Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4850-4858
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4850
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4850
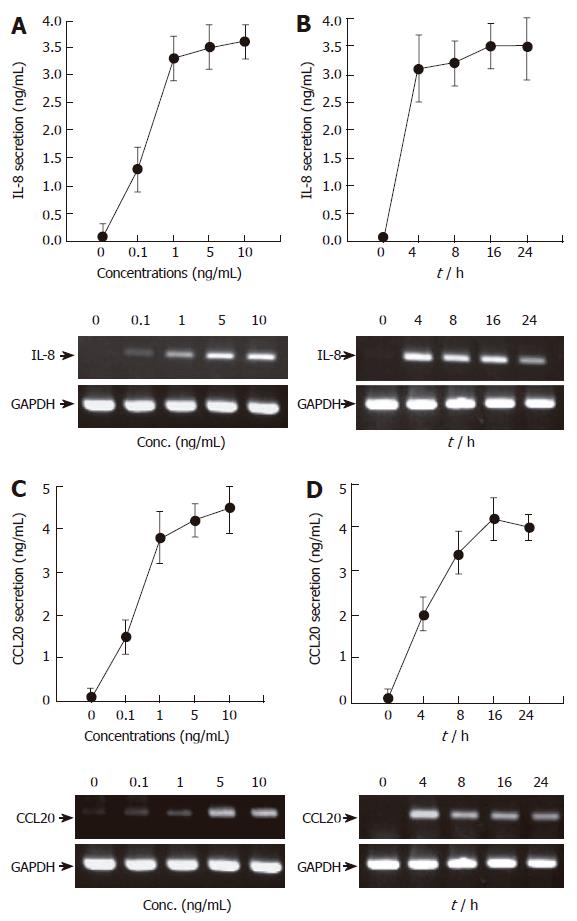
Figure 1 TNF-α induces IL-8 and CCL20 secretion and mRNA accumulation in AGS cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
(A and C) AGS cells (5 x 105/well) were treated for 16 h with the indicated concentrations of TNF-α (0-10 ng/mL). After incubation, the supernatants were collected, and the levels of IL-8 (A) and CCL20 (C) were determined by ELISA (top). At the same time, the cells were colleted and the expression of two chemokines was determined by RT-PCR (bottom). (B and D) AGS cells (5 x 105/well) were treated with TNF-α (5 ng/mL) for the indicated time points (0-24 h). IL-8 and CCL20 secretion and mRNA accumulation were determined as described above. For ELISA, results are expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments.
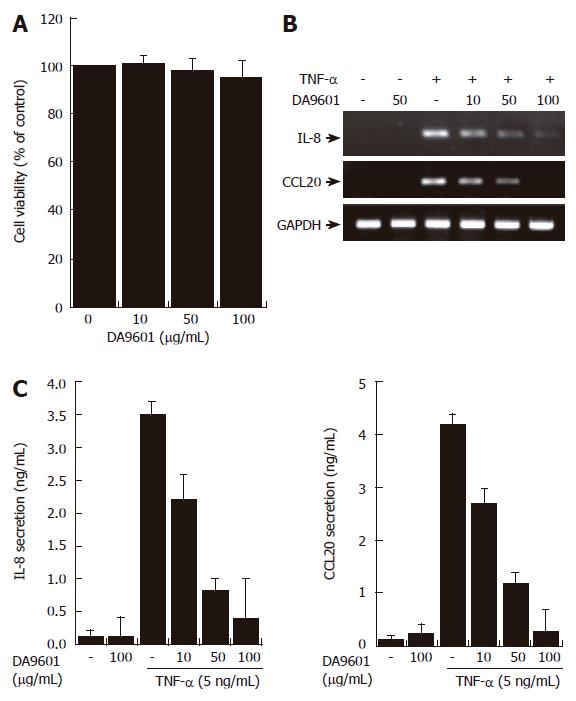
Figure 2 DA-9601 inhibits the expression and secretion of CCL20 in AGS cells.
(A) AGS cells (1 x 105) were treated with various concentrations of DA-9601 (0-100 μg/mL) for 16 h. Quantitative analysis of cell viability was determined by the MTT assay (mean ± SD., n = 3). (B) Cells (5 x 105) were pretreated with various concentrations of DA-9601 (0-100 μg/mL) for 1 h, and then the cells were further incubated for 8 h with TNF-α (5 ng/mL). Levels of IL-8 and CCL20 mRNAs were determined by RT-PCR. (C) Cells (5 x 105) were pretreated with various concentrations of DA-9601 (0-100 μg/mL) for 1 h, and then the cells were further incubated for 16 h with TNF-α (5 ng/mL). IL-8 and CCL20 protein levels were determined by ELISA. These data are representative of three independent experiments.
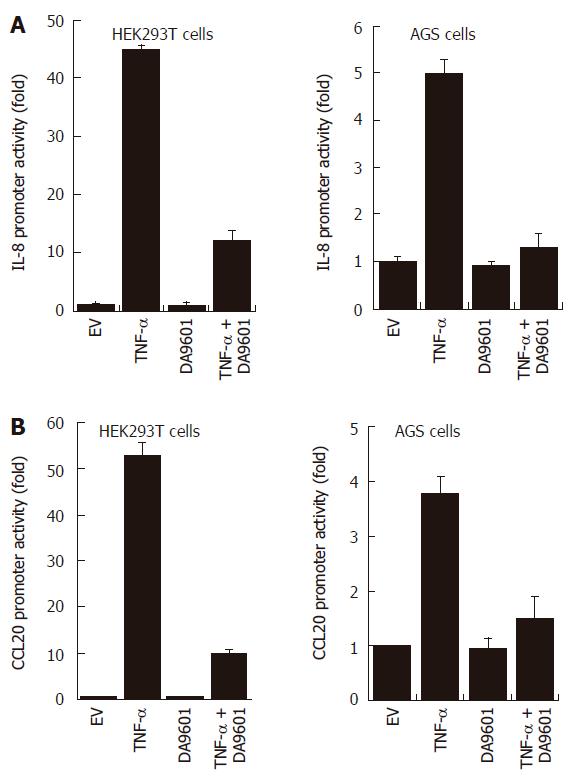
Figure 3 DA-9601 blocks IL-8 and CCL20 promoter activities in HEK293T and AGS cells.
HEK293T (left) and AGS (right) cells were transfected with pGL3-pIL-8 (A) or pGL3-pCCL20 (B) luciferase vectors. After 24 h of incubation, cells (1 x 105) were pre-treated for 1 h with DA-9601 (50 μg/mL) and stimulated for additional 16 h with medium alone or medium containing TNF-α (5 ng/mL). At the end of incubation, cells were lysed, and the relative luciferase activity was measured using Luciferase Assay System. Results are expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments.
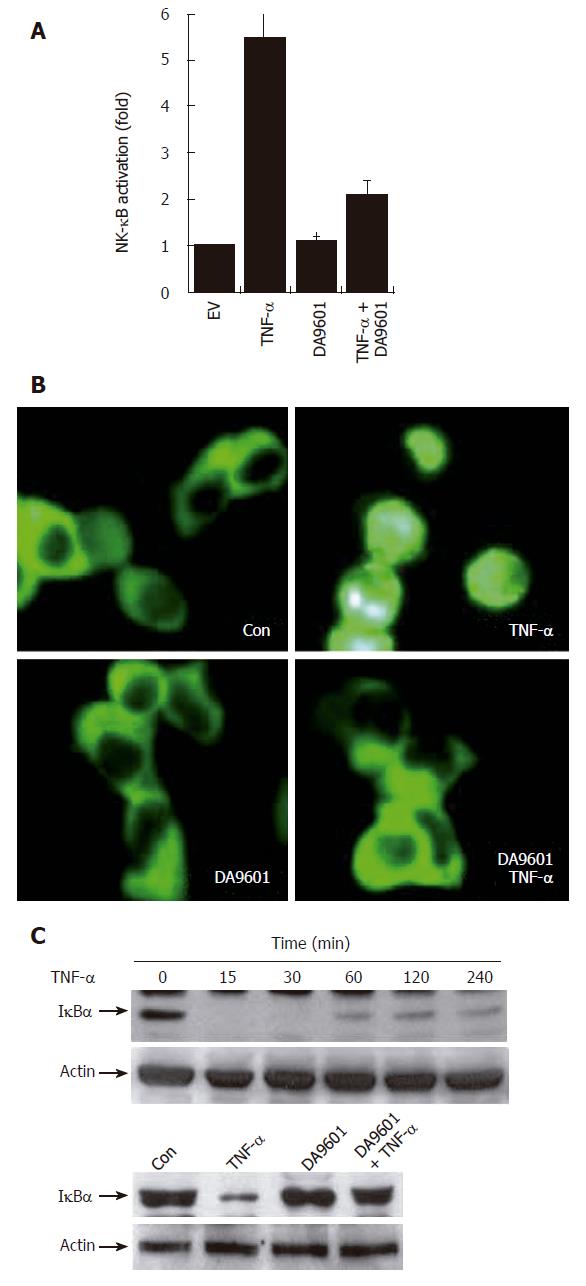
Figure 4 DA-9601 blocks NF-κB activity in AGS cells.
A: AGS cells (1 x 105) were transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter vector (0.8 μg/well). After 24 h of incubation, cells (1 x 105) were pre-treated for 1 h with DA-9601 (50 μg/mL) and stimulated for additional 16 h with medium alone or medium containing TNF-α (5 ng/mL). At the end of incubation, cells were lysed, and the relative luciferase activity was measured using Luciferase Assay System; B: AGS cells (1 x 105) were transfected with p65-EGFP vector (0.8 μg/well). After 24 h of incubation, cells were pre-treated for 1 h with DA-9601 (50 μg/mL) and stimulated for 1 h with medium alone or TNF-α. Nuclear translocation of p65-EGFP was observed under the fluorescence microscope (original magnification, 200 X); C: AGS cells (5 x 105) were incubated with TNF-α (5 ng/mL) for the indicated time points (0-240 min) (top) or were pretreated with medium alone or with DA-9601 (50 μg/mL) for 1 h, and incubated with TNF-α for 30 min (bottom). The cell lysates were blotted with antibodies specific for the I-κBα and β-actin.
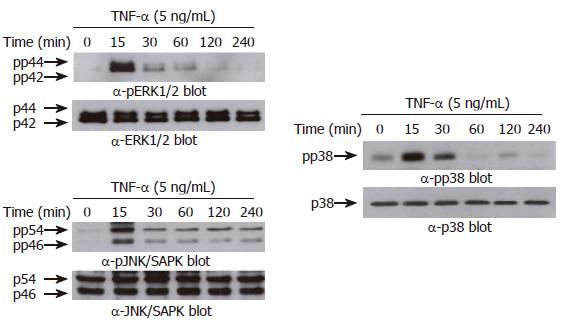
Figure 5 TNF-α induces phosphorylation of MAPKs in AGS cells.
AGS cells (5 x 105 cells/well) were incubated for various times (0-240 min) with TNF-α (5 ng/mL). Protein extracts were prepared at the indicated time points, and then the levels of phosphorylated or total MAPKs (ERK-1/2 (top), p38 kinase (middle), and JNK/SAPK (bottom)) were determined by Western blotting using specific antibodies. The arrows indicate the position of specific immunoreactive bands corresponding to distinct MAPKs.
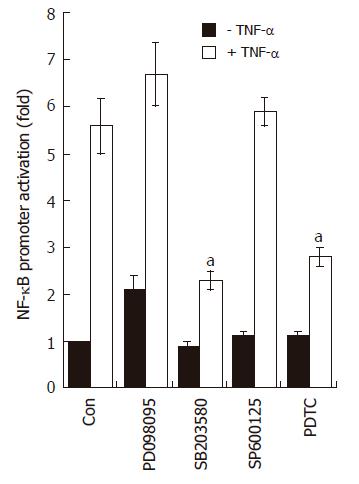
Figure 6 SB203580 blocks NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity in AGS cells.
AGS cells (5 x 105) were transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter vector (0.8 μg/well). After 24 h of incubation, cells were pre-treated for 1 h with PD098059 (20 μmol/L), SB203580 (10 μmol/L), SP600125 (2 μmol/L), and PDTC (10 μmol/L); the cells were stimulated for additional 16 h with medium alone or medium containing TNF-α (5 ng/mL). At the end of incubation, cells were lysed, and the relative luciferase activity was measured using Luciferase Assay System. Note, aP < 0.05, significantly different from control (n = 4).
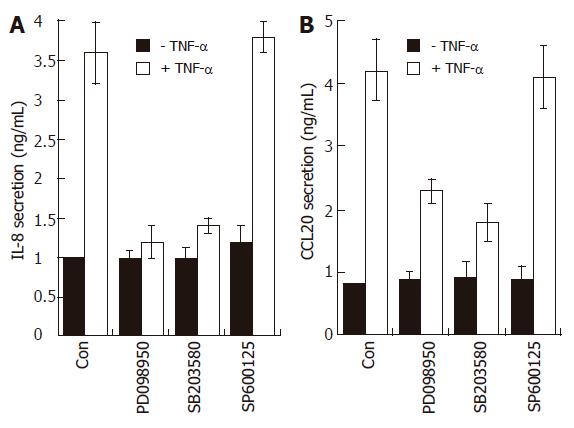
Figure 7 Effects of MAPK modulators on IL-8 and CCL20 release by TNF-α in AGS cells.
AGS cells (1 x 105) were pre-treated for 1 h with or without selective MAPK inhibitors (PD098059, 20 μmol/L; SB203580, 10 μmol/L; SP600125, 2 μmol/L). The cells were then further incubated for 16 h with TNF-α (5 ng/mL). Levels of IL-8 and CCL20 protein were determined by ELISA. These data are representative of three independent experiments.
Figure 8 DA-9601 selectively attenuates TNF-α-mediated phosphorylation of p38 kinase in AGS cells.
Cells (5 x 105 cells/well) were pretreated for 1 h with medium alone or medium containing DA-9601 (50 μg/mL). Then, the cells were stimulated for 15 min with or without TNF-α (5 ng/mL). The cell lysates were blotted with antibodies specific for the phosphorylated or total forms of ERK1/2, p38 kinase, and JNK/SAPK, and visualized using a peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody and the ECL system.
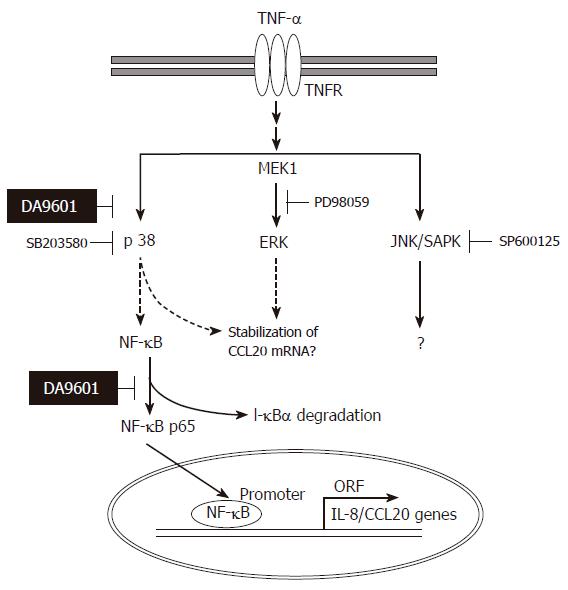
Figure 9 Hypothetical mechanism of action of DA-9601 on TNF-α-induced CCL20 expression in AGS cells.
TNF-α induces activation of three MAPKs. Among three MAPKs, however, activation of p38 kinase involves in NF-κB signaling system. DA-9601 may inhibit NF-κB directly or indirectly through the inhibition of p38 kinase pathway. See text for discussion.
- Citation: Choi SC, Choi EJ, Oh HM, Lee S, Lee JK, Lee MS, Shin YI, Choi SJ, Chae JR, Lee KM, Lee WJ, Park JS, Shin CY, Oh TY, Jun CD. DA-9601, a standardized extract of Artemisia asiatica, blocks TNF-α-induced IL-8 and CCL20 production by inhibiting p38 kinase and NF-κB pathways in human gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4850-4858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4850