Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2006; 12(13): 2024-2030
Published online Apr 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2024
Published online Apr 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2024
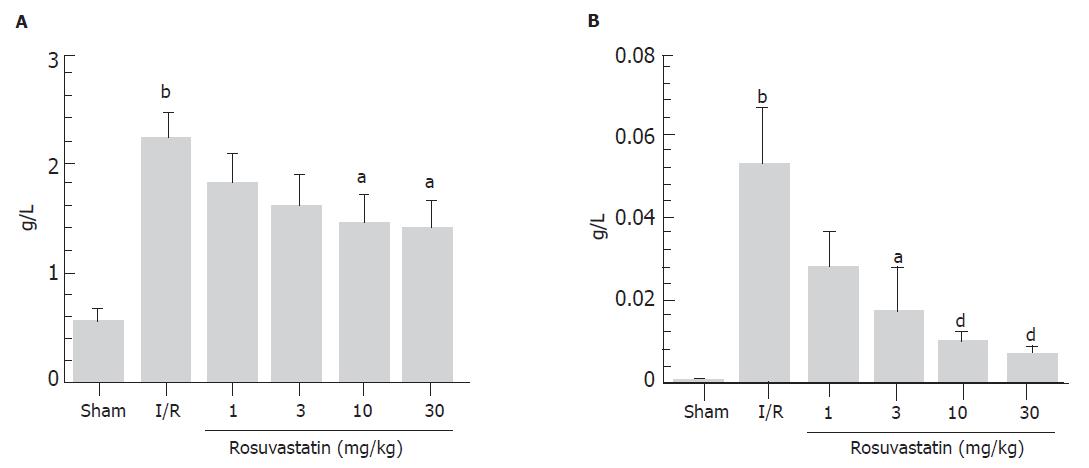
Figure 1 Dose-response of rosuvastatin on acute intestinal I-R injury in rats (mean ±SE).
A: Intraluminal protein; B: Hemoglobin. bP<0.01 vs Sham, aP<0.05, dP<0.01 vs Vehicle + I-R.
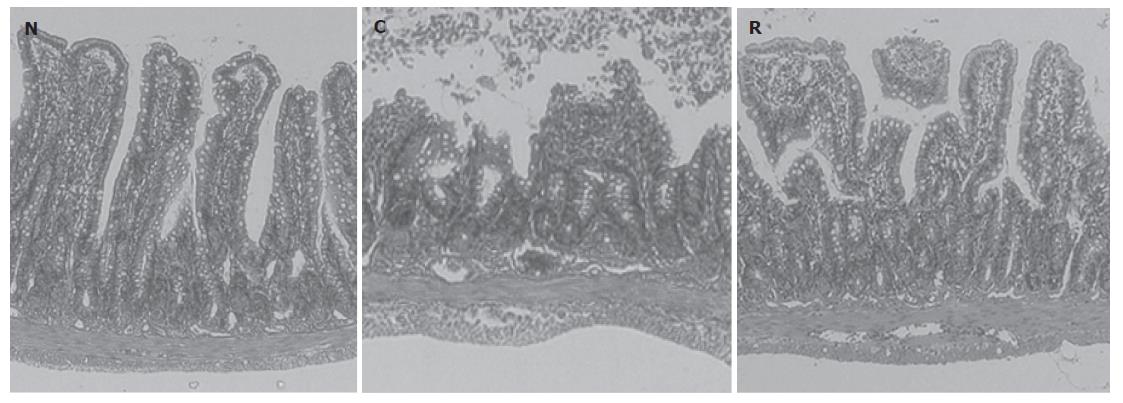
Figure 2 Histological appearance of the small intestine in rats (HE ×20).
N: Sham. C: I-R. R: I-R plus rosuvastatin.
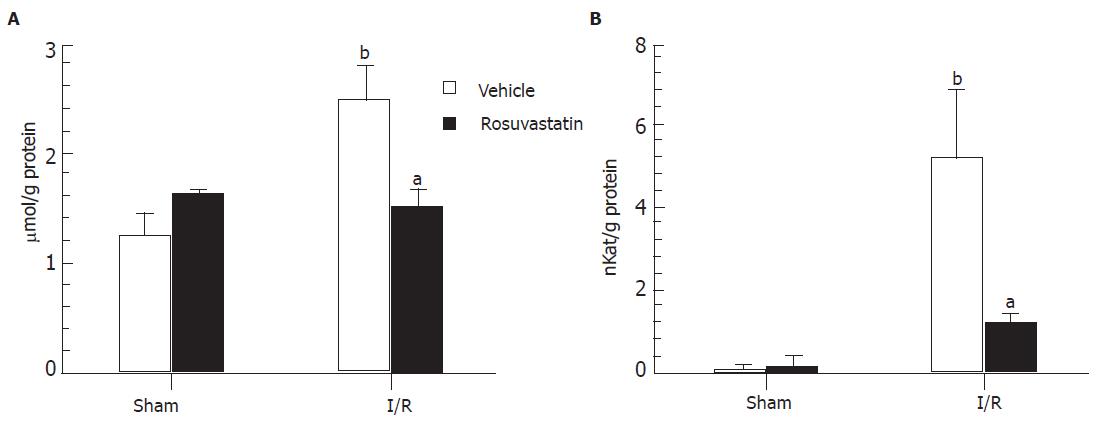
Figure 3 Effects of rosuvastatin on lipid peroxide concentrations and neutrophil accumulation in the intestinal mucosa of rats treated with I-R (mean±SE).
A: TBA-reactive substance; B: Myeloperoxidase activity. bP<0.01 vs Sham, aP<0.05 vs Vehicle + I-R.
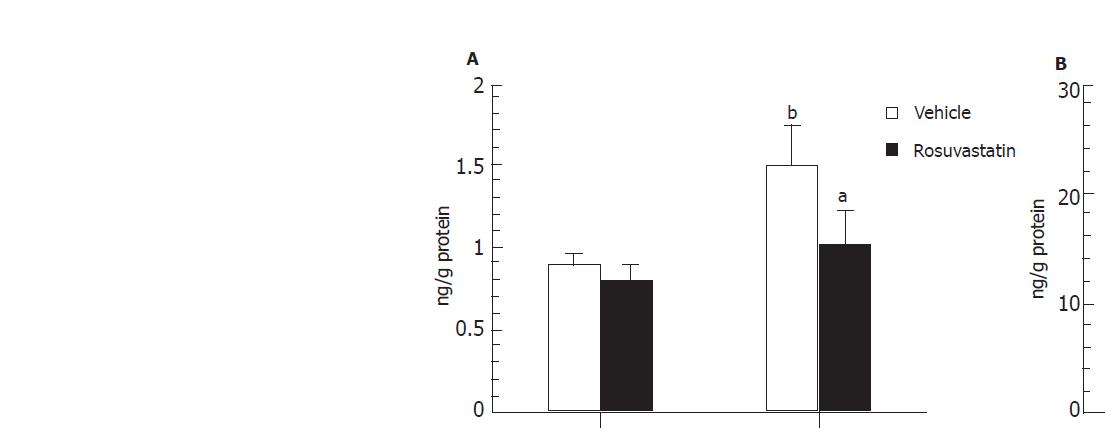
Figure 4 Effects of rosuvastatin on the intestinal CINC-1 and TNF-α after I-R in rats (mean+SE).
A: CINC-1; B: TNF-α. bP<0.01 vs Sham, aP<0.05 vs Vehicle + I-R.
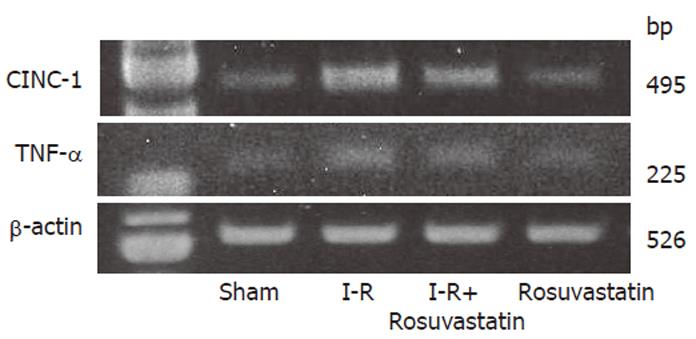
Figure 5 Effects of rosuvastatin on the expression of CINC-1 and TNF-α mRNA in the intestinal mucosa after I-R in rats.
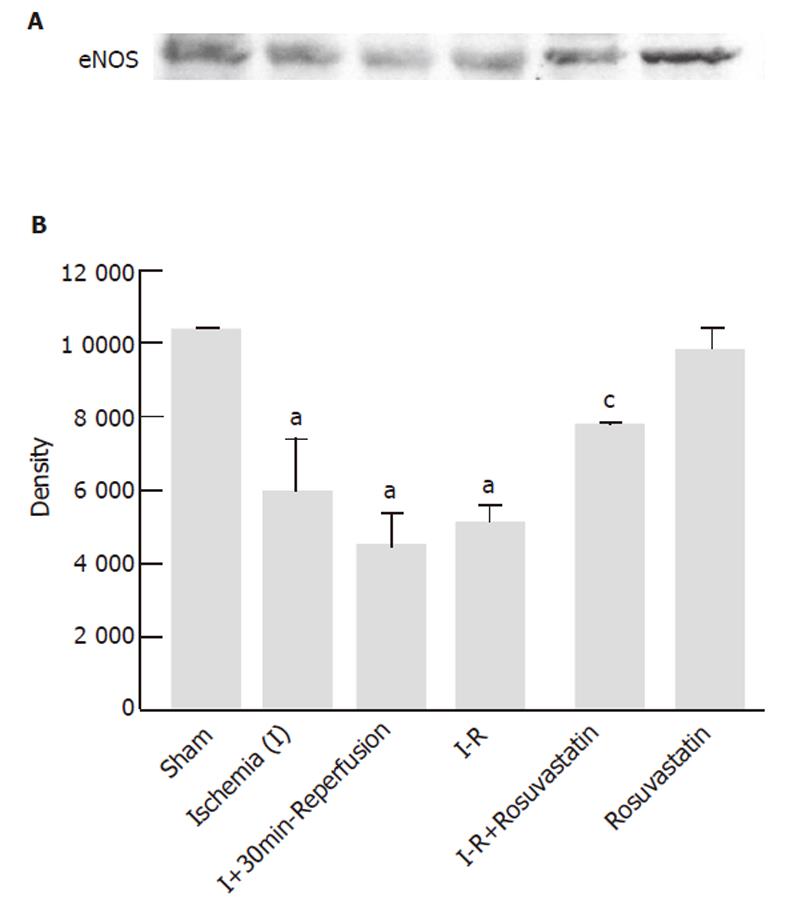
Figure 6 Effect of rosuvastatin on eNOS protein expression during I-R.
aP<0.05 vs Sham, cP<0.05 vs Vehicle + I-R.
- Citation: Naito Y, Katada K, Takagi T, Tsuboi H, Kuroda M, Handa O, Kokura S, Yoshida N, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T. Rosuvastatin reduces rat intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury associated with the preservation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase protein. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(13): 2024-2030
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i13/2024.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2024