Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2010; 16(27): 3385-3393
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3385
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3385
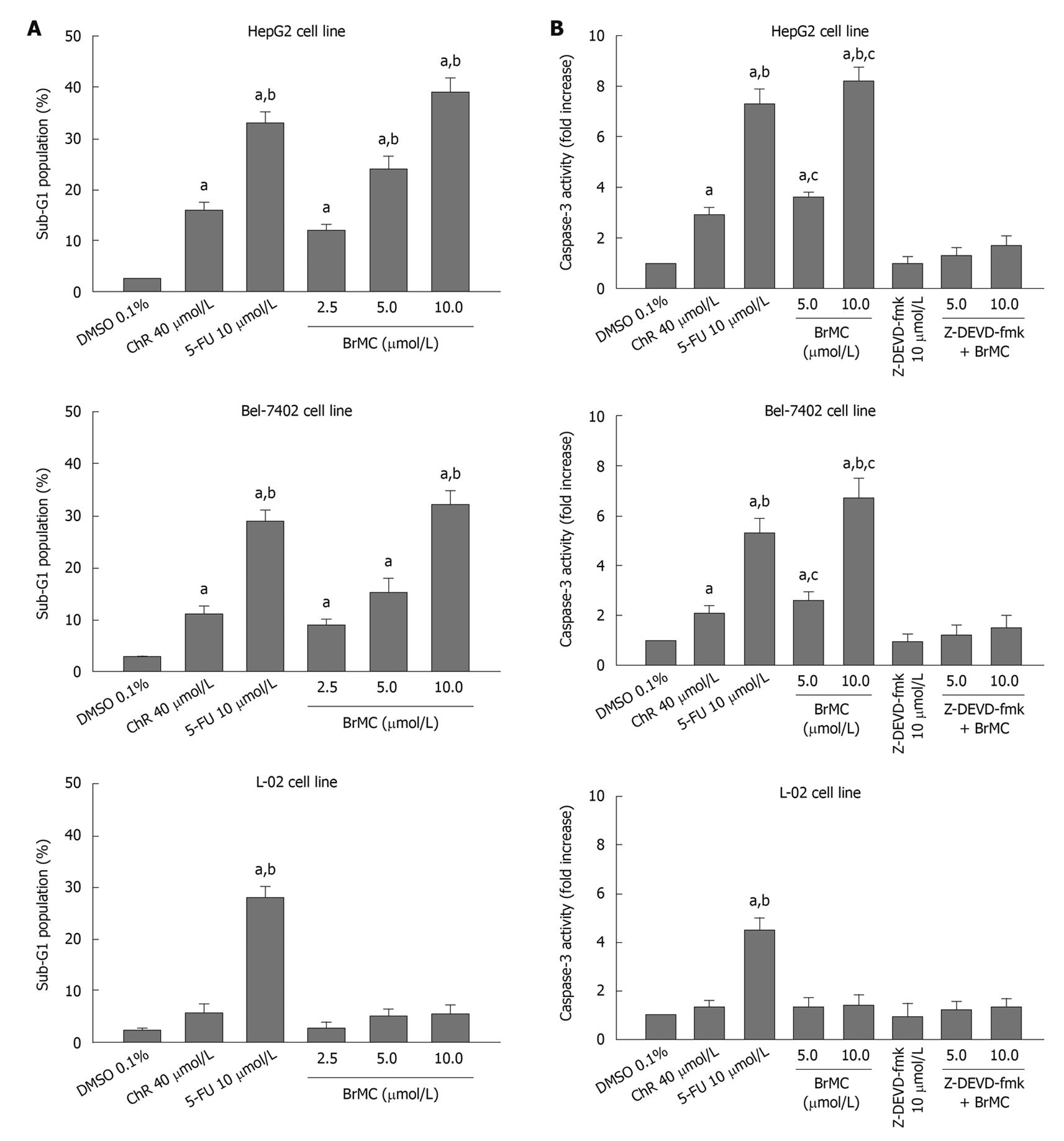
Figure 1 Effects of 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin on the percentage sub-G1 cell population (A), caspase-3 activity (B) in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2, Bel-7402 and human embryo liver L-02 cells.
aP < 0.05 vs treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); bP < 0.05 vs treatment with chrysin (ChR); cP < 0.05 vs treatment with Z-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-CH2F (Z-DEVD-fmk) plus BrMC. 5-FU: 5-flurouracil.
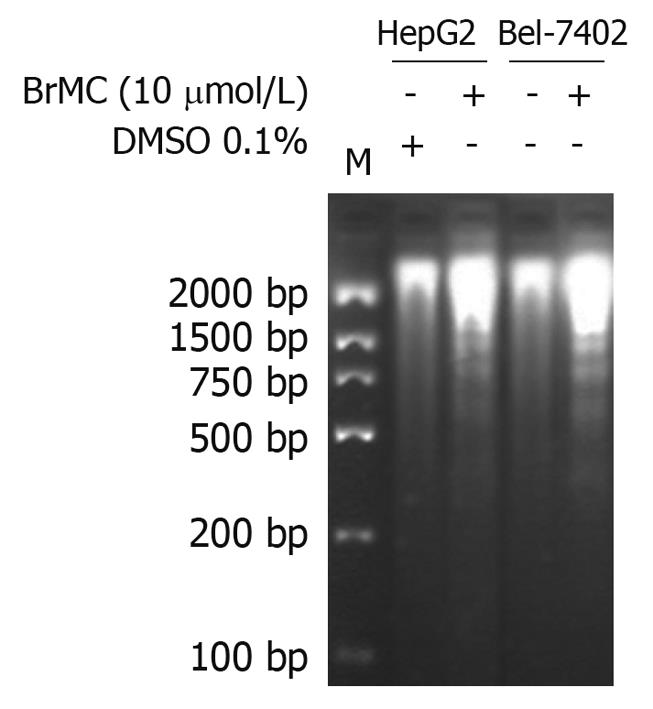
Figure 2 Effects of 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin on DNA fragmentation in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 and Bel-7402 cells.
DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
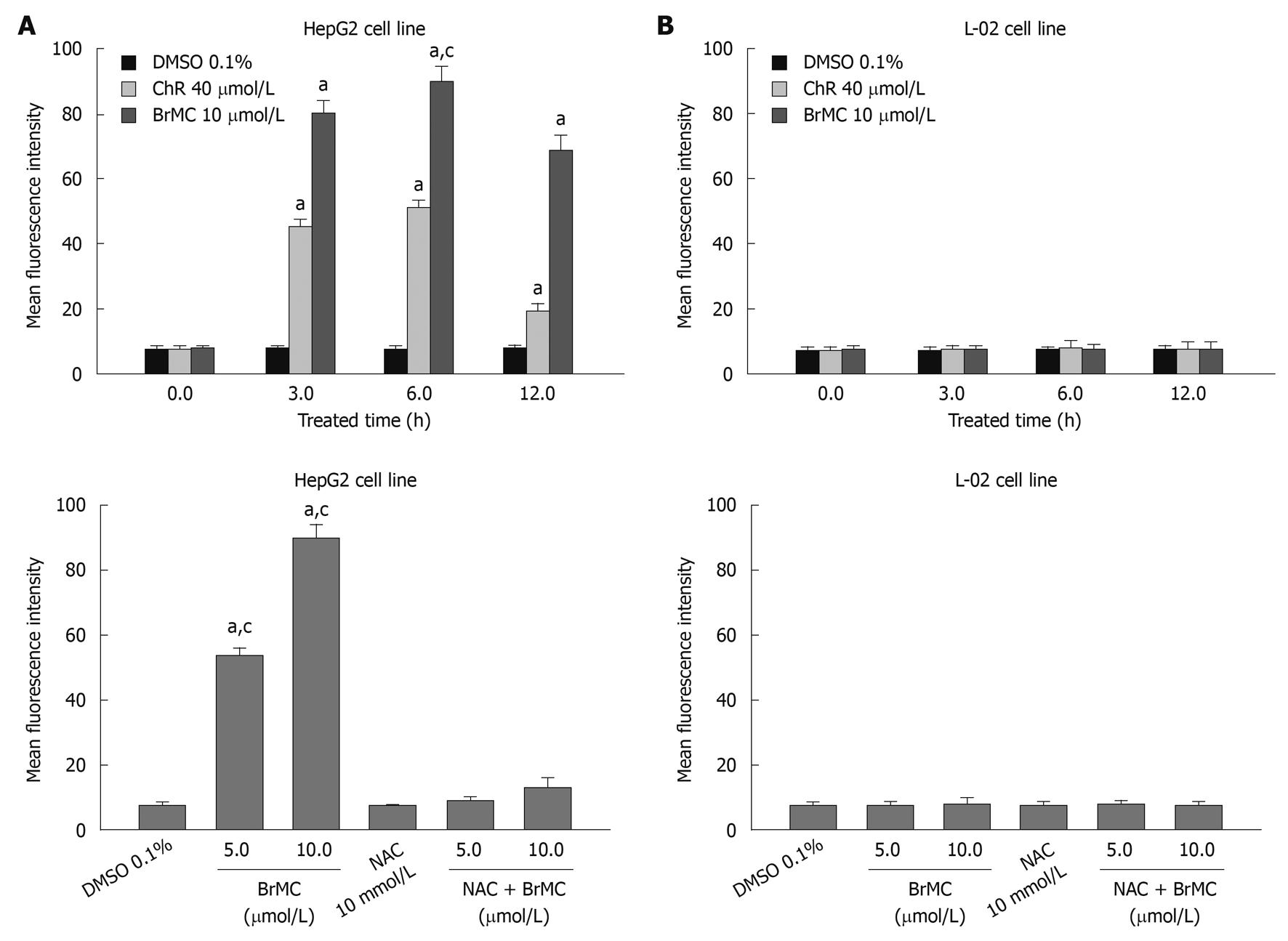
Figure 3 Effects of 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin on reactive oxygen species generation in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 (A) and human embryo liver L-02 cells (B).
aP < 0.05 vs baseline or treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); cP < 0.05 vs treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) plus 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin (BrMC).
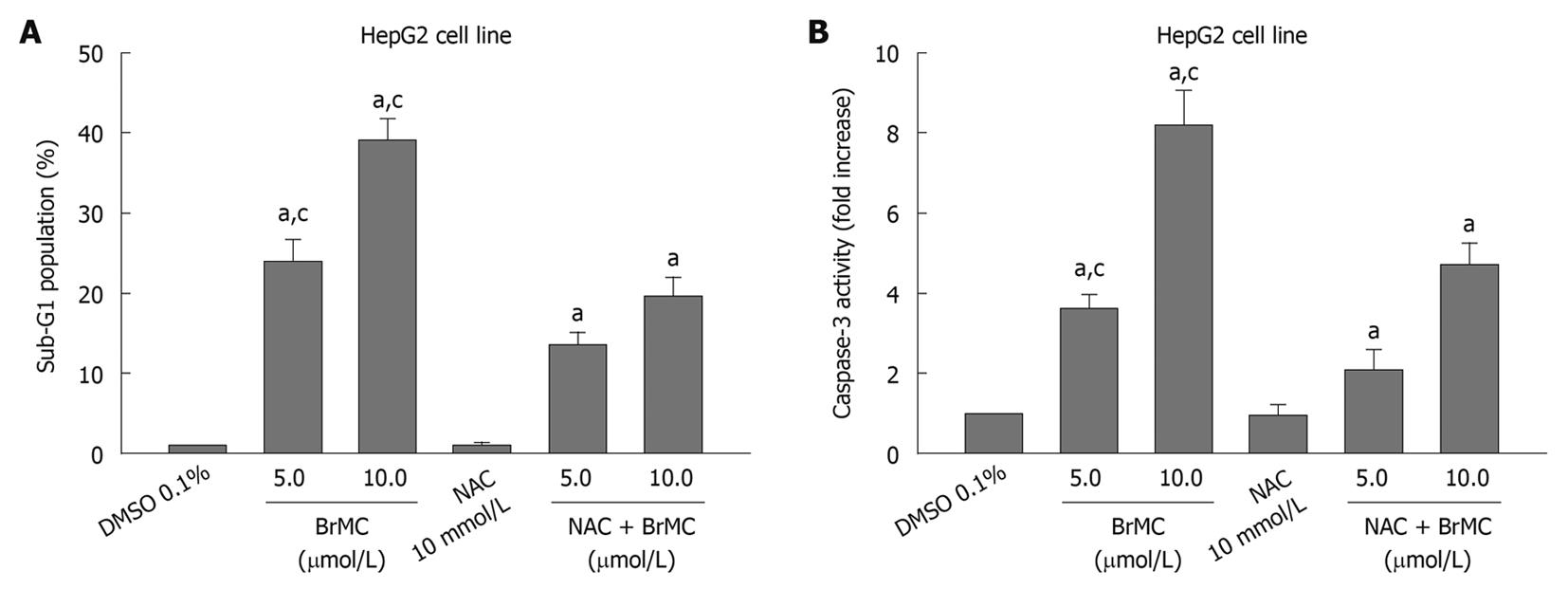
Figure 4 Effects of N-acetylcysteine on 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin-induced apoptosis rate (A) and caspase-3 activity (B) in HepG2 cells.
aP < 0.05 vs treatment with medium (0 h) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); cP < 0.05 vs treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) plus 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin (BrMC).
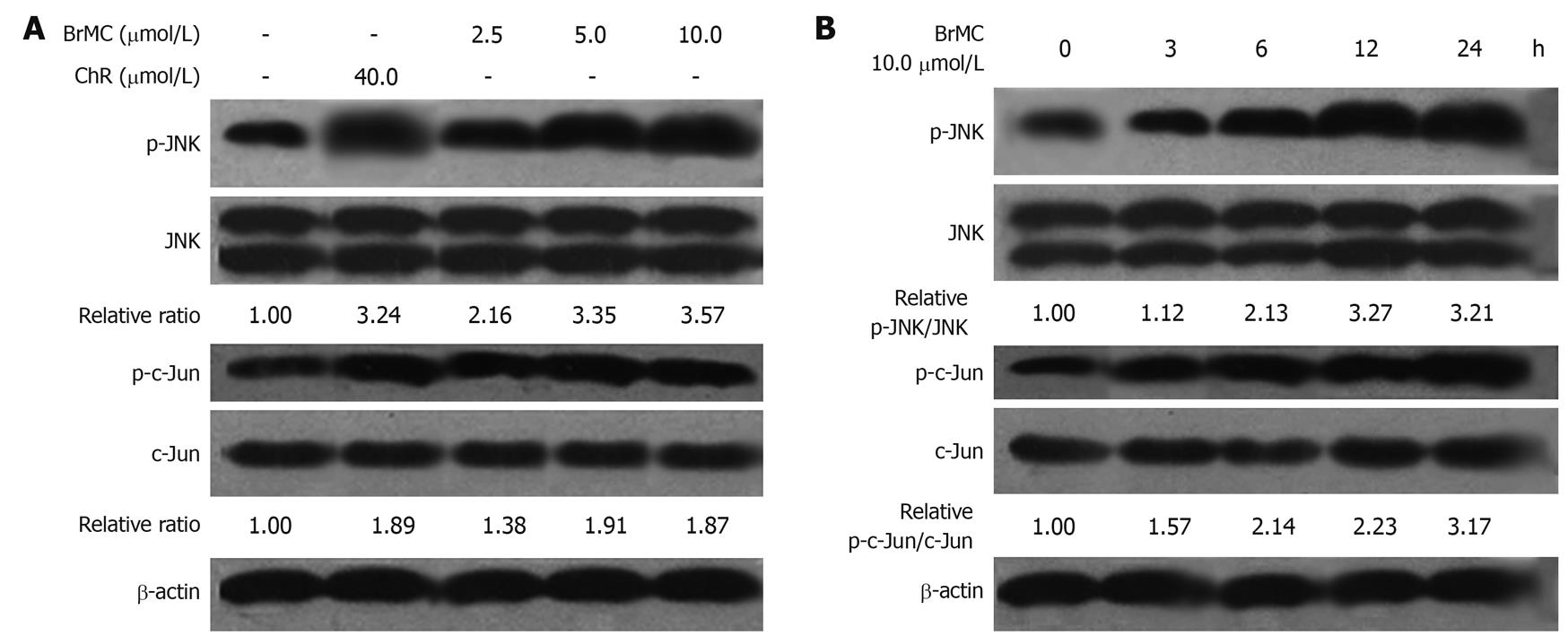
Figure 5 Effects of 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin on the level of phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase and phosphorylated c-Jun in HepG2 cells (Western blotting, mean ± SD, n = 3).
8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin (BrMC) elevated the level of phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and phosphorylated c-Jun in a concentration-dependent manner (A) and in a time-dependent manner (B). The ratio of p-JNK/JNK or p-c-Jun/c-Jun was normalized to 0 h or the untreated group.
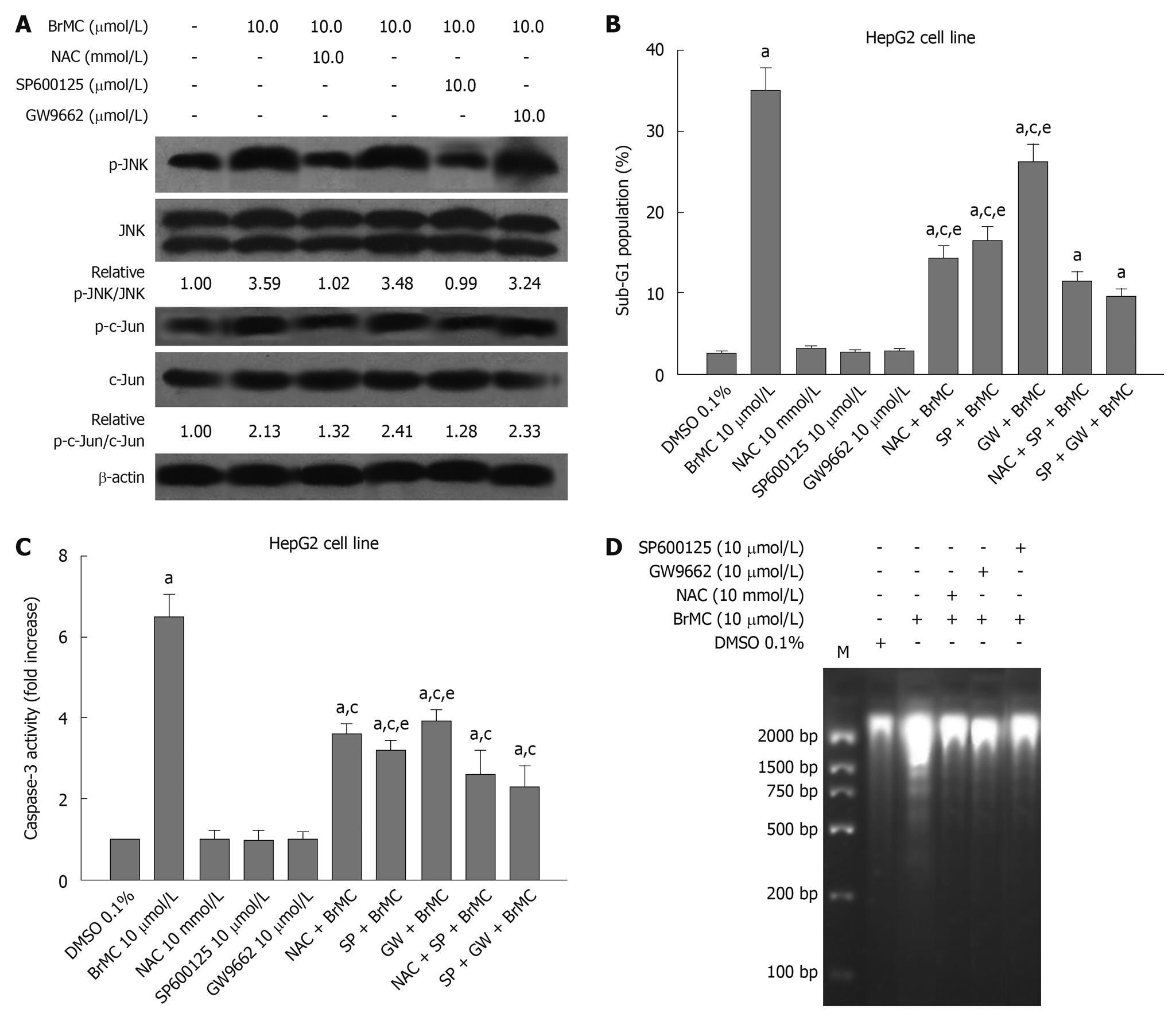
Figure 6 Effect of N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant, and GW9662, a blocker of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ, and Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125 on 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin-induced activation of Jun N-terminal kinase (A), apoptosis (B), activation of caspase-3 (C), and DNA fragmentation (D) in HepG2 cells.
The ratio of p-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/JNK or p-c-Jun/c-Jun was normalized to 0 h or the untreated group. aP < 0.05 vs treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); cP < 0.05 vs treatment with 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin (BrMC) alone; eP < 0.05 vs treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in combination with SP600125 and BrMC or GW9662 in combination with SP600125 and BrMC.
- Citation: Yang XH, Zheng X, Cao JG, Xiang HL, Liu F, Lv Y. 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells involves ROS and JNK. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(27): 3385-3393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i27/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3385