Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2005; 11(34): 5336-5341
Published online Sep 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5336
Published online Sep 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5336
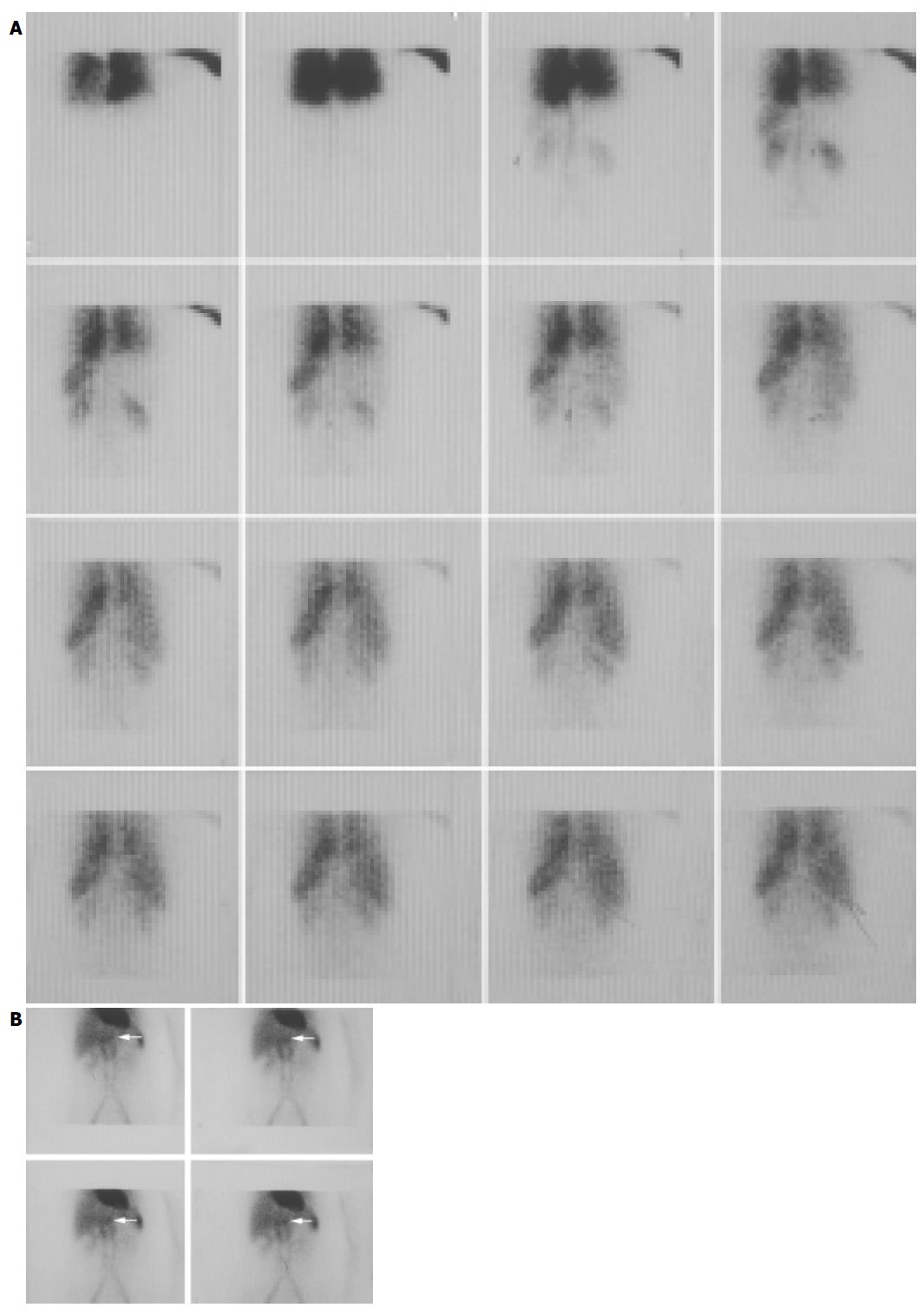
Figure 1 Female, 46 years old.
US showed that there was a lesion in the left liver with the size 3.6×2.3 cm2. The function of liver was normal. SPECT/CT test was carried out to exclude hepatic hemangioma. A: The hepatic blood perfusion imaging. The abnormal focal accumulation of the radioactivity was not shown obviously; B: The radioactivity accumulation of the focus (pointed by the red arrows) in the left liver was a little higher than the normal liver tissue.
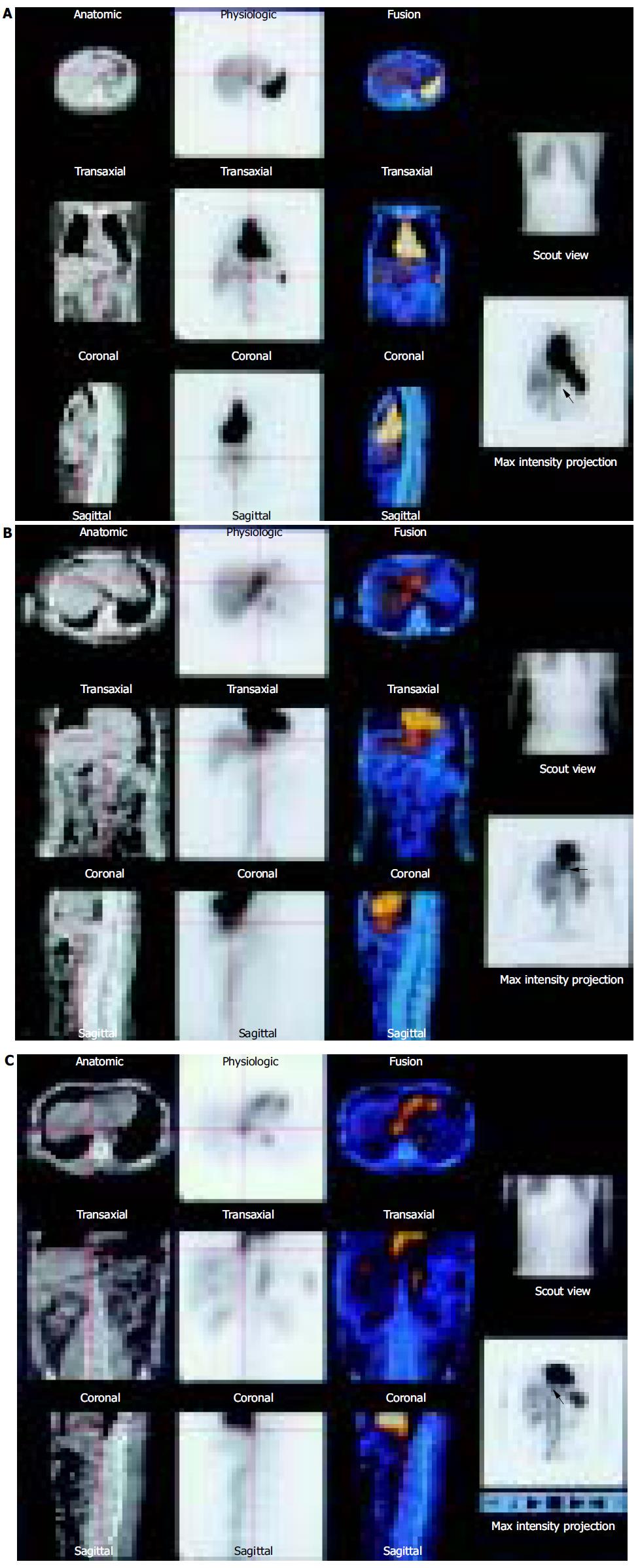
Figure 2 The round-like radioactive accumulation region (pointed by the red arrow) was just on the abdominal aorta.
If fusion imaging was not obtained, then to decide whether it was abdominal aorta or hepatic hemangioma would have been difficult. As shown in the CT of fusion imaging, the focus (the red cross) was located in the left liver, but not in abdominal aorta, thus diagnosed as hepatic hemangioma. Female, 39 years old. A lesion in the liver with the diameter of 4 cm was found in the physical examination by US. It might be a hepatic hemangioma. SPECT/CT was performed for differentiation (A). The hepatic lesion (pointed by the red arrow) situated adjacent to the heart, whose abnormal radioactive concentration was a bit lower than the heart. The CT showed that the lesion (the red cross) was located in the left liver. The diagnosis was a left hepatic hemangioma. Male, 43 years old. The US showed a few lesions in the liver. They were sceptical of hepatic hemangiomas to go through SPECT/CT examination (B). The abnormal focal radioactive concentration region of left liver (pointed by the red arrow) was not only close to the heart, but also close to the inferior cava. The CT indicated that it was a part of the inferior cava (the red cross), and exclude the possibility of hepatic hemangioma. But other three round-like radioactive accumulation regions in the right liver were diagnosed as hepatic hemangiomas (C).
- Citation: Zheng JG, Yao ZM, Shu CY, Zhang Y, Zhang X. Role of SPECT/CT in diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(34): 5336-5341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i34/5336.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5336