Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2008; 14(37): 5730-5737
Published online Oct 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5730
Published online Oct 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5730
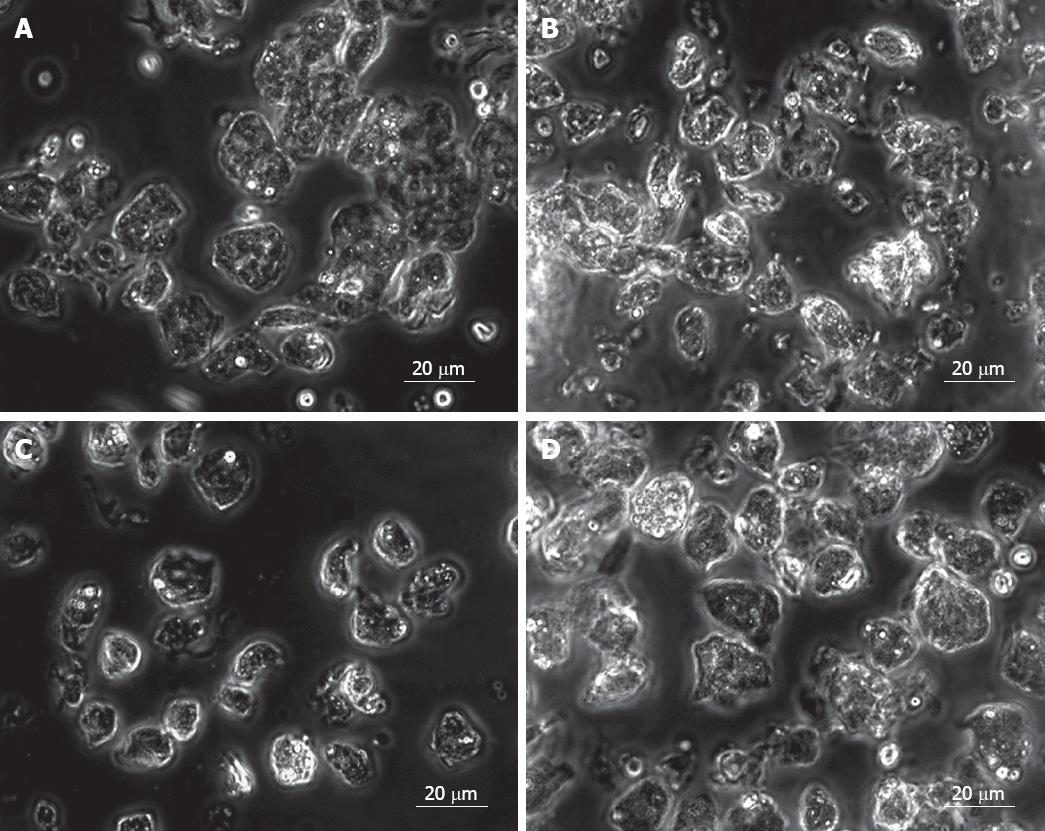
Figure 1 Purification of EpCAM +ve cell population.
An unsorted fetal liver cell shows a heterogeneous population in group 1 (A) and group 2 (B). After double selection, the EpCAM +ve sorted fetal liver cells shows a homogeneous epithelial cell population (C). EpCAM -ve sorted fetal liver cells shows irregular shape of cells (D).
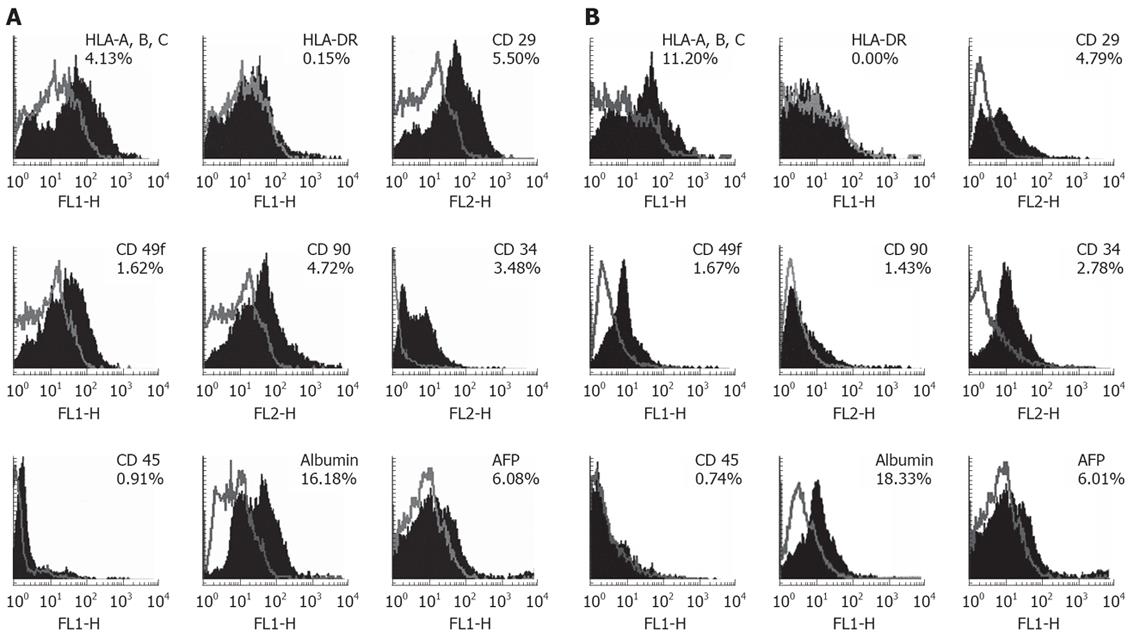
Figure 2 Identification of hepatic progenitor and HLA markers on EpCAM + sorted fetal liver cells by Flow cytometry.
A: The overlaid histograms of analyzed markers with their unstained controls. Results indicated EpCAM +ve cells expressed surface markers such as, HLA-A, B, C, HLA-DR, CD29, CD49f, CD90, Albumin, AFP, CD34, CD45 By contrast HLA-DR did not express on EpCAM + cells in group 1. B: Expression of markers in group 2. In which HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and albumin was increased but CD90 expression was decreased on EpCAM +ve cells. Other markers such as CD29, CD49f, AFP, CD34 and CD45 expression levels were almost same in both age groups.
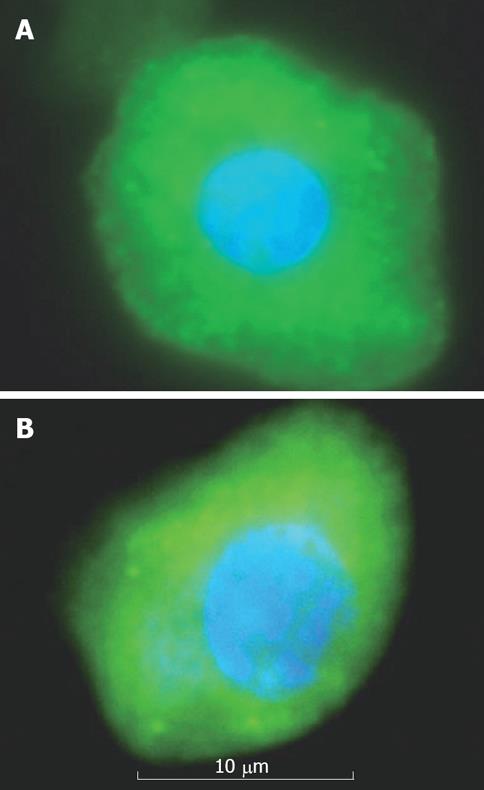
Figure 3 EpCAM + sorted fetal liver cells that are positive for CK18 (A) and albumin (B) in 18 wk gestation.
These cells have high cytoplasm-to-nucleus ratio and observed mononucleated cells.
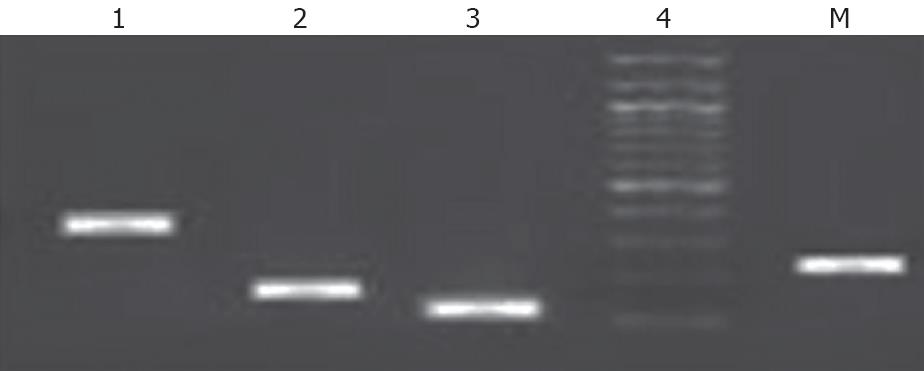
Figure 4 RT-PCR results indicate that the EpCAM + cells expressed hepatic stem cells markers such as CK18, CK19, albumin and AFP.
1: CK 19; 2: Albumin; 3: CK 18; 4: AFP; M: 100 bp Marker.
- Citation: Rao MS, Khan AA, Parveen N, Habeeb MA, Habibullah CM, Pande G. Characterization of hepatic progenitors from human fetal liver during second trimester. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(37): 5730-5737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i37/5730.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5730