Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2006; 12(23): 3657-3667
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657
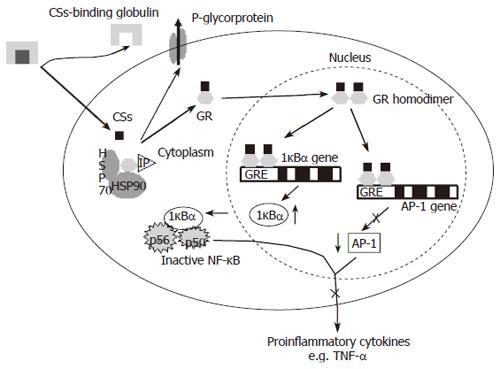
Figure 3 Anti-inflammatory mechanism of glucocorticoids (CSs).
CSs enter the cell and interact with the glucocorticoid receptor (GRα) to change the GR conformation, induce formation of GR homodimers and translocation to the nucleus. GR homodimers specifically bind to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) in target genes. HSP90, 90-kDa heat shock protein; HSP70, 70-kDa heat shock protein; IP, 56-kDa immunophilin; IκBα inhibitor kappa B alpha; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; AP-1, activator protein 1.
- Citation: Pierik M, Rutgeerts P, Vlietinck R, Vermeire S. Pharmacogenetics in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(23): 3657-3667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i23/3657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3657