Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2010; 16(36): 4583-4588
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4583
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4583
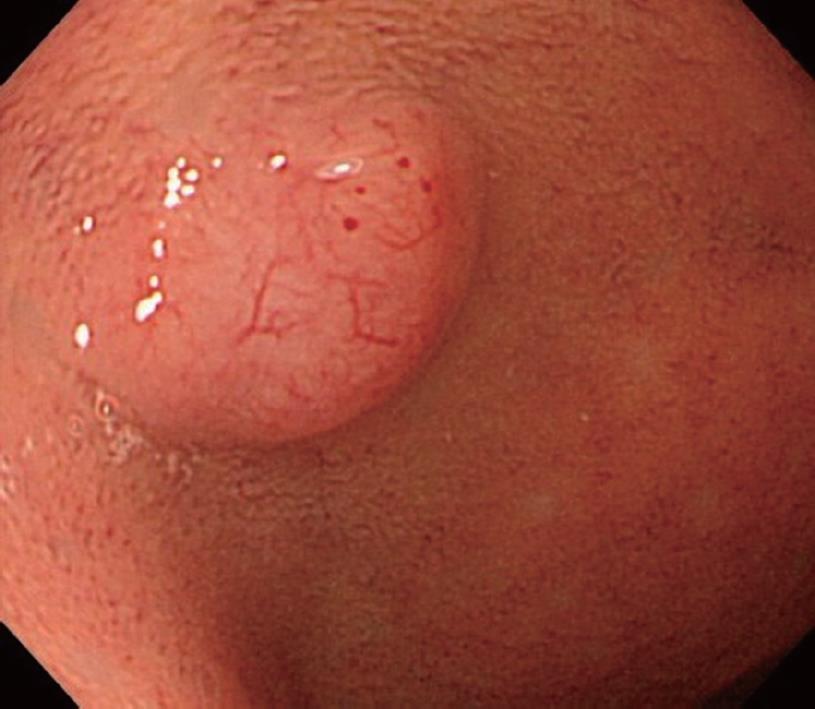
Figure 1 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed a submucosal-tumor-like, protruding lesion 0.
7 cm in diameter, arising in the anterior wall of the duodenal bulb. The top of the tumor was yellowish white, with dilated blood vessels.
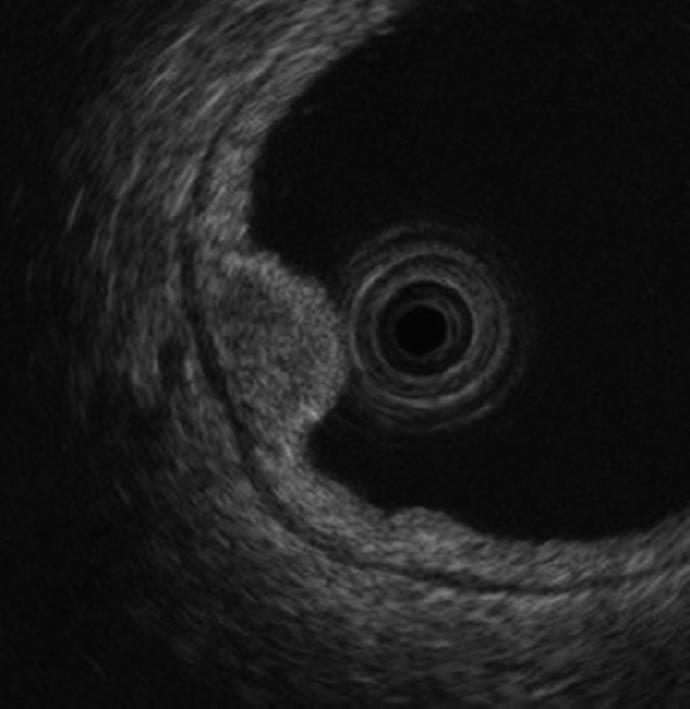
Figure 2 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed a homogenous, oval hypoechoic mass, mainly located in the third layer.
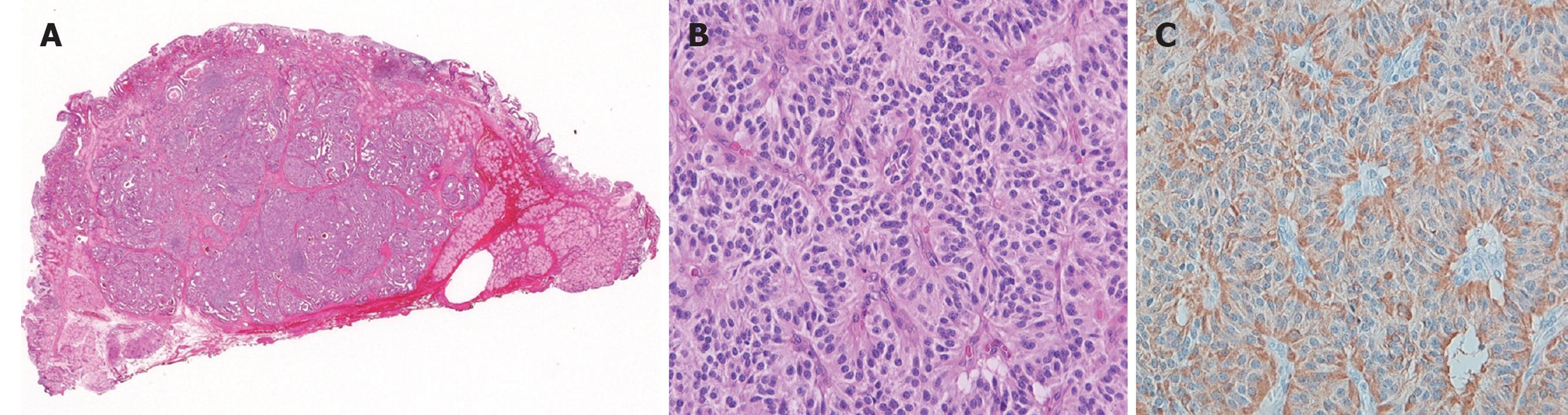
Figure 3 Histopathological examination.
A: Macroscopic view of resected specimens obtained by endoscopic mucosal resection (hematoxylin and eosin staining). The longest diameter was 0.7 cm; B: Histopathological examination of specimens (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 10) showed that cubic, atypical cells forming follicular or glandular patterns, with rounded nuclei and eosinophilic syncytia; C: Histopathological examination of specimens (chromogranin A staining, × 10) showed that tumors stained positively for chromogranin A.
- Citation: Ishido K, Tanabe S, Higuchi K, Sasaki T, Katada C, Azuma M, Naruke A, Koizumi W, Mikami T. Clinicopathological evaluation of duodenal well-differentiated endocrine tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(36): 4583-4588
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i36/4583.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4583