Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2008; 14(9): 1378-1382
Published online Mar 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1378
Published online Mar 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1378
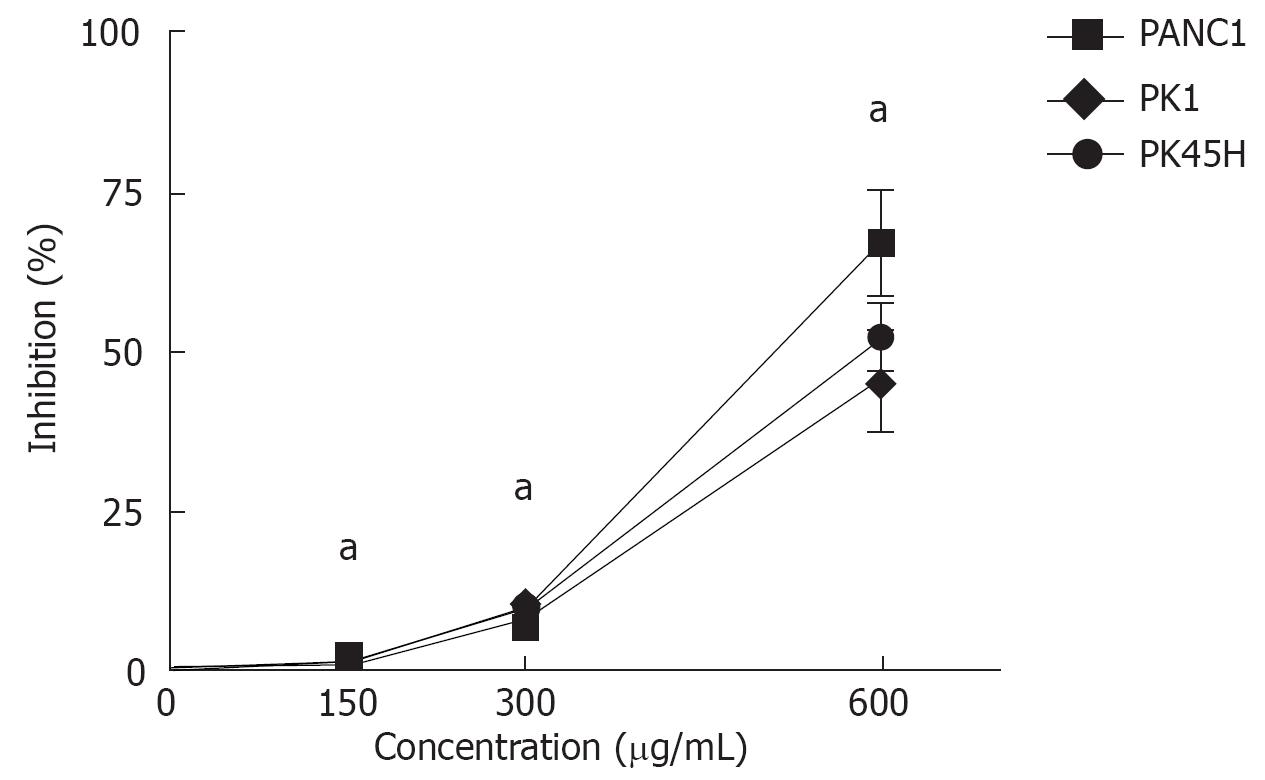
Figure 1 Growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer cells by MK615.
MK615 significantly inhibited the growth of PANC1, PK1, and PK45H cells in a dose-dependent manner (aP < 0.05). Cells were cultured for 48 h. The assay was carried out in triplicate.
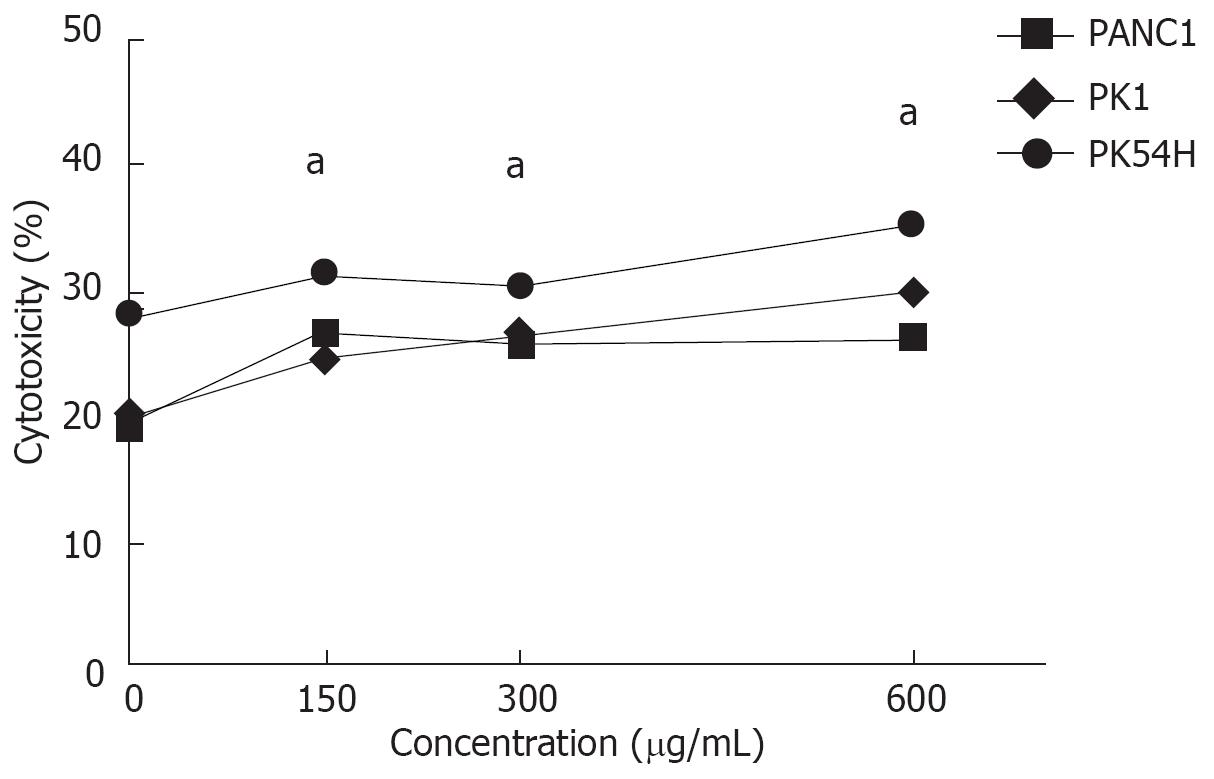
Figure 2 Lysis of pancreatic cells by MK615.
MK615 lysed PANC1, PK1, and PK45H cells at concentrations of 150, 300, and 600 &mgr;g/mL. The percentage cytotoxicities at 150, 300, and 600 &mgr;g/mL MK615 were significantly higher than those at 0 &mgr;g/mL MK615 (aP < 0.05). Cells were cultured for 48 h. The assay was carried out in triplicate.
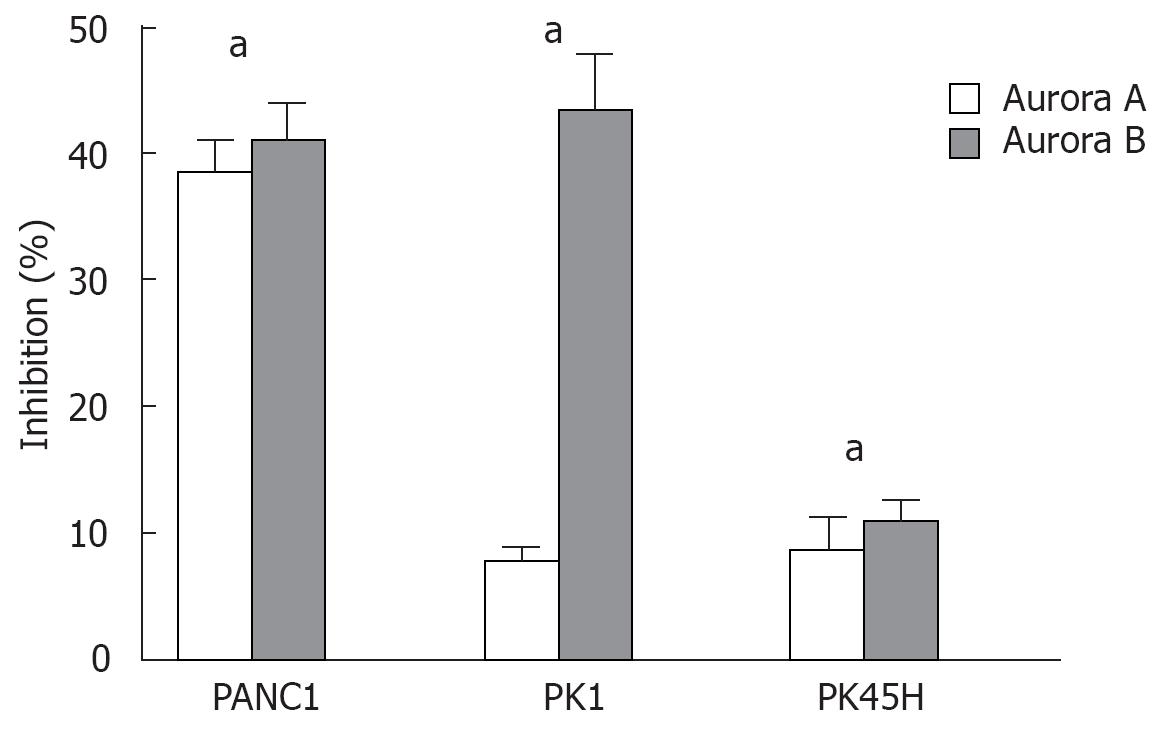
Figure 3 Dual inhibition of mRNA expression of Aurora A and Aurora B kinases by MK615.
MK615 significantly inhibited the transcription of Aurora A and Aurora B mRNA. The percentage inhibition in PANC1, PK1, and PK45H cells was statistically significant (aP < 0.05). RNA was extracted from the cells cultured with MK615 at a concentration of 300 &mgr;g/mL for 48 h.
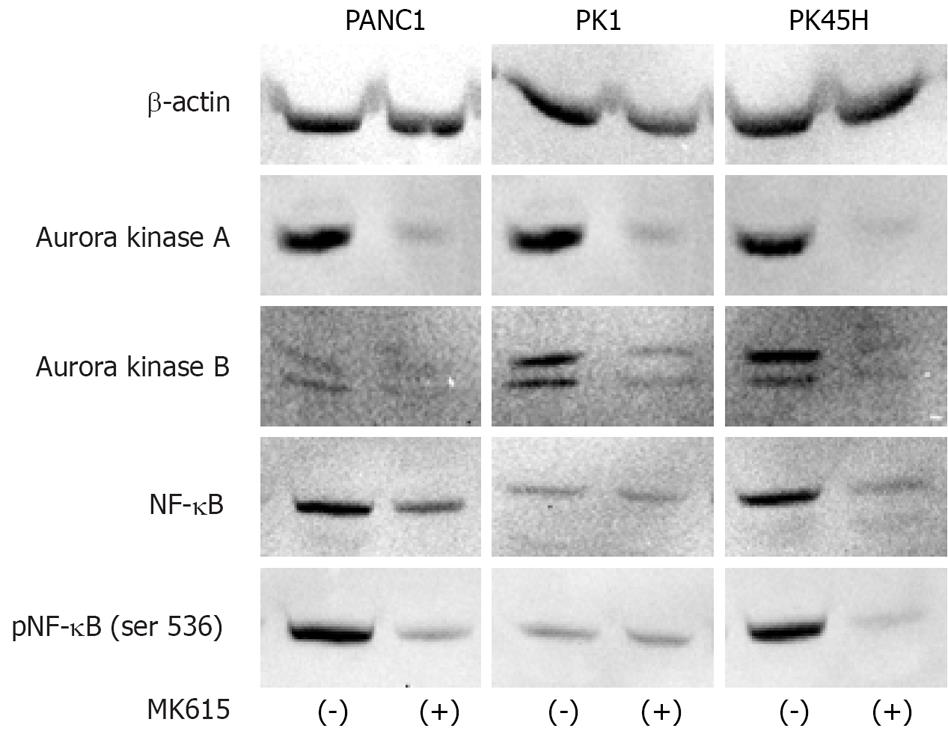
Figure 4 Inhibition of protein expression of Aurora A and Aurora B kinases, and NF-κB by MK615.
MK615 dually inhibited the expression of Aurora A and Aurora B kinases in PANC1 and PK45H cells. However, no inhibition was evident in PK1 cells. NF-κB inhibition was more evident when anti-phosphorylated NF-κB antibody was used. Protein was extracted from the cells cultured with MK615 at a concentration of 300 &mgr;g/mL for 48 h.
- Citation: Okada T, Sawada T, Osawa T, Adachi M, Kubota K. MK615 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth by dual inhibition of Aurora A and B kinases. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(9): 1378-1382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i9/1378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1378