Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2006; 12(23): 3657-3667
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657
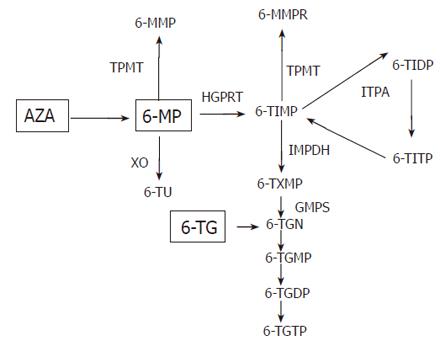
Figure 1 Simplified scheme of AZA metabolism: AZA is non-enzymatically converted to 6-MP.
6-MP is converted into the 6-thioinosine monophosphate (6-TIMP) by the enzyme hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase (HGPRT). 6-TIMP is further metabolized to thioguanine mono, di and triphosphates [6-thioguanine nucleotides (TGN)]. Alternatively 6-MP can be inactivated by xanthine oxidase (XO) into 6-thiouric acid (6-TU) or by TPMT into 6-methylmercaptopurine (6-MMP). TPMT also catalyses the methylation of the nucleotide metabolites including 6-TIMP and 6-thioguanosine-5’-monophosphate to 6-methylmercaptopurine (6-MMPR). Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) and guanine monophosphate synthetase (GMPS). Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA), 6-thioinosine triphosphate pyrophosphate (6-TITP).
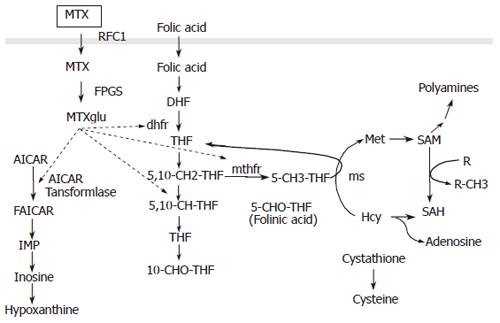
Figure 2 The dotted arrows indicate inhibitory effects of MTX methotrexate.
RFC1 reduced folate carrier 1; MTXglu methotrexate polyglutamate; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide; DHF, dihydrofolate; THF, tetrahydrofolate; dhfr, dihydrofolate reductase; mthfr, methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase; 5,10-CH-THF, 5,10 methenyl THF; 5,10-CH2 THF, 5,10 methylene THF; 10-CHO THF, 10-formyl THF; Hcy, homocysteine; 5-CHO THF, 5-formyl THF; ms, methionine synthetase; Met, methionine; SAM, S-adenosyl-L-methionine; R, methyl acceptor; SAH, S-adenosyl–L-homocysteine.
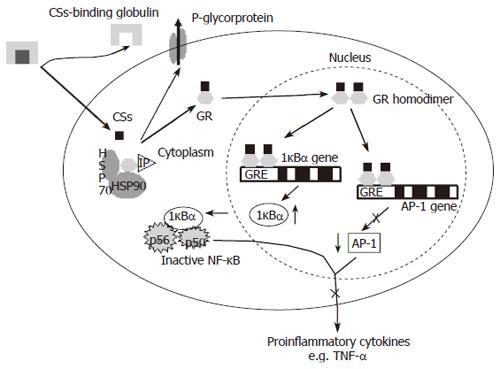
Figure 3 Anti-inflammatory mechanism of glucocorticoids (CSs).
CSs enter the cell and interact with the glucocorticoid receptor (GRα) to change the GR conformation, induce formation of GR homodimers and translocation to the nucleus. GR homodimers specifically bind to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) in target genes. HSP90, 90-kDa heat shock protein; HSP70, 70-kDa heat shock protein; IP, 56-kDa immunophilin; IκBα inhibitor kappa B alpha; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; AP-1, activator protein 1.
- Citation: Pierik M, Rutgeerts P, Vlietinck R, Vermeire S. Pharmacogenetics in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(23): 3657-3667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i23/3657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657