Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2010; 16(8): 1019-1024
Published online Feb 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1019
Published online Feb 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1019
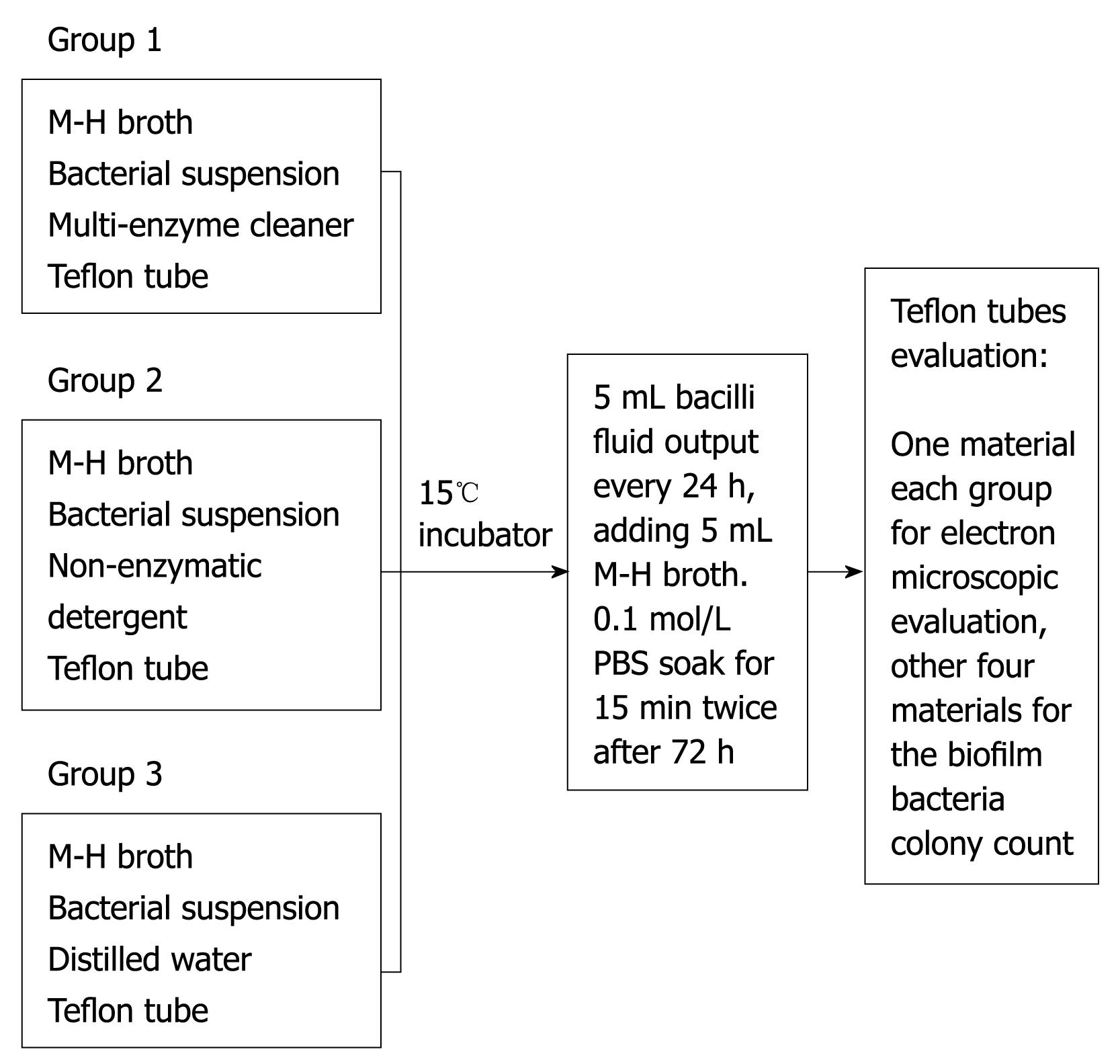
Figure 1 Bacterial biofilm formation assay.
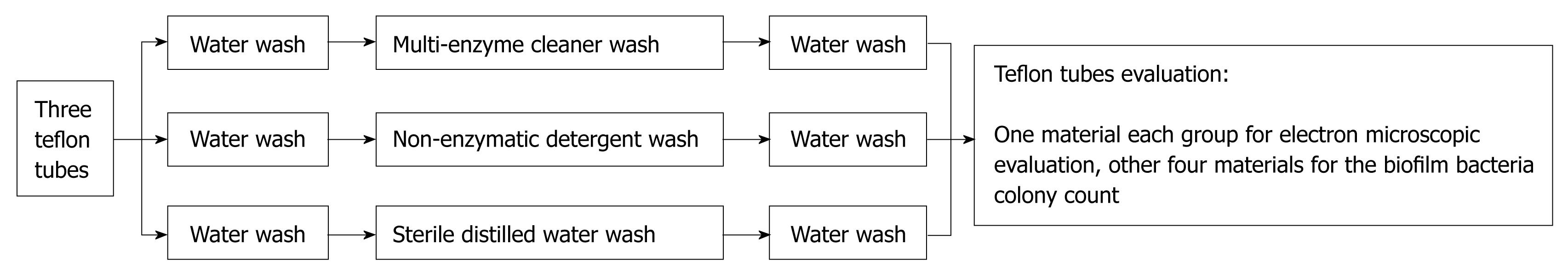
Figure 2 Cleaning steps of biofilm-coated sample tubes.
Figure 3 Mixture of detergent and bacteria cultured for 72 h.
Left: The enzyme-containing washing, showing a homogeneous transparent liquid; Middle: A non-enzyme-containing detergent, showing in addition to a large amount of sediment at the bottom, the upper part was clean liquid; Right: The control group, showing bacteria bacilli and a small amount of sediment at the bottom.
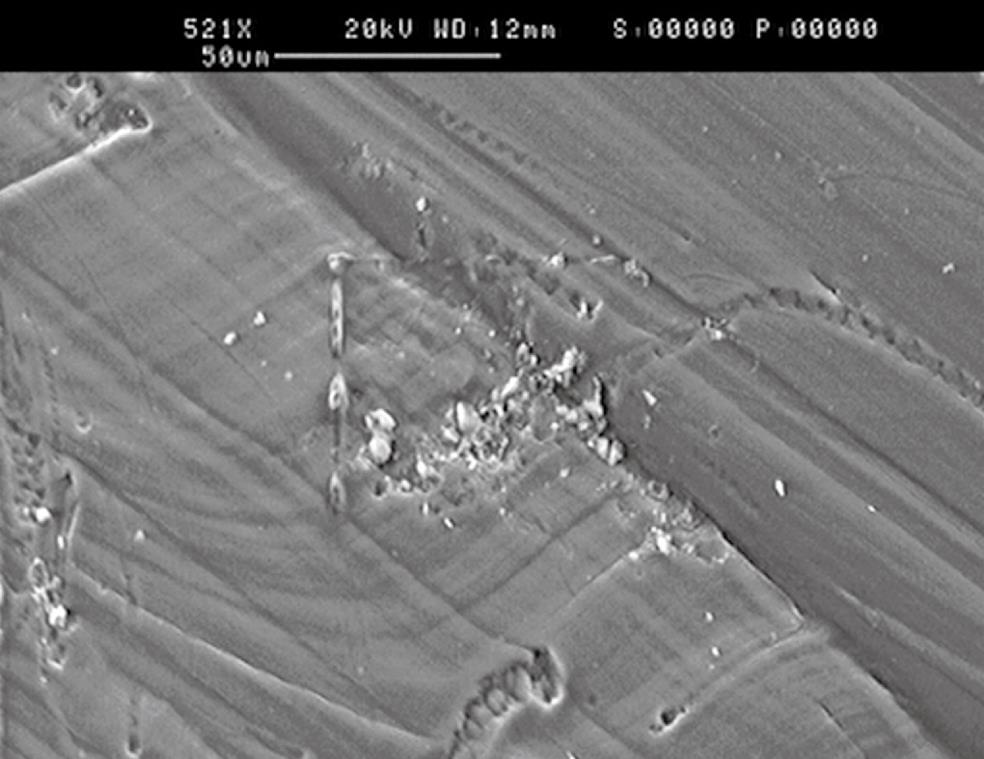
Figure 4 The concave wall structure after mixture of detergent and Escherichia coli cultured; surfaces are part of the biofilm formation.
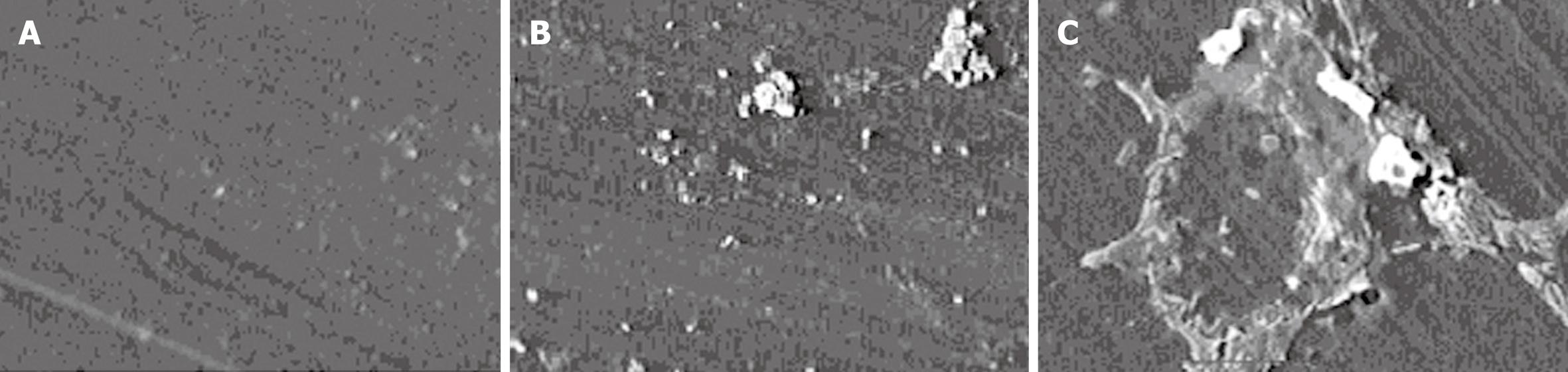
Figure 5 The concave wall structure after non-enzyme detergent (A), enzyme-containing detergent (B), and sterile distilled water (C) washing.
A: No obvious biofilm residue; B: Massive biofilm structure residue; C: Relatively large biofilm attached to bacterial biomass, respectively.
- Citation: Fang Y, Shen Z, Li L, Cao Y, Gu LY, Gu Q, Zhong XQ, Yu CH, Li YM. A study of the efficacy of bacterial biofilm cleanout for gastrointestinal endoscopes. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(8): 1019-1024
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i8/1019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i8.1019