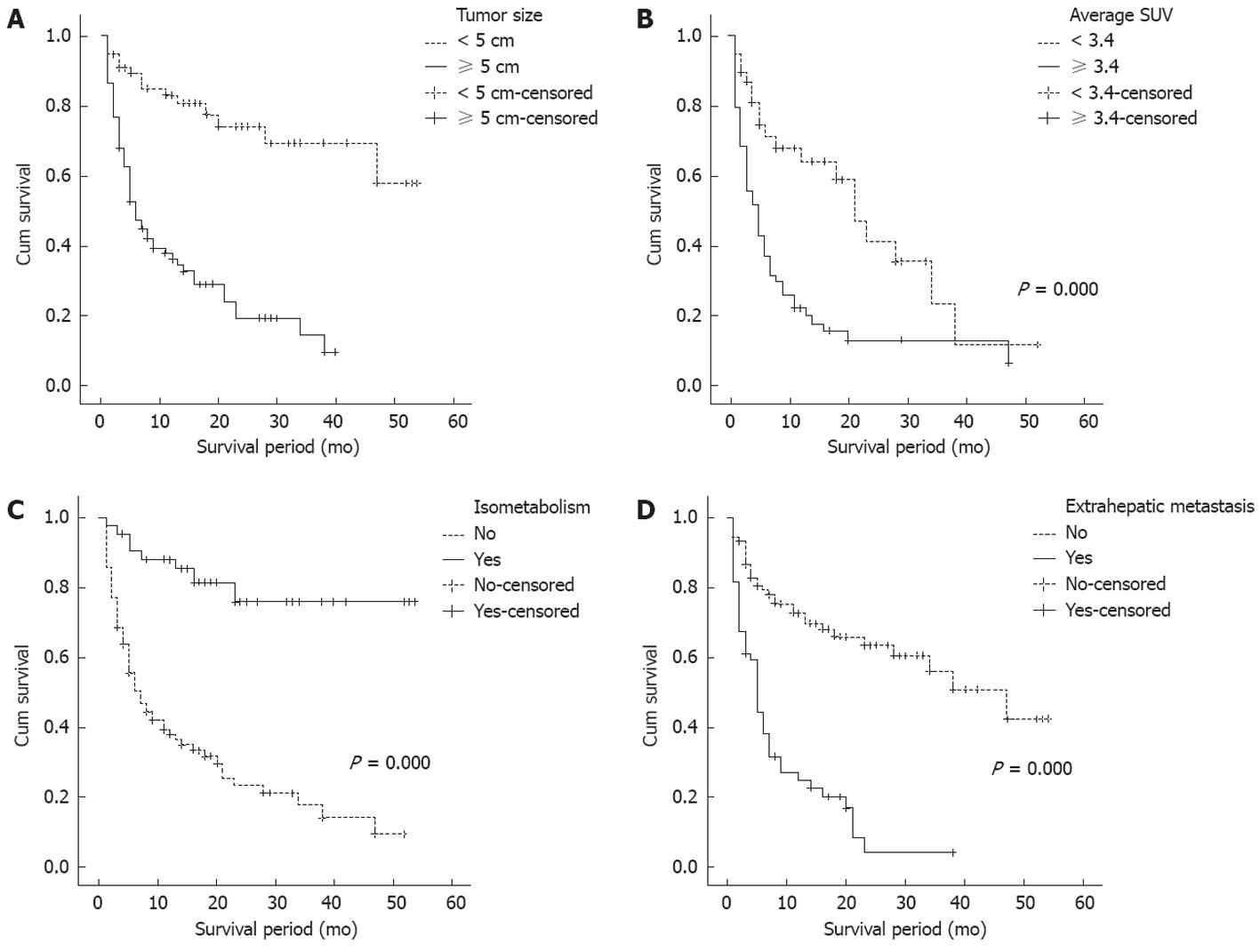
Figure 3 Cumulative survival rate in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma by intrahepatic tumor size (A), average standardized uptake value (B), isometabolic hepatocellular carcinoma (C) and extrahepatic metastasis (D).
SUV: Standardized uptake value.
- Citation: Lee JE, Jang JY, Jeong SW, Lee SH, Kim SG, Cha SW, Kim YS, Cho YD, Kim HS, Kim BS, Jin SY, Choi DL. Diagnostic value for extrahepatic metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma in positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2979-2987
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2979.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2979