Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2010; 16(14): 1804-1807
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1804
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1804
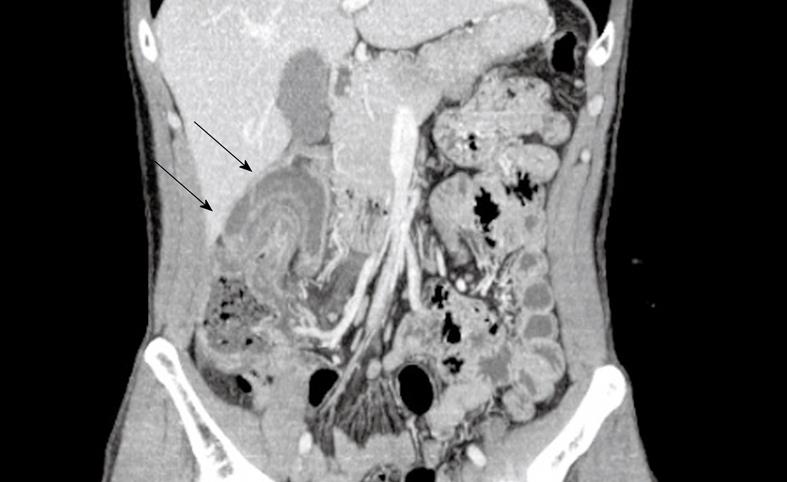
Figure 1 Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) imaging.
The coronal multiplanar reconstruction imaging in abdominal contrast-enhanced CT clearly reveals the invaginations of the ascending colon itself (arrows).
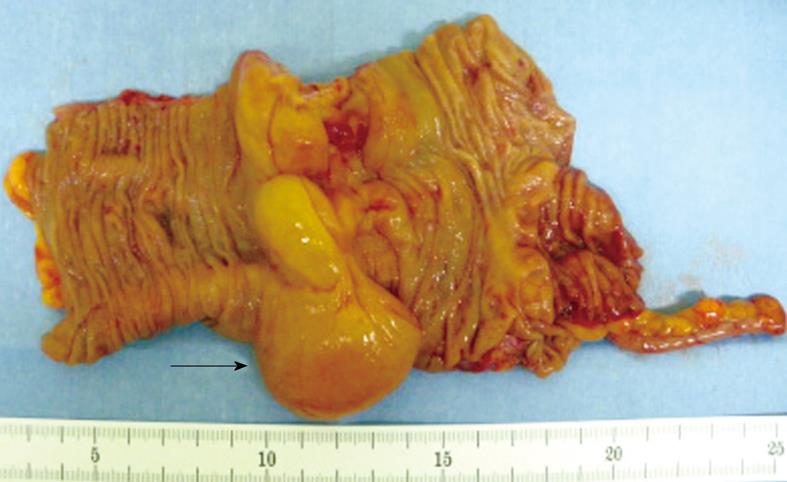
Figure 2 A gross view of the resection specimen.
The extirpated mass is 4 cm in diameter and its surface is smooth, yellowish, edematous and slightly soft (arrow).
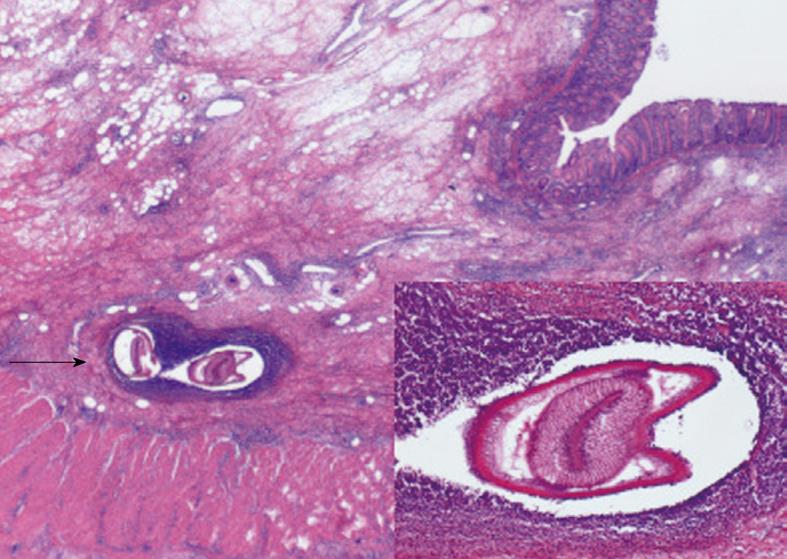
Figure 3 Histopathological findings of the resection specimen.
An anisakis body (arrow) is demonstrated in the edematously inflamed submucosa of the extirpated ascending colon (hematoxylin and eosin stain; × 20). Note that many eosinophils and lymphocytes infiltrate around the anisakis body, forming an eosinophilic granuloma. A magnified picture of the anisakis body is shown in the inset below right (hematoxylin and eosin stain; × 40).
- Citation: Miura T, Iwaya A, Shimizu T, Tsuchiya J, Nakamura J, Yamada S, Miura T, Yanagi M, Usuda H, Emura I, Takahashi T. Intestinal anisakiasis can cause intussusception in adults: An extremely rare condition. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(14): 1804-1807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i14/1804.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1804