Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2005; 11(27): 4268-4271
Published online Jul 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4268
Published online Jul 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4268
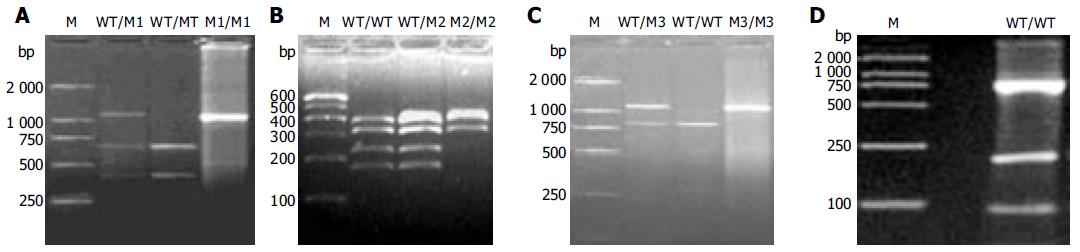
Figure 1 NAT2 genotype analysis by PCR-RFLP.
M: DNA Marker (100, 250, 500, 750, 1 000, 2 000 bp); A: digest with Kpnl (M1 allele) shows wildtype genotype (lane 2: 660 and 433 bp, WT/WT), variant genotype (lane 3: 1 093 bp, M1/M1) and heterozygote genotype (lane 1: 1 093, 660 and 433 bp, WT/M1); B: digest with Taq1 (M2 allele) shows wildtype genotype (lane 1: 380, 317, 226 and 170 bp, WT/WT), variant genotype (lane 3: 396, 380 and 317 bp, M2/M2) and heterozygote genotype (lane 2: 396, 380, 317, 226 and 170 bp, WT/M2); C: digest with BamHI (M3 allele) shows wildtype genotype (lane 2: 811 and 282 bp, WT/WT), variant genotype (lane 3: 1 093 bp, M3/M3) and heterozygote genotype (lane 1: 1 093, 811 and 282 bp, WT/M3); D: digest with MspI/AluI (M4 allele) shows wildtype genotype (lane 1: 759, 189, 91 and 53 bp, WT/WT).
-
Citation: He LJ, Yu YM, Qiao F, Liu JS, Sun XF, Jiang LL. Genetic polymorphisms of
N -acetyltransferase 2 and colorectal cancer risk. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(27): 4268-4271 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i27/4268.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4268