Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2006; 12(2): 251-258
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.251
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.251
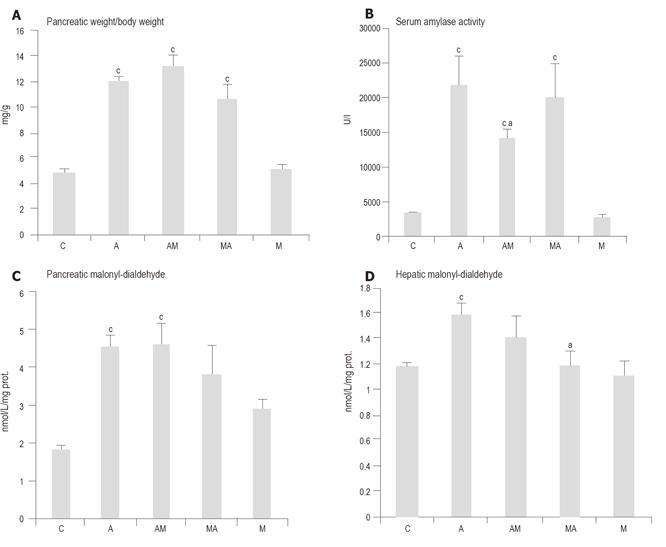
Figure 1 Effects of melatonin (50 mg/kg) treatment on the pancreatic weight/body weight ratio (p.
w./b.w.) (A), serum amylase activity (B), amount of malonyl-dialdehyde in the pancreas (C) and liver (D) in L-arginine-induced (2 x 3.2 g/kg) acute pancreatitis. Means ± SE of results on 5 animals in each group are shown. aP<0.05 vs group A; cP<0.05 vs group C.
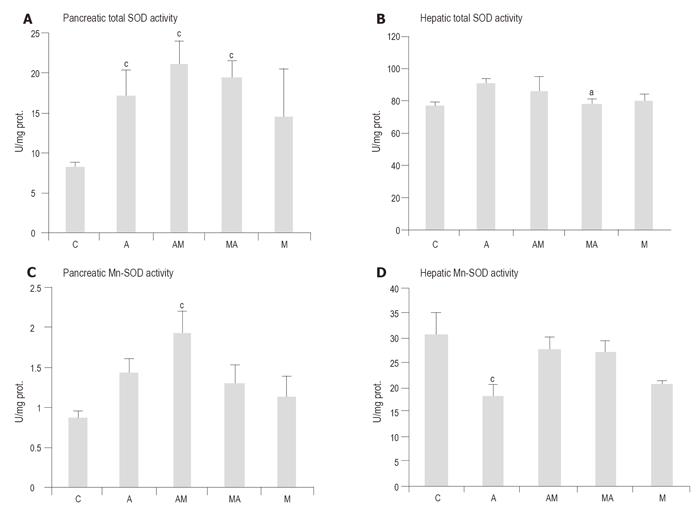
Figure 2 Effects of melatonin (50 mg/kg) treatment on the total SOD and Mn-SOD activities of the pancreas (A, C) and liver (B, D) in L-arginine-induced (2 x 3.
2 g/kg) acute pancreatitis. Means ± SE of results on 5 animals in each group are shown. aP<0.05 vs group A; cP<0.05 vs group C.
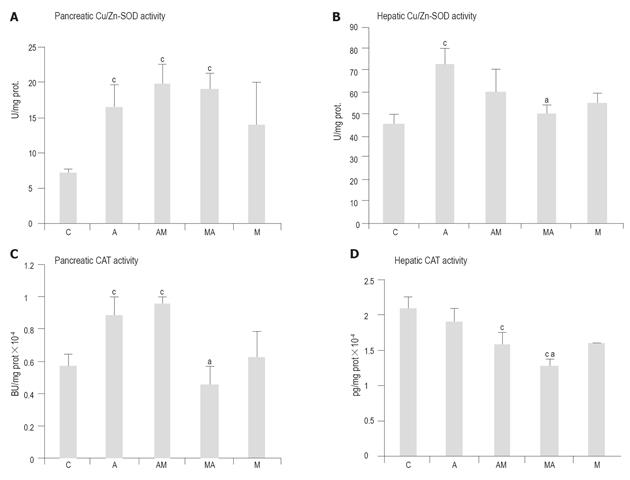
Figure 3 Effects of melatonin (50 mg/kg) treatment on the Cu/Zn-SOD and CAT activities of the pancreas (A, C) and liver (B, D) in L-arginine-induced (2 x 3.
2 g/kg) acute pancreatitis. Means ± SE of results on 5 animals in each group are shown. aP<0.05 vs group A; cP<0.05 vs group C.
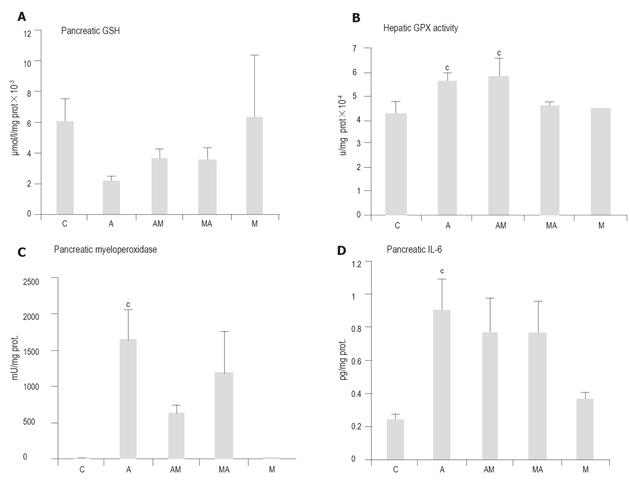
Figure 4 Effects of melatonin (50 mg/kg) treatment on the pancreatic GSH content (A), liver GPx activity (B), pancreatic myeloperoxidase activity (C) and pancreatic IL-6 content (D) in L-arginine-induced (2 x 3,2 g/kg) acute pancreatitis.
Means ± SE of results on 5 animals in each group are shown. aP < 0.05 vs group A; cP < 0.05 vs group C.
- Citation: Szabolcs A, Reiter RJ, Letoha T, Hegyi P, Papai G, Varga I, Jarmay K, Kaszaki J, Sari R, Jr ZR, Lonovics J, Takacs T. Effect of melatonin on the severity of L-arginine-induced experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(2): 251-258
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i2/251.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.251