Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2007; 13(13): 1962-1965
Published online Apr 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1962
Published online Apr 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1962
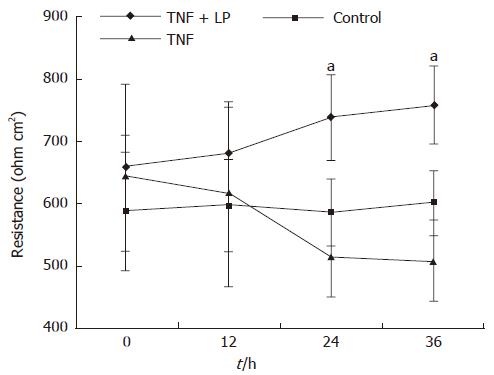
Figure 1 Effect of L.
plantarum on transepithelial resistance. TNF-α decreased Caco-2 monolayer resistance. L. plantarum reversed TNF-α-induced decreases in transepithelial resistance. aP < 0.05, compared with TNF-α. TER: transepithelial electrical resistance; LP: L. plantarum; TNF, TNF-α.
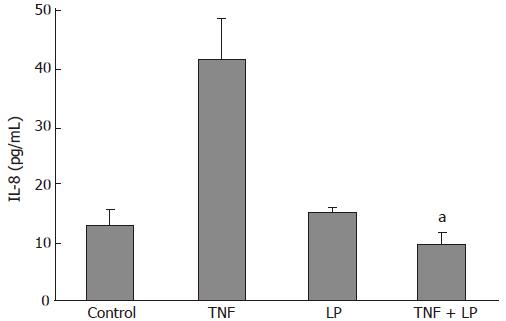
Figure 2 Effect of L.
plantarum on TNF-α-induced IL-8 secretion by Caco-2 cells. TNF-α-induced IL-8 secretion was significantly reduced by L. plantarum. aP < 0.05, compared with TNF-α. LP: L. plantarum; TNF, TNF-α.
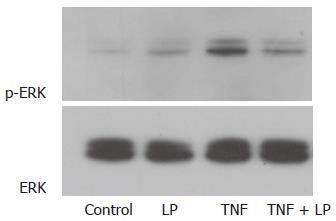
Figure 3 Effect of L.
plantarum on the ERK pathway. Caco-2 cells were incubated with L. plantarum, TNF-α or L. plantarum plus TNF-α. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against phosphorylated ERK and total ERK. L. plantarum inhibited TNF-α-induced activation of ERK-1 and -2. LP: L. plantarum; TNF, TNF-α.
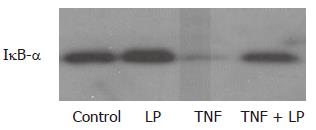
Figure 4 Effect of L.
plantarum on IκB-α degradation. Caco-2 cells were incubated with L. plantarum, TNF-α or L. plantarum plus TNF-α. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against IκB-α. TNF-α caused degradation of IκB-α. L. plantarum inhibited TNF-α-induced IκB-α degradation. LP: L. plantarum; TNF, TNF-α.
-
Citation: Ko JS, Yang HR, Chang JY, Seo JK.
Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits epithelial barrier dysfunction and interleukin-8 secretion induced by tumor necrosis factor-α. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(13): 1962-1965 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i13/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1962