Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2005; 11(20): 3060-3064
Published online May 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i20.3060
Published online May 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i20.3060
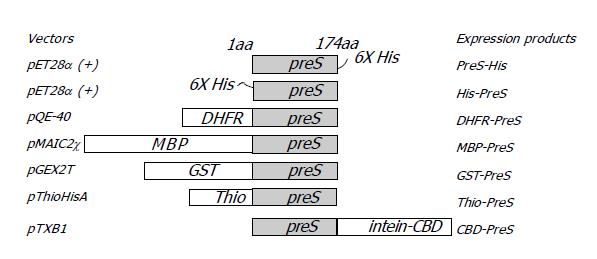
Figure 1 Diagram of various PreS fusion proteins.
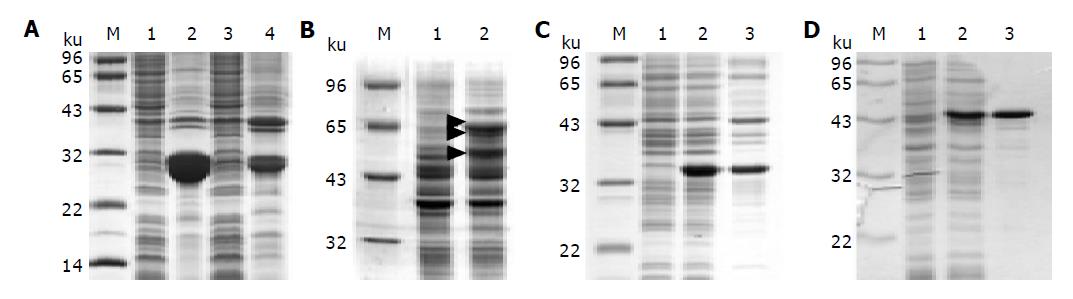
Figure 2 SDS-PAGE of the PreS fusion proteins.
A: His-tagged PreS. Lanes 1 and 2: His-PreS; lanes 3 and 4: PreS-His; lanes 1 and 3: supernatants of the E.coli lysate; lanes 2 and 4: insoluble pellets; B: MBP-PreS. Lane 1: bacteria lysate without IPTG induction; lane 2: supernatant of the bacteria lysate after IPTG induction. The 60 kD intact protein and degradation products of MBP-PreS are indicated with triangles; C: thio-PreS. Lane 1: bacteria lysate without IPTG induction; lane 2: whole lysate after IPTG induction; lane 3: supernatant of the E.coli lysate after IPTG induction; D: PreS-CBD. Lane 1: bacteria lysate without IPTG induction; lane 2: PreS-CBD in the supernatant of the bacteria lysate after IPTG induction; lane 3: Purified PreS-CBD coupled to the chitin resin. Molecular weight marker is denoted as M in all figures.
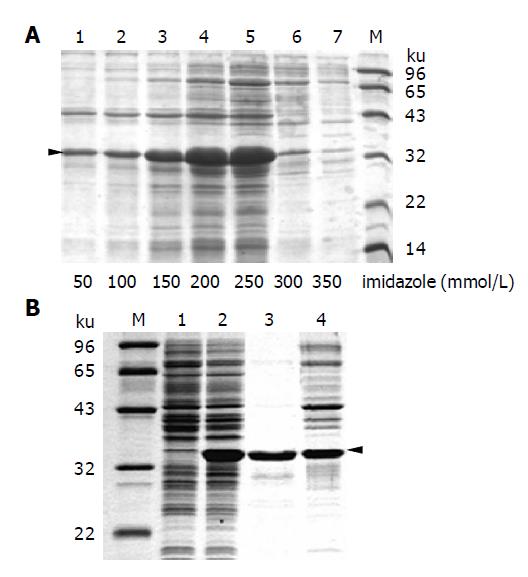
Figure 3 Purification of thio-PreS.
A: Fractions of thio-PreS eluted with increasing imidazole concentrations listed at the bottom of each lane. The triangle indicates the position of thio-PreS; B: Further purification with a freeze-thaw treatment. Lanes 1 and 2: supernatants of the bacteria lysate before or after IPTG induction, respectively; lanes 3 and 4: supernatant and precipitate of the affinity purified thio-PreS sample after a freeze-thaw treatment. Molecular weight maker is denoted as M.
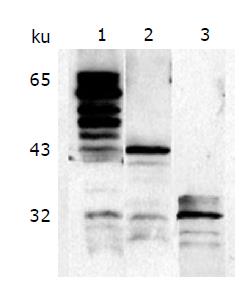
Figure 4 Characterization of the fusion proteins with Western blot.
Figure 5 Virus capture assay.
- Citation: Deng Q, Kong YY, Xie YH, Wang Y. Expression and purification of the complete PreS region of hepatitis B Virus. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(20): 3060-3064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i20/3060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i20.3060