Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2006; 12(45): 7371-7374
Published online Dec 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7371
Published online Dec 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7371
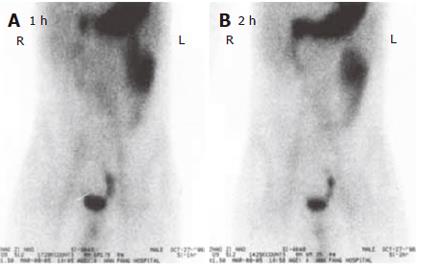
Figure 1 ECT examination showing small intestinal bleeding at 1 h (A) and 2 h (B) after intravenous injection of the tracer.
Serial planar imaging (1, 5, 15 and 30 min, 1 and 2 h) of the whole abdomen was performed. There was a radioactive accumulation at 5 min on the upper-left corner of the gall bladder, becoming increasingly dense till 2 h. Its emerging time was almost simultaneously as the image of the stomach with the density being slightly lower than that of the stomach image. During the whole period of imaging, its location was comparatively stable. The dynamic imaging of the whole abdomen showed an abnormal radioactive imaging near the upper-left corner of the gall bladder, which was considered the ectopic stomach mucous tissue inside the Meckel's diverticulum.
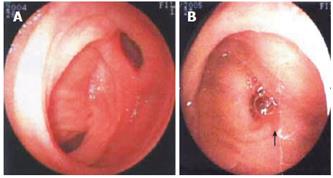
Figure 2 Double-balloon enteroscopy showing small intestinal bleeding (A) and Meckel’s diverticulum (B).
Double-balloon enteroscope was pushed 200 cm into the ileum through the anus. There was a diverticulum in the ileum 90-100 cm away from the ileocecal valve, at the opening of which there was an ulcer (1.2 cm × 1.0 cm). The ulcer was covered by a thin lichenoid substance without active bleeding. No other abnormalities were found. The diagnosis of Meckel’s diverticulum was established.
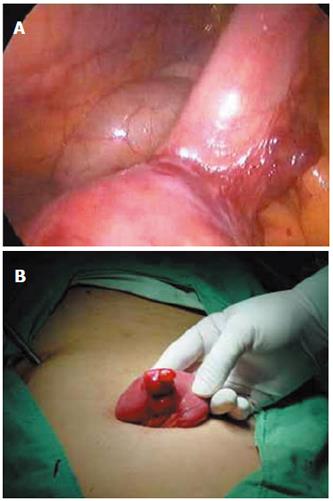
Figure 3 Laparoscopic laparotomy showing small intestinal bleeding (A) and oval stromal tumor (B).
An oval stromal tumor was found on the upper segment of jejunum with clear borderline and smooth surface but without adhesion to other tissues during laparoscopic laparotomy. Expansive abdominal excision was performed to draw out the tumor.
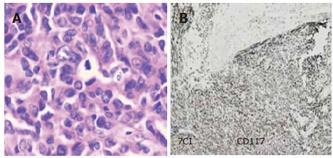
Figure 4 Pathological and immunohistological examination of small intestinal bleeding caused by small intestinel stromal tumor.
Arrangement of tumor cells in interlock weaving form with abundant cytoplasm, light staining, unclear borderline and diffused infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells but without necrosis and hemorrhage, karyokinesis could be seen (in the middle of A). Immunohistochemical findings were as follows: CD117 (+) (B), CD34 (-), S-100 (-), Vimentin (weak +) (HE × 200).
- Citation: Ba MC, Qing SH, Huang XC, Wen Y, Li GX, Yu J. Diagnosis and treatment of small intestinal bleeding: Retrospective analysis of 76 cases. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(45): 7371-7374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i45/7371.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7371