Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2010; 16(43): 5481-5489
Published online Nov 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5481
Published online Nov 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5481
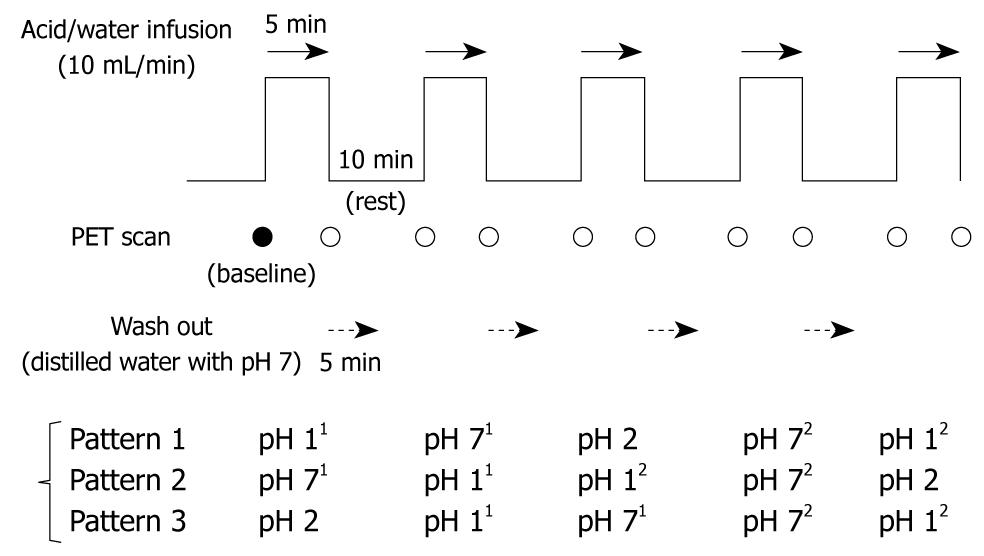
Figure 1 This schema illustrates the procedure of esophageal infusion and brain positron emission tomography scanning.
The infusions were performed twice for pH 1 and 7 solutions (distilled water) and once for the pH 2 solution. In order to counterbalance the effects of the infusion order, the order was randomly selected per each subject from pH 1-7-2-7-1, pH 7-1-1-7-2 and pH 2-1-7-7-1 as shown. 1First infusion; 2Second infusion; PET: Positron emission tomography.
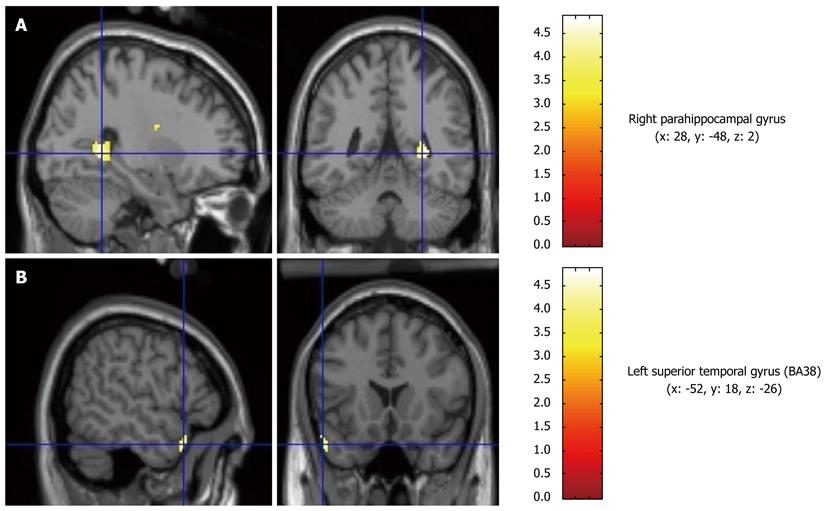
Figure 2 Representative images from the subtraction analysis of the second pH 1 infusion minus the baseline.
Left: Sagittal view; Right: Cranial view. A: Right parahippocampal gyrus (x: 28, y: -48, z: 2); B: Left superior temporal gyrus (temporal pole, BA38) (x: -52, y: 18, z: -26).
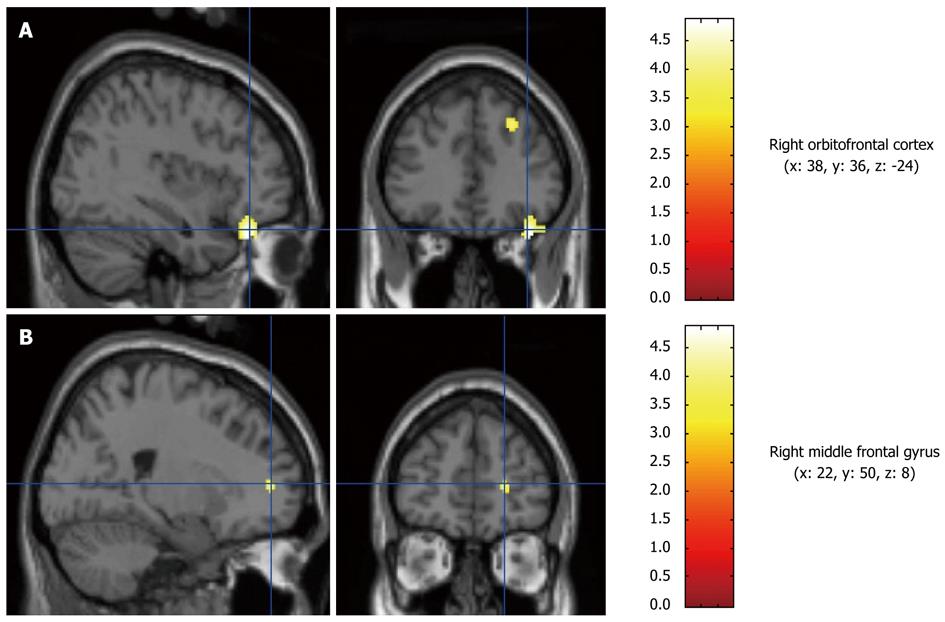
Figure 3 Representative images from the subtraction analysis of the second pH 1 infusion minus the first.
Left: Sagittal view; Right: Cranial view. A: Right orbitofrontal cortex (x: 38, y: 36, z: -24); B: Right middle frontal gyrus (x: 22, y: 50, z: 8).
- Citation: Kobayashi S, Abe Y, Tashiro M, Koike T, Iijima K, Imatani A, Ohara S, Watanabe S, Fukudo S, Shimosegawa T. Brain activity following esophageal acid infusion using positron emission tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(43): 5481-5489
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i43/5481.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5481