Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2011; 17(31): 3585-3590
Published online Aug 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3585
Published online Aug 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3585
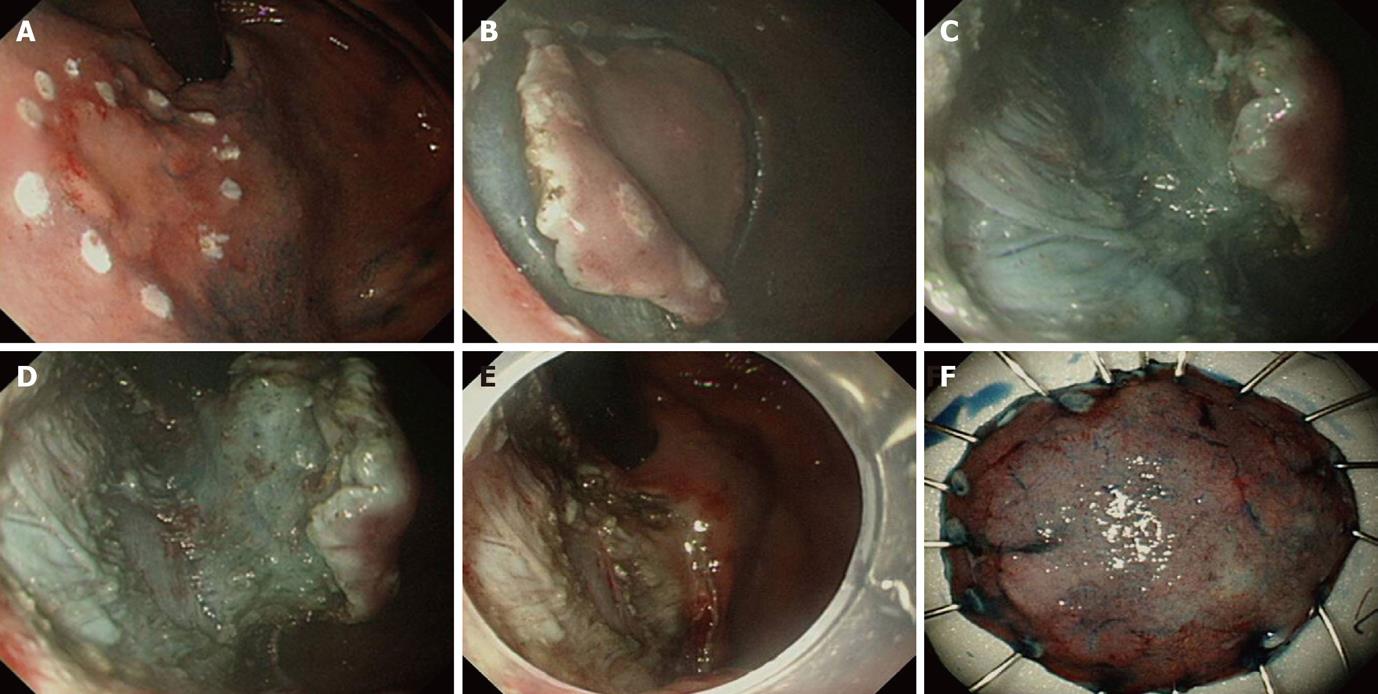
Figure 1 The cardinal steps of endoscopic submucosal dissection technique.
A: Marking around early gastric cancer at fundus, marking at least 5 mm apart from the outer circumferential margin of the lesion with the argon plasma coagulation; B: Mucosal incision (precut), circumferential cutting around the lesion prior to submucosal dissection. Incision must be deep enough to expose submucosal layer fully; C, D: Submucosal dissection, early gastric cancer located in upper stomach or fundus like in this case should be dealt with great care to avoid bleeding or perforation. It is advised to always maintain a visual landmark between submucosa and underlying proper muscle layer; E: Completion of endoscopic submucosal dissection, large artificial ulcer was formed after submucosal dissection; F: Acquisition and fixation of the specimen, the specimen was fixated on the board with the pin spreading the lesion circumferentially for the preparation of the pathologic interpretation.
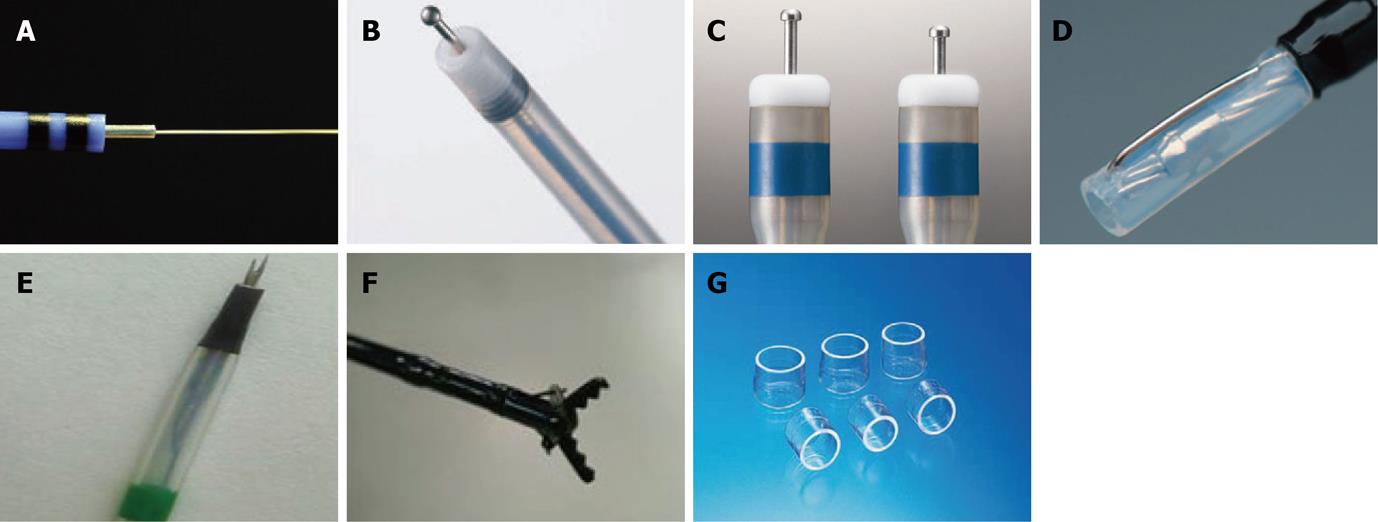
Figure 2 New devices.
A: Water-jet hybrid knife allows needleless infusion and lifting of the lesion as well as cutting and coagulation at the same time without the need of changing instruments; B: Ball tipped flush knife (Flush knife-BT) features improved hemostatic efficacy and dissection speed compared with standard flush knife; C: Dual knife is a newly-devised version of pre-existing flex knife, having 0.3 mm needle tip shaped like a doorknob makes the needle less likely to slip, simplifies marking and hemostasis; D: Mucosectome is made of non-conducted tip and endo-knife which is located at the side of the non-conducted tip; E: Fork knife has two interchangeable knives, a fixed flexible snare and a forked knife, which form a single working unit, and has an inlet for material injection or saline irrigation during the procedure; F: Grasping-type scissors forceps has a 0.8-mm-wide and 6-mm-long serrated cutting edge to facilitate grasping of tissue; G: Distal attachment helps keep the field of view clear throughout the procedure and can be chosen from various sized and shaped models fitted with endoscopes.
- Citation: Lee WS, Cho JW, Kim YD, Kim KJ, Jang BI. Technical issues and new devices of ESD of early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(31): 3585-3590
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i31/3585.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3585