Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2011; 17(16): 2143-2149
Published online Apr 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2143
Published online Apr 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2143
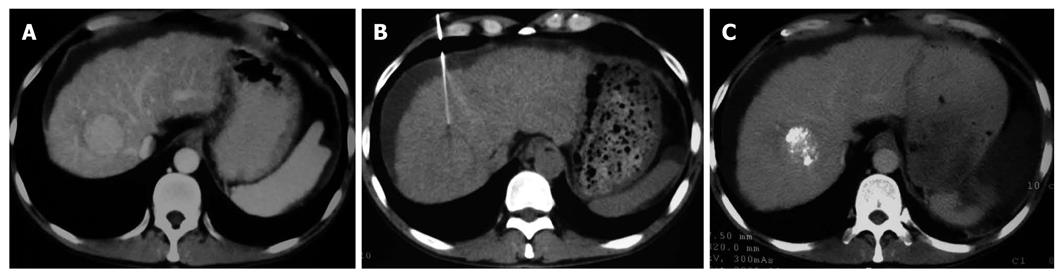
Figure 1 Contrast computed tomography showing a nodule (3.
5 cm in diameter) in the right upper liver lobe manifested as homogenous enhancement (A); computed tomography scan (b) demonstrating the course of fine needle biopsy under computed tomography guidance with the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma confirmed (B); computed tomography follow-up (c) revealing lipiodol deposit in the mass and spleen infarction after spleen embolization (C) in a 52-year-old man with multiple hepatic nodules, liver cirrhosis, splenomegaly and elevated alpha-fetoprotein.
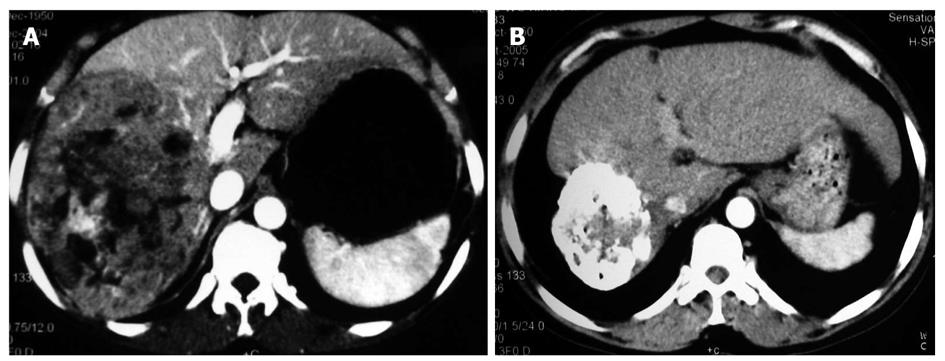
Figure 2 Contrast computed tomography scan showing a 15 cm × 11.
5 cm hepatocellular carcinoma in the right liver lobe manifested as a heterogenous lower density, partial enhancement and well-differentiated contour (A) and computed tomography follow-up displaying the significant regression of a 8.5 cm x 6 cm lesion with compact lipiodol deposit in a 72-year-old man after 3 p53 gene injections and 4 courses of transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization.
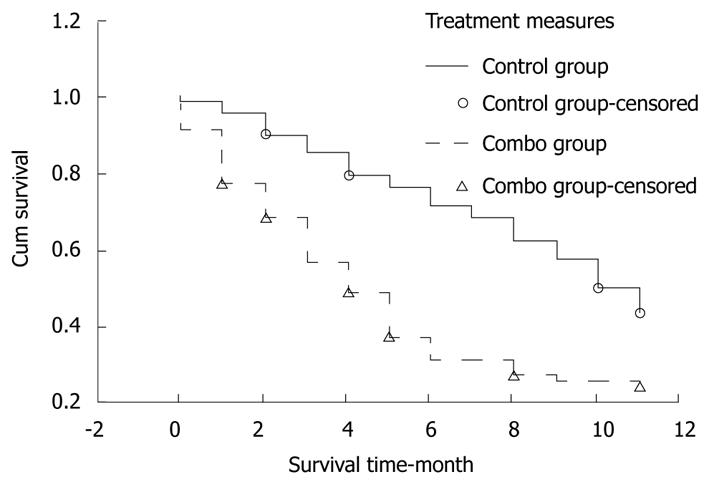
Figure 3 Survival curves for patients following treatment.
-
Citation: Guan YS, Liu Y, He Q, Li X, Yang L, Hu Y, La Z.
p53 gene therapy in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for HCC: One-year follow-up. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(16): 2143-2149 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i16/2143.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2143