Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2010; 16(8): 1034-1038
Published online Feb 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1034
Published online Feb 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1034
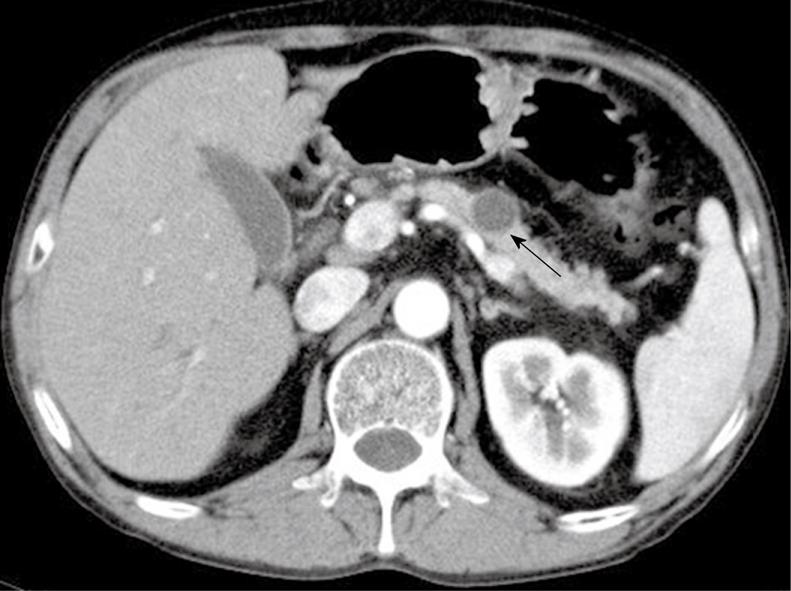
Figure 1 Image of the cystic lesion by contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography (arrow).
There was a 17-mm well-marginated, round, low-density lesion in the body of the pancreas. The central contents of the lesion showed no enhancement in the post-contrast-enhanced image.
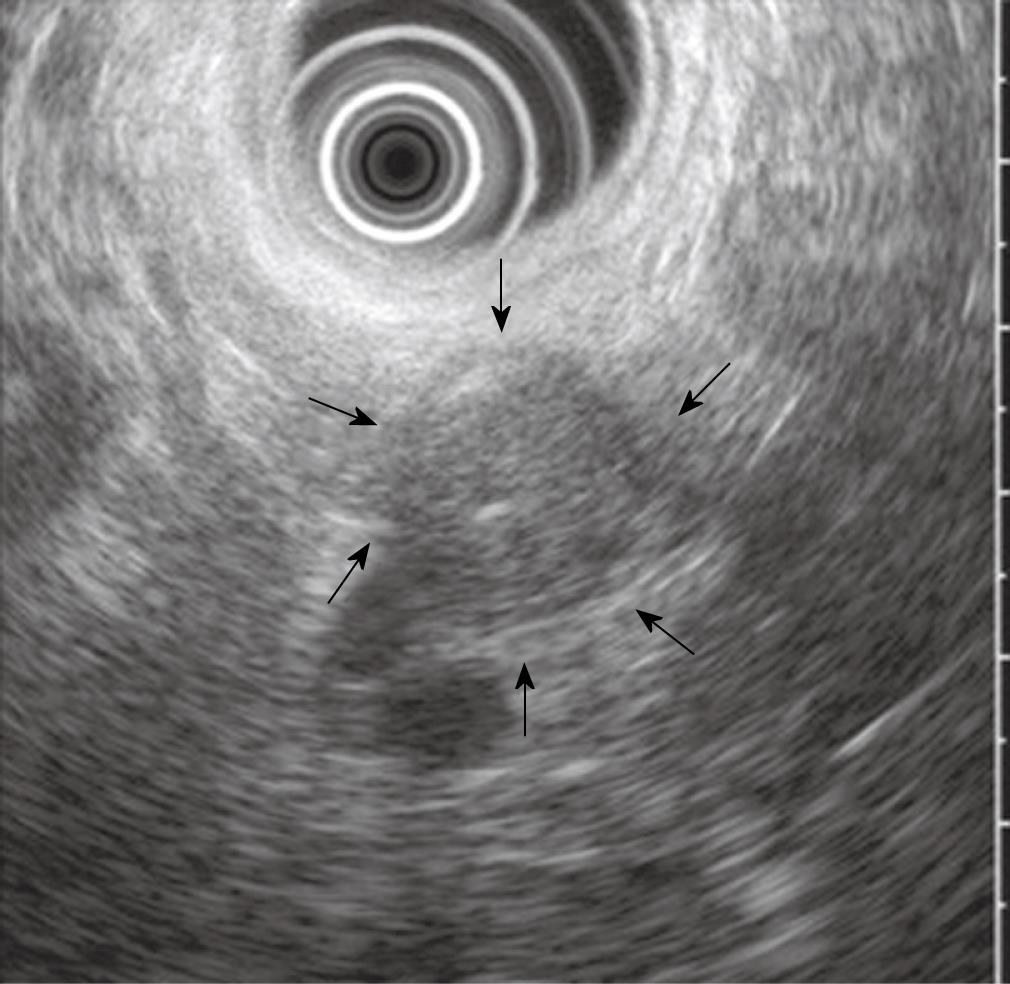
Figure 2 Image of the cystic lesion on EUS.
It showed a 17-mm × 19-mm, well-circumscribed, round, homogenous, hypoechoic solid lesion with central echogenicity (arrows).
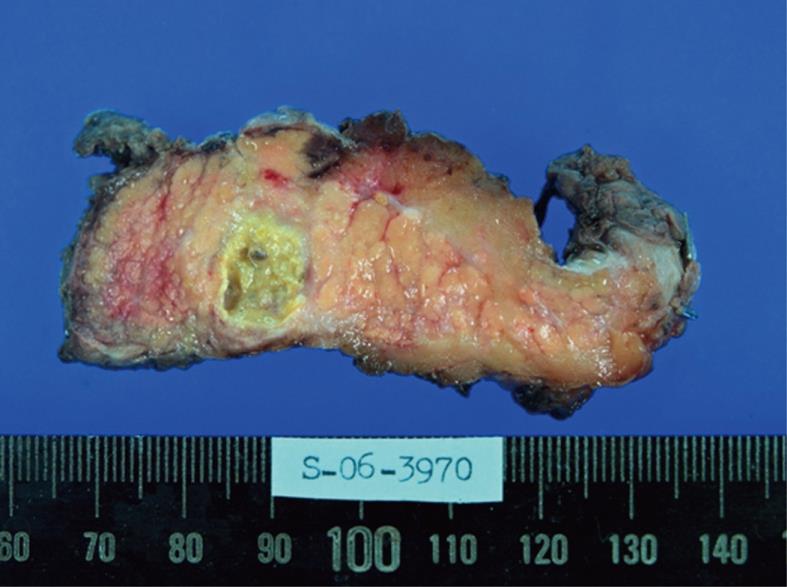
Figure 3 Gross finding of the pancreatic cystic lesion.
There was a 17-mm, unilocular, well-encapsulated cystic lesion filled with yellowish muddy material in the body of the pancreas.
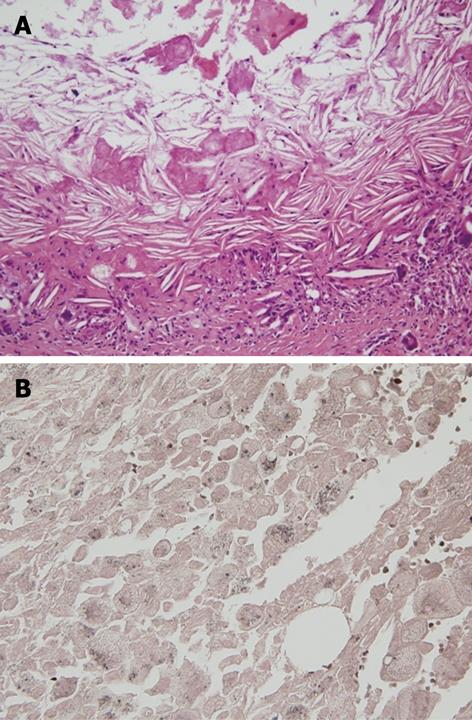
Figure 4 Microscopic finding of the pancreatic pseudocyst.
A: Microscopic finding of the pancreatic pseudocyst. HE staining showed multiple lipid droplets and cholesterol clefts; B: Sudan black B stain showed positive findings for lipid droplets, stained with a dark brown color.
- Citation: Cha SW, Kim SH, Lee HI, Lee YJ, Yang HW, Jung SH, Kim A, Lee MK, Han HY, Kang DW. Pancreatic pseudocyst filled with semisolid lipids mimicking solid mass on endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(8): 1034-1038
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i8/1034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1034