Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2005; 11(16): 2402-2407
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2402
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2402
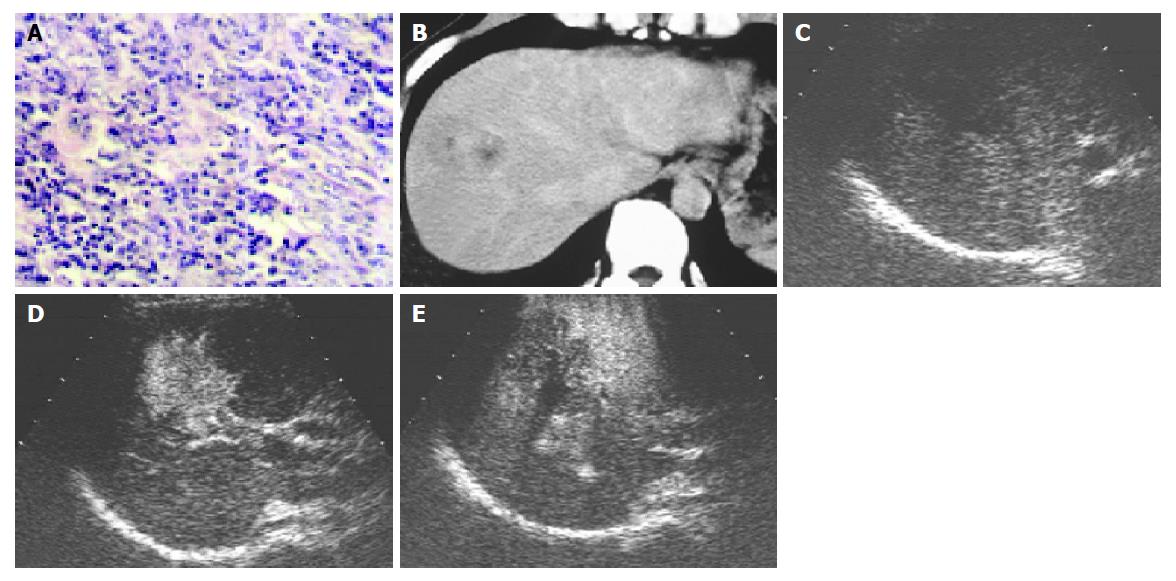
Figure 1 A: hepatocellular carcinoma; B: heterogenous high attenuation on contrast-enhanced CT; C: low echo on B-mode image; D: the hypervascularity in early arterial phase on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology; E: perfusion defect in the late phase on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology.
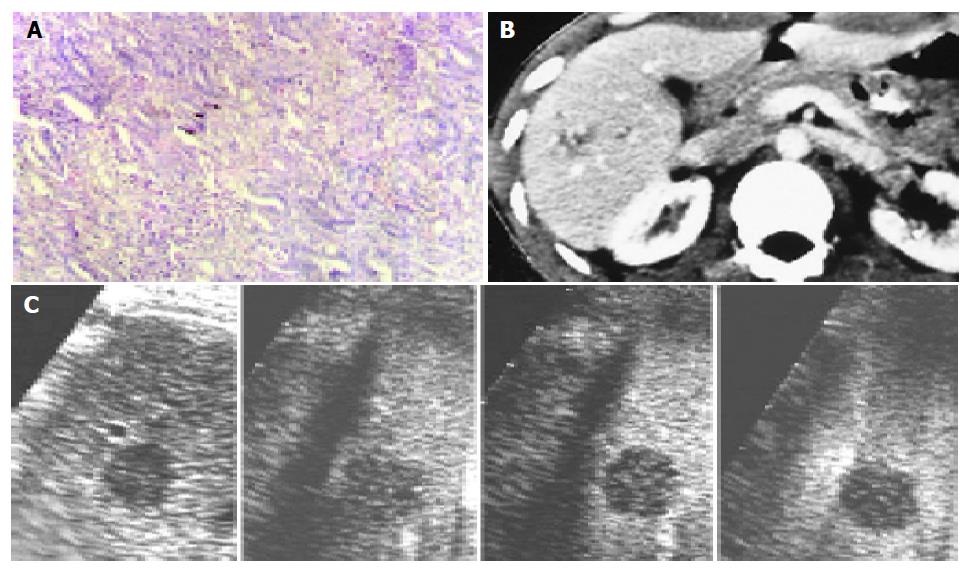
Figure 2 A: a 1.
5 cm-sized metastatic adenocacinoma in liver; B: low attenuation on contrast-enhanced CT; C: rim-like enhancement in early arterial phase (28 s) and perfusion defect (46-130 s) on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology.
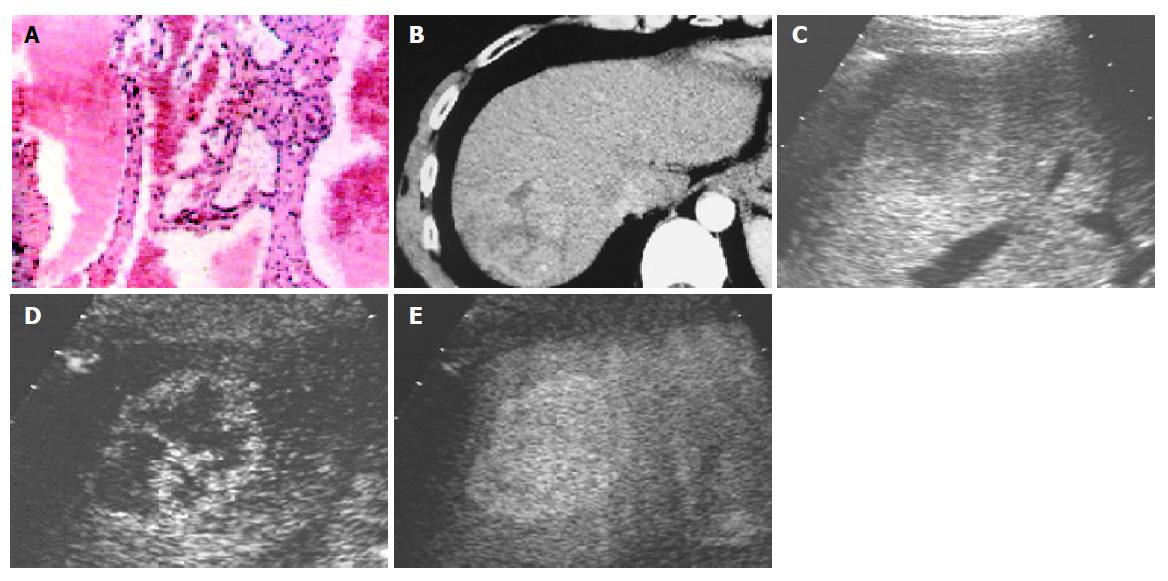
Figure 3 A: a 4.
1 cm-sized hemangioma; B: heterogenous high attenuation on contrast-enhanced CT; C: hypoechoic lesion on B-mode image; D: the spot-like enhancement in early arterial phase on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology; E: centripetal filling in late phase (e) on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology.
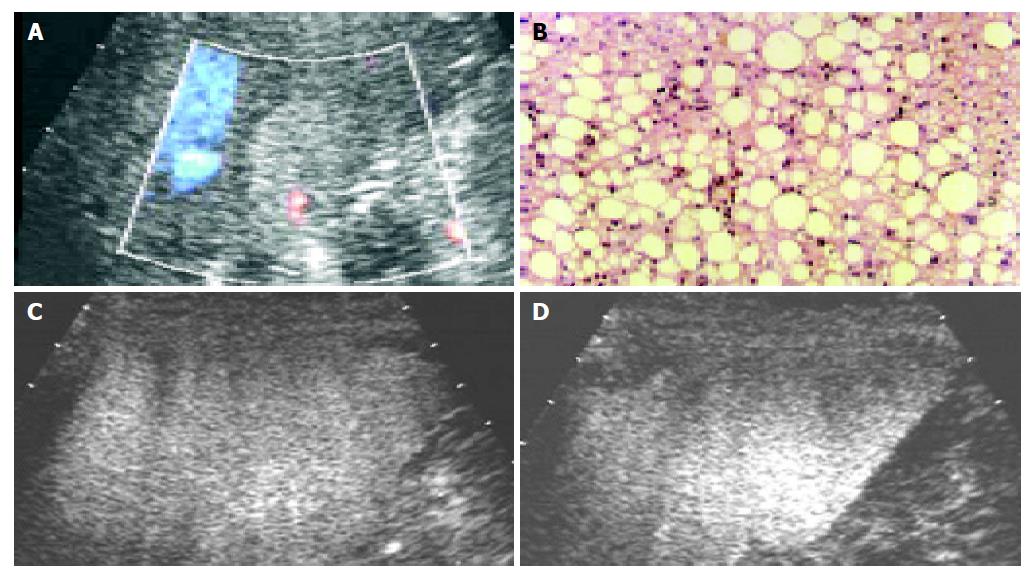
Figure 4 A: a hyperechoic lesion; B: pathological diagnosis of fatty degeneration; C: the intranodular enhancement on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology in the early arterial phase; D: the intranodular enhancement in the late phase on contrast-enhanced C3-MODE technology.
- Citation: Luo BM, Wen YL, Yang HY, Zhi H, Ou B, Ma JH, Pan JS, Dai XN. Differentiation between malignant and benign nodules in the liver: Use of contrast C3-MODE technology. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(16): 2402-2407
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i16/2402.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2402