Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2006; 12(13): 2040-2046
Published online Apr 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2040
Published online Apr 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2040
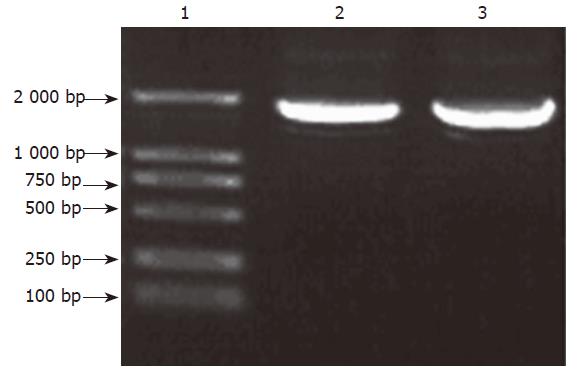
Figure 1 PCR products on agarose electrophoresis.
Lane1: DL2000 marker; Lanes 2, 3: PCR products.
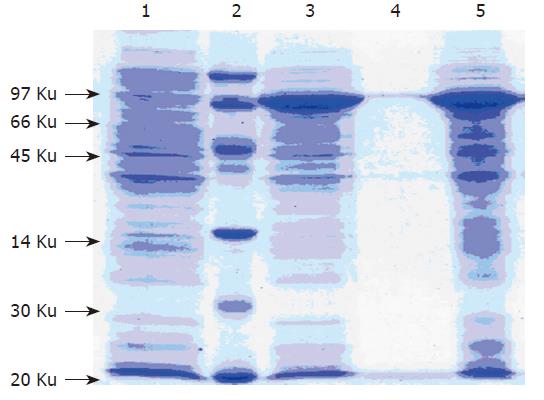
Figure 2 15 % SDS-PAGE analysis of expression products.
Lane 1: Non-recombinant bacteria; Lane 2: Low molecular protein marker; Lane 3: Recombinant bacteria; Lane 4: Deposition after sonication; Lane 5: Supernatant after sonication.
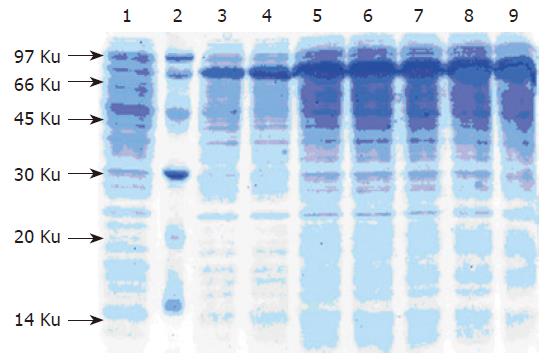
Figure 3 The expression of G17P64K protein in bioreactor.
Lane 1: Low molecular protein marker; Lane 2: Sample before IPTG induction; Lanes 3-9: Sample after induction 1-7 h.
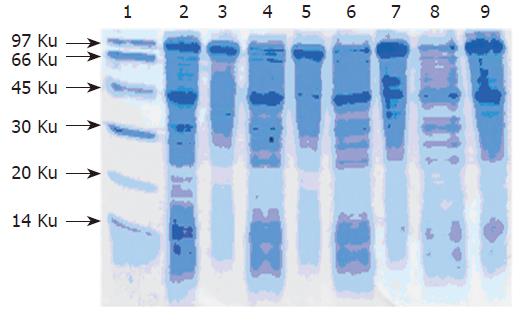
Figure 4 15 % SDS-PAGE analysis of sample after ammonium sulfate deposition.
Lane 1: Low molecular protein marker; Lanes 2, 4, 6, 8: Supernatant after ammol/Lonium sulfate deposition; Lanes 3, 5, 7, 9: Deposition after 20 %, 30 %, 40 %, 50 % ammonium sulfate deposition.
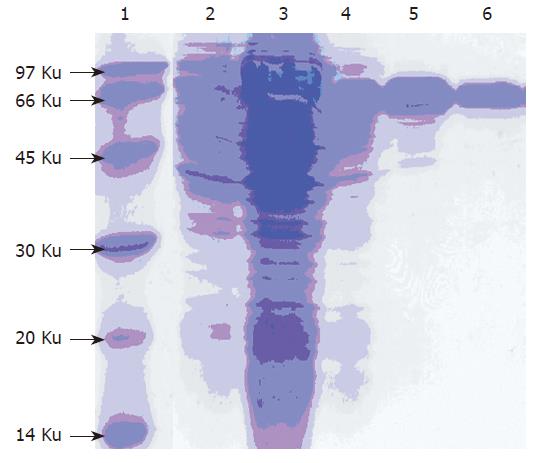
Figure 5 15 % SDS-PAGE analysis of purified G17P64K fusion protein.
Lane 1: Low molecular protein marker; Lane 2: Total protein after induction; Lane 3: Supernatant after sonication; Lane 4: Sample after hydrophobic chromatography; Lane 5: Sample after gel filtration chromatography; Lane 6: Sample after anion exchanger chromatography.
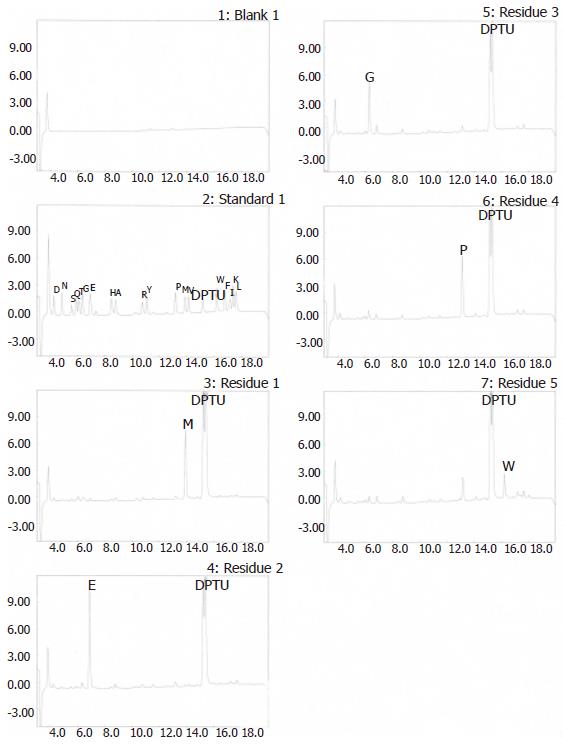
Figure 6 N-terminal amino acid sequence of G17P64K protein.
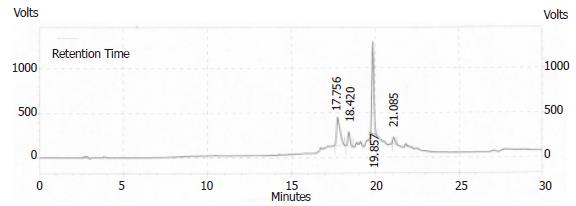
Figure 7 HPLC identification of the purity of synthetic polypeptide.
Figure 8 Effects of rabbit anti-gastrin 17 antibody on the in vitro growth of SW480.
◆: anti-gastrin 17(9): P64; ■Red: rabbit anti-gastrin 17(9): DT; ▲: rabbit control IgG
- Citation: Xiong XH, Zhao HL, Xue C, Zhang W, Yang BF, Yao XQ, Liu ZM. Construction and evaluation of anti-gastrin immunogen based on P64K protein. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(13): 2040-2046
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i13/2040.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2040