Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2010; 16(43): 5474-5480
Published online Nov 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5474
Published online Nov 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5474
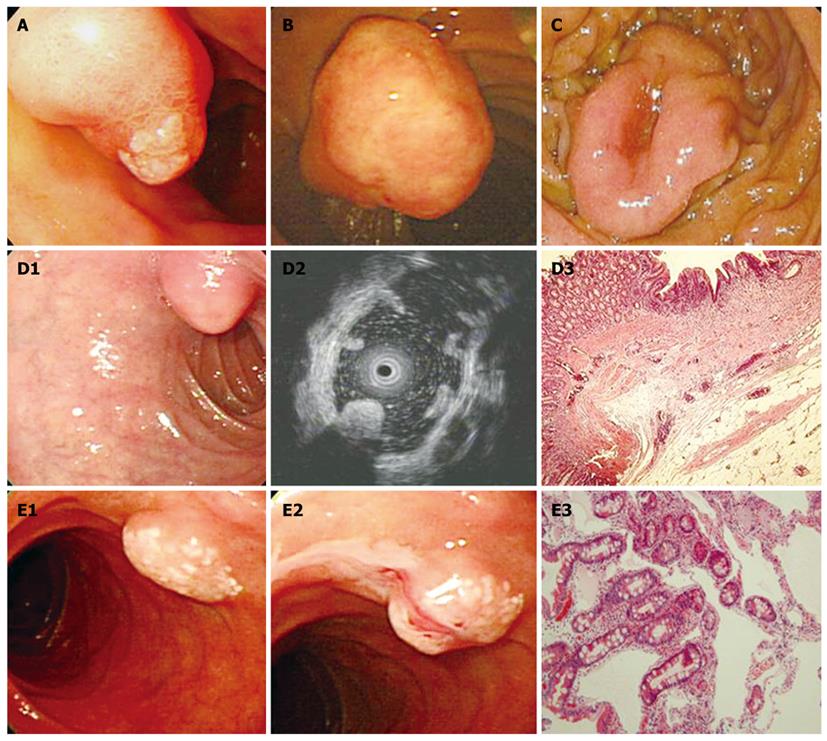
Figure 1 Ampullary polyps and submucosal lesions in the duodenum.
A: Ampullary adenoma; B: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor; C: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; D: Duodenal lipoma. The surface of the tumor was covered by a normal mucosa, but it had a yellowish coloration (D1). Endoscopic ultrasound showed a homogeneous and hyperechoic mass with post-acoustic shadowing (D2). Histopathological examination revealed the tumor that was composed of mature adipose tissue (HE, × 40) (D3); E: Duodenal lymphangiectasia. On the surface of the tumor, focal small whitish macules or nodules were observed (E1). After forceps biopsy, whitish milk-like material flowed out (E2). A dilated lymphatic duct in the subepithelial area was observed under microscopic examination (HE, × 40) (E3).
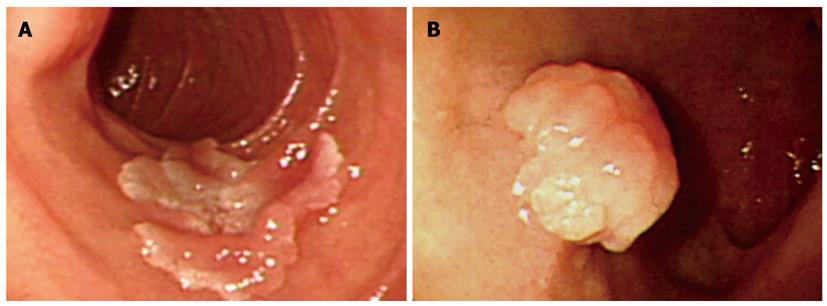
Figure 2 Endoscopic findings of duodenal adenomas.
Geographic shaped flat elevated lesions (A) or semi-pedunculated polyps (B) were found in the duodenum.
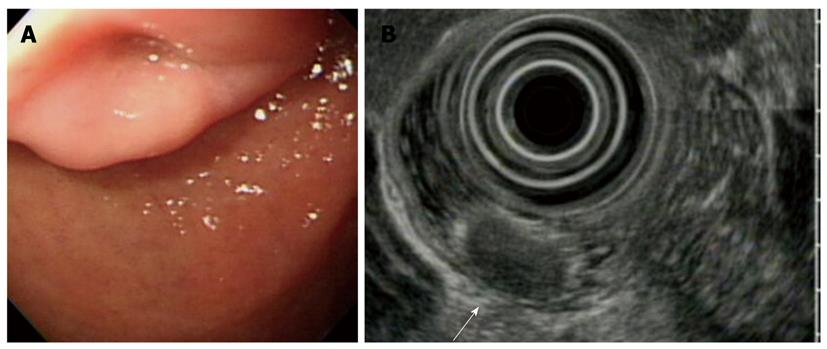
Figure 3 Endoscopic findings of carcinoid tumors.
A: Endoscopy revealed an elevated lesion with a central dimpling in the bulb of the duodenum; B: Endoscopic ultrasound finding showed a round-shaped homogenous hypoechoic mass in the mucosal and muscularis mucosal layer (arrow).
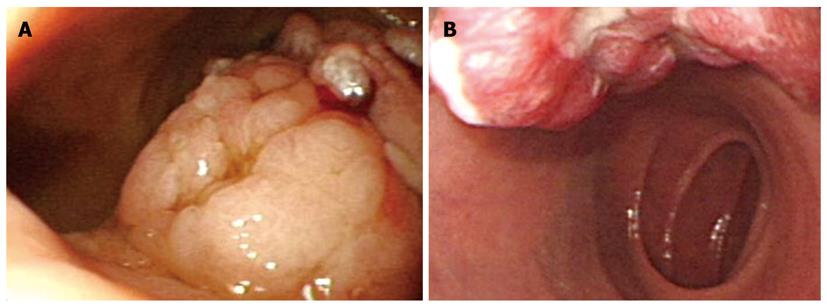
Figure 4 Serrated adenoma (A) and focal cancer change of adenomas (B).
Large pedunculated polyps were observed in the duodenal bulb. They had multilobulated and friable surfaces.
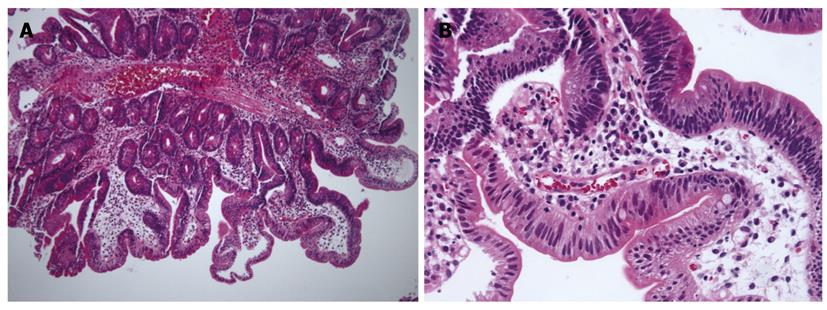
Figure 5 Microscopic finding of serrated adenomas.
A: Vascular stalk and saw-tooth appearance were observed (HE, × 40); B: At high magnification, hyperplastic foveolar cells were found. In part, epithelia with pleomorphic, stratified nuclei and irregular chromatin deposits were observed (HE, × 200).
- Citation: Jung SH, Chung WC, Kim EJ, Kim SH, Paik CN, Lee BI, Cho YS, Lee KM. Evaluation of non-ampullary duodenal polyps: Comparison of non-neoplastic and neoplastic lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(43): 5474-5480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i43/5474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5474