Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2010; 16(32): 4039-4046
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.4039
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.4039
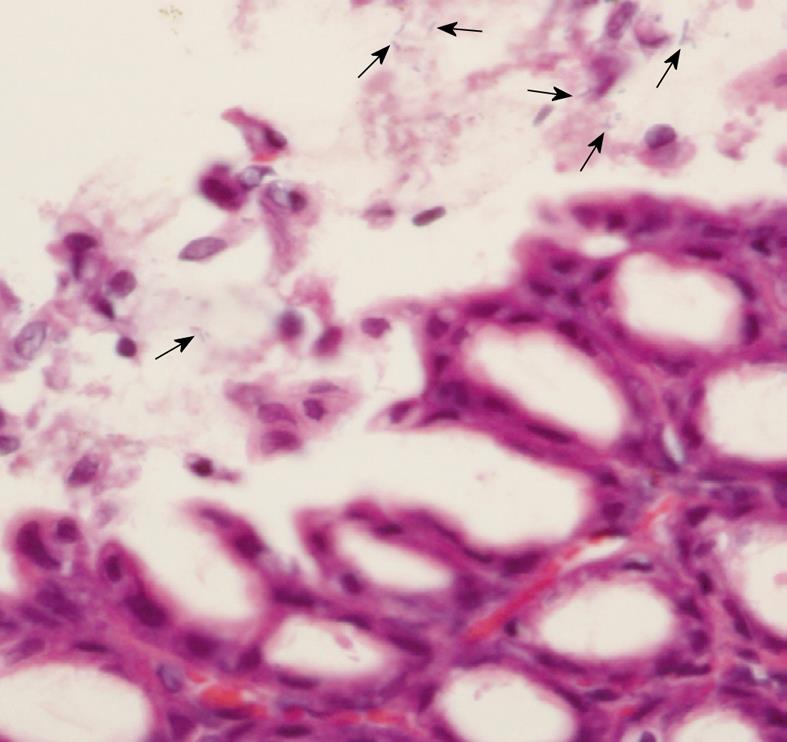
Figure 1 Histological examination (HE stain, × 1000) of Helicobacter pylori-infected rats.
Helicobacter pylori (arrows) in the gastric mucosa identified by the pathologist.
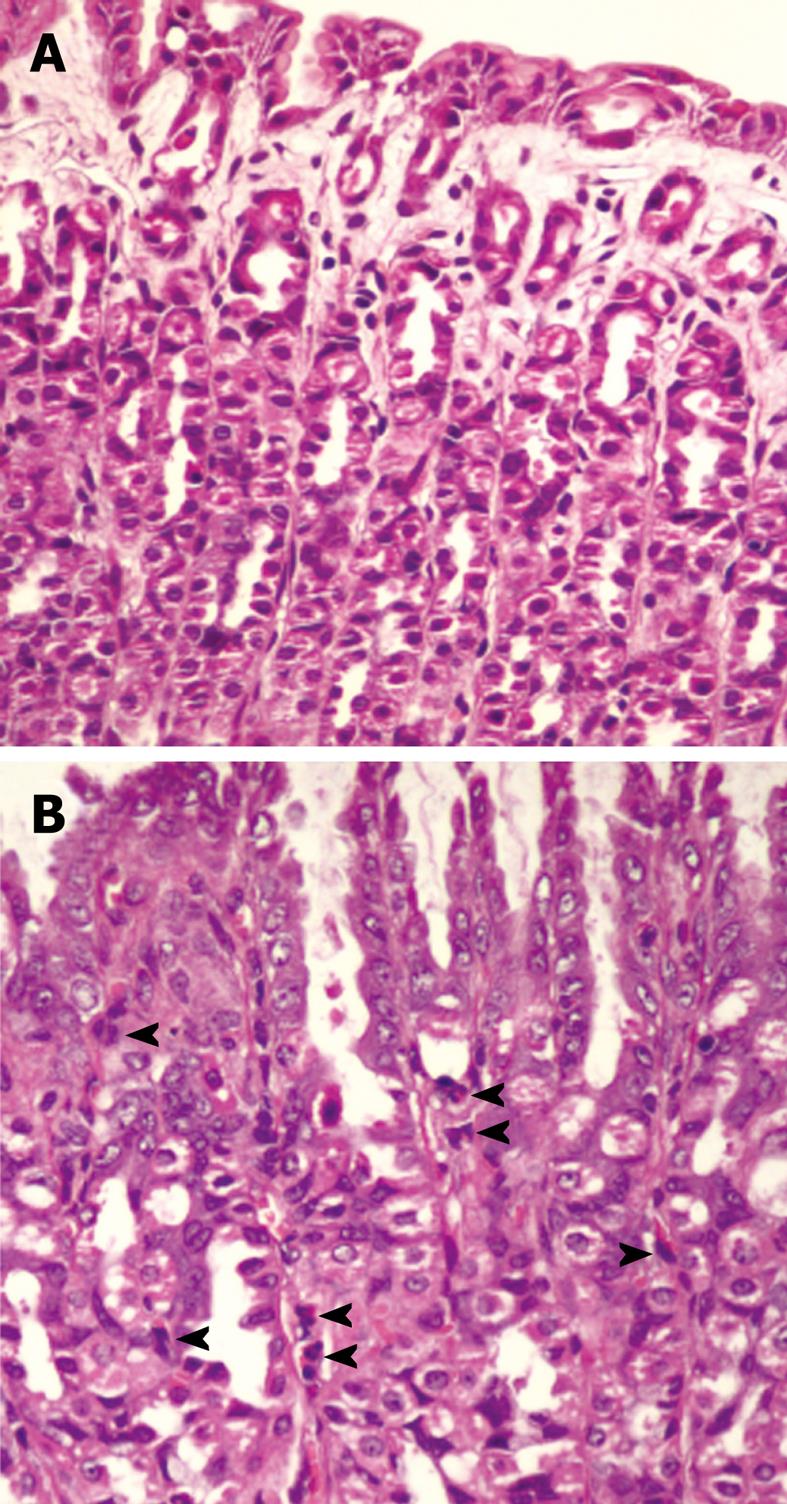
Figure 2 Pathological changes of rat gastric mucosa in control (A) and Helicobacter pylori-infected rats (B) (HE stain, × 400).
A: Normal gastric mucosa; B: Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa showing inflammatory cell infiltration in the lamina propria (arrowheads).
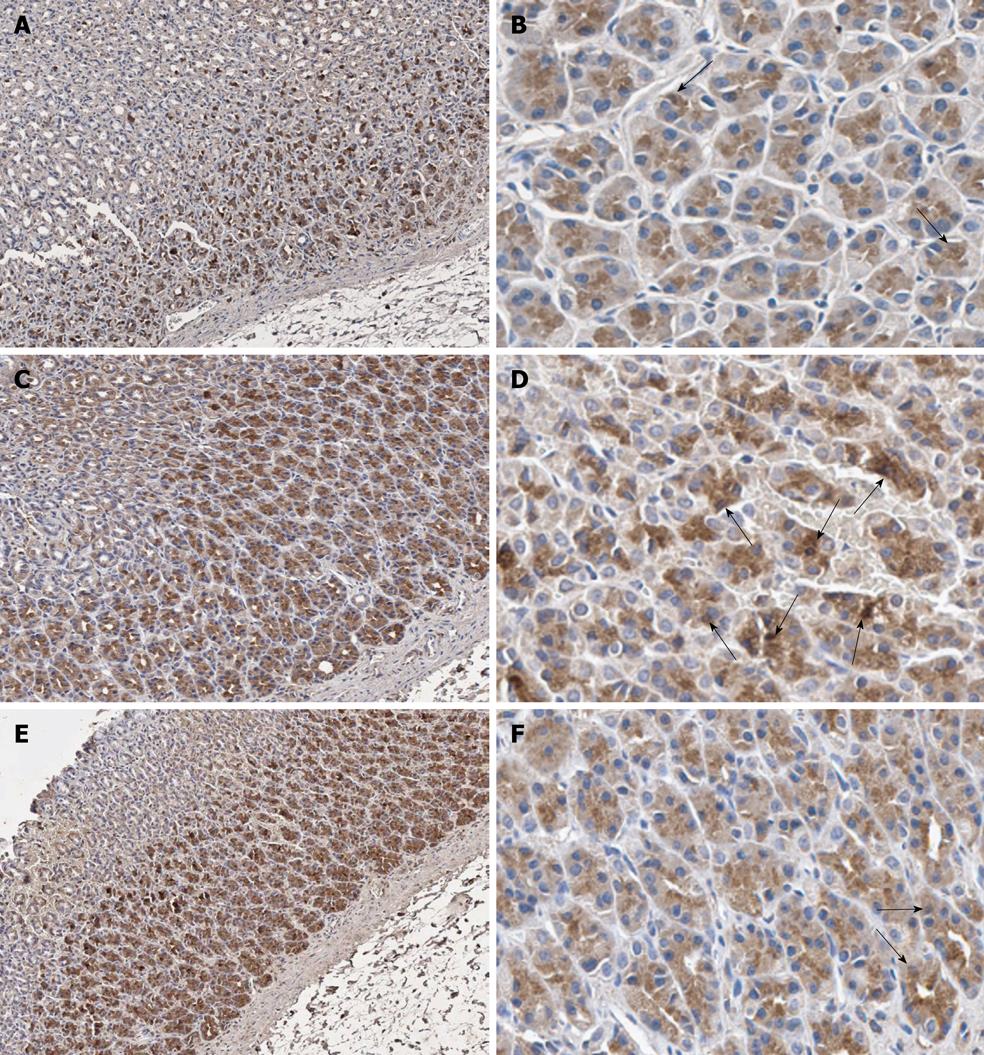
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of nuclear factor-κB p65 antibody in representative tissue specimens.
A, B: Control rats; C, D: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected rats; E, F: H. pylori-infected rats supplemented with 200 mg/kg curcumin. Nuclear counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. The examples of immunoreactive cells are those with dark brown stain in their nuclei (arrows). Images were obtained at × 100 (A, C and E) and × 400 (B, D and F).
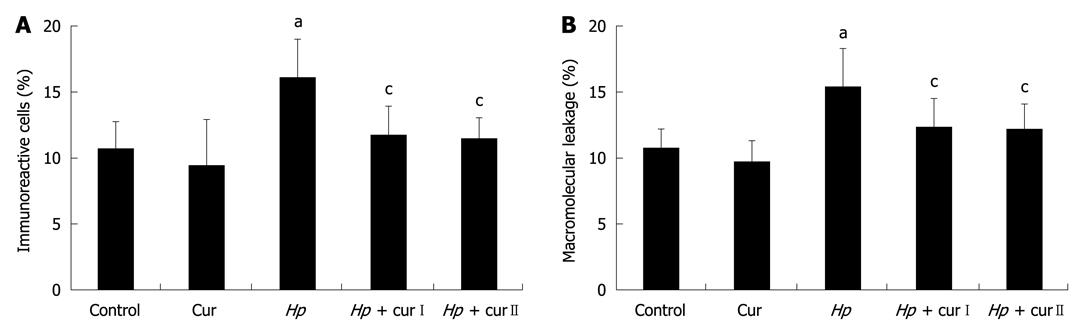
Figure 4 mean ± SD of the percentage of nuclear factor-κB p65 immunoreactive cells (A) and macromolecular leakage (B) in all experimental groups.
aP < 0.05 vs control rats (Control); cP < 0.05 vs Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected rats (Hp). Cur: Control rats supplemented with 600 mg/kg curcumin; Hp + curI: H. pylori-infected rats supplemented with 200 mg/kg curcumin; Hp + curII: H. pylori-infected rats supplemented with 600 mg/kg curcumin.
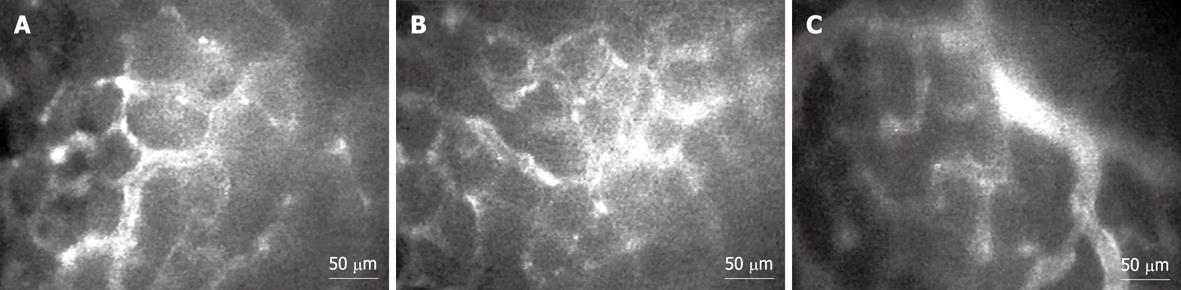
Figure 5 Intravital fluorescent microscopic images (× 200) demonstrate macromolecular leakage from vessels to the interstitial space at 30-min time points.
A: Control rats; B: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected rats; C: H. pylori-infected rats supplemented with 200 mg/kg curcumin.
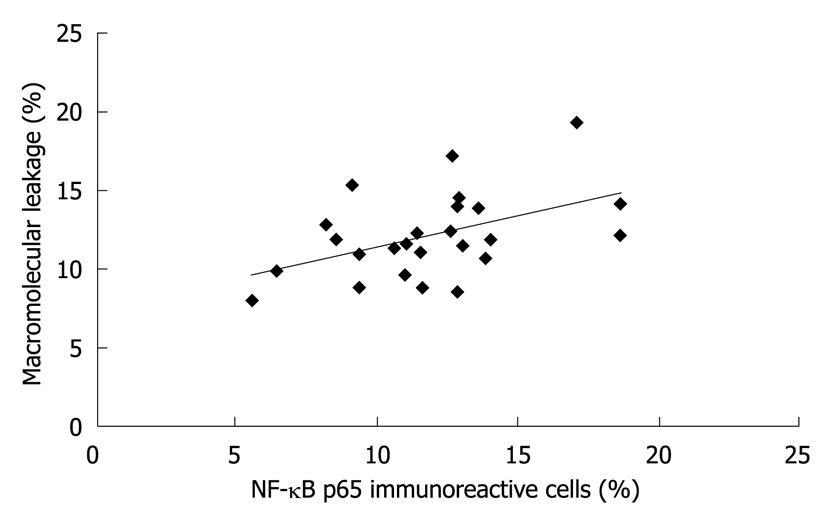
Figure 6 Correlation between the percentage of nuclear factor-κB p65 expression in gastric epithelial cells and the macromolecular leakage (r2 = 0.
2228, P = 0.017). NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
-
Citation: Sintara K, Thong-Ngam D, Patumraj S, Klaikeaw N, Chatsuwan T. Curcumin suppresses gastric NF-κB activation and macromolecular leakage in
Helicobacter pylori -infected rats. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(32): 4039-4046 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i32/4039.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.4039