Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2006; 12(2): 280-286
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.280
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.280
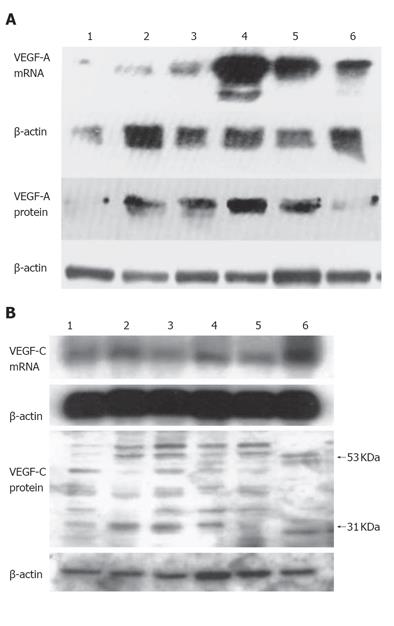
Figure 1 Expression of VEGF-A (A) and VEGF-C (B) in six human pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Lane 1: COLO-357; lane 2: MIA-PaCa-2; leane 3: PANC-1; lane 4: T3M4; lane 5: ASPC-1; lane 6: CAPAN-1.
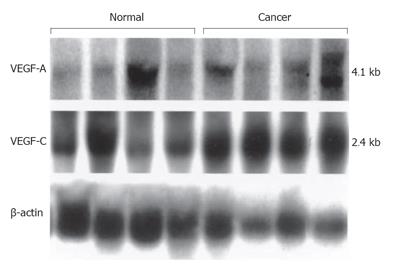
Figure 2 Northern blot analysis of VEGF-A and VEGF-C expression in human pancreatic tissues.
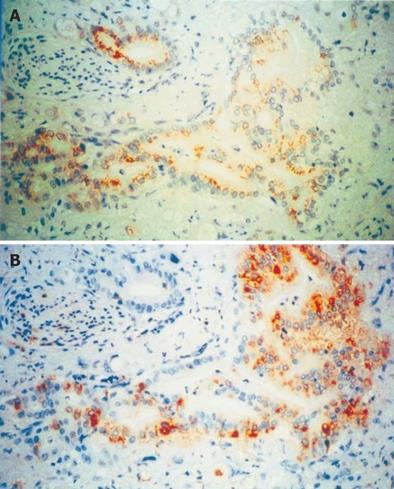
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical analysis of VEGF-A (A) and VEGF-C (B) expression in human pancreatic cancer tissues.
In the pancreatic cancers, moderate to strong VEGF-A and VEGF-C immunoreactivity was present in the cytoplasm of cancer cells, ×400.
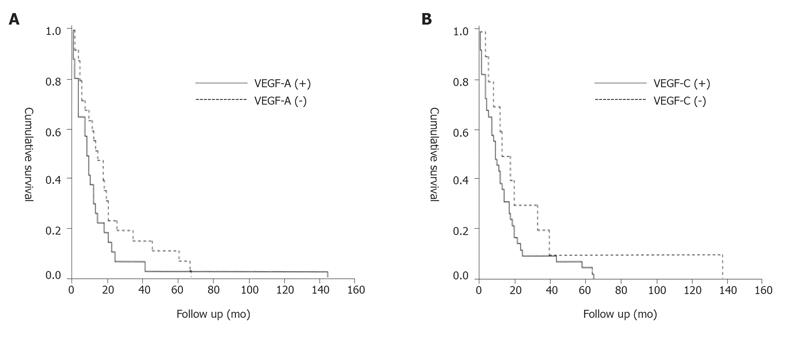
Figure 4 Survival curve.
A: Cumulative survival (Kaplan-Meier) plot of the postoperative survival period of patients whose pancreatic tumors exhibited cytoplasmic VEGF-A immunostaining (solid line) versus those whose tumors were negative for VEGF-A (broken line), (P = 0.184); B: Cumulative survival (Kaplan-Meier) plot of the postoperative survival period of patients whose pancreatic tumors exhibited cytoplasmic VEGF-C immunostaining (solid line) versus those whose tumors were negative for VEGF-C (broken line), (P = 0.159).
- Citation: Tang RF, Wang SX, Peng L, Wang SX, Zhang M, Li ZF, Zhang ZM, Xiao Y, Zhang FR. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C in human pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(2): 280-286
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i2/280.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.280