Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2005; 11(12): 1747-1752
Published online Mar 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i12.1747
Published online Mar 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i12.1747
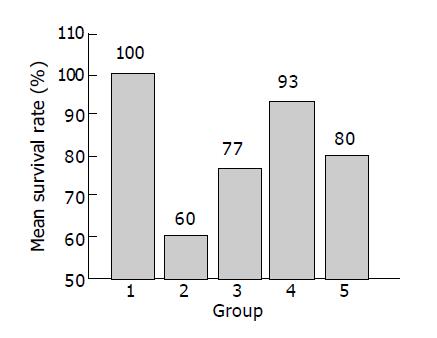
Figure 1 Effects of curcumin on the survival rate of rats with TNBS-induced colitis.
Group 1: 50% ethanol group. Group 2: TNBS group. Group 3: 0.5 % SASP group. Group 4: 2.0% curcumin preventive group. Group 5: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
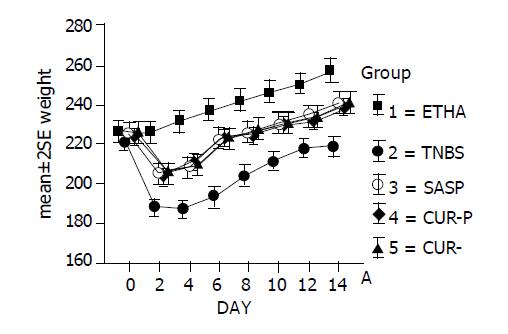
Figure 2 Effects of curcumin on body weights of rats with TNBS-induced colitis.
■: 50%ethanol group. ●: TNBS group. 〇: 0.5 % SASP group. ◆: 2.0% curcumin preventive group. ▲: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
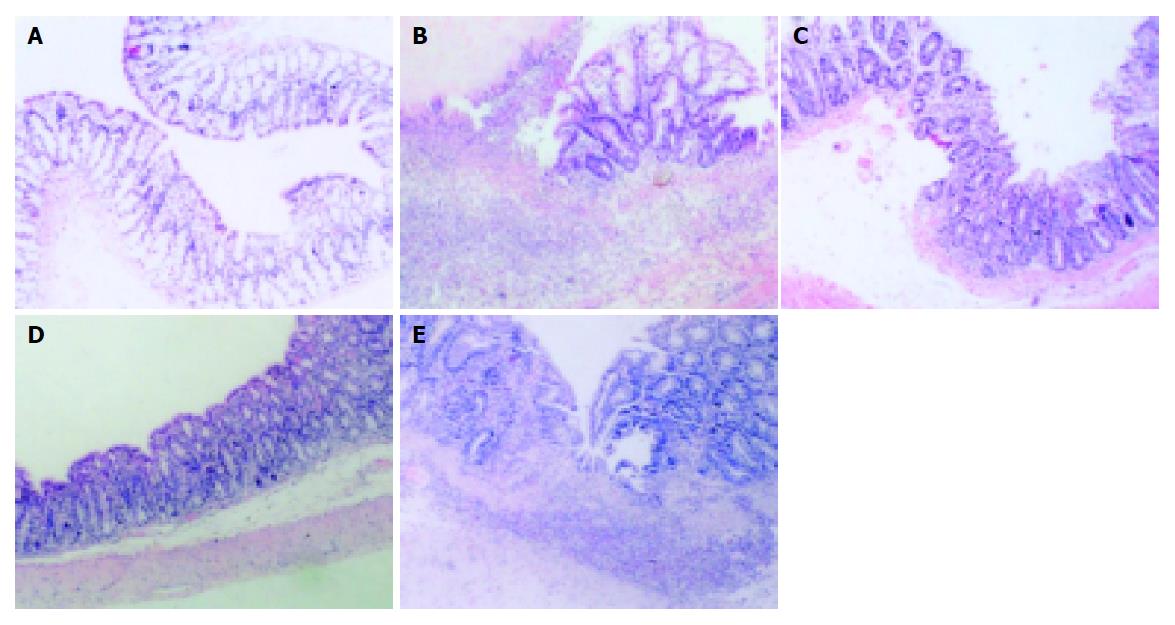
Figure 3 Results are shown as the intestinal histologic features of each group rats stained with HE.
A: 50% ethanol group; B: TNBS group; C: 0.5 % SASP group; D: 2.0% curcumin preventive group; E: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
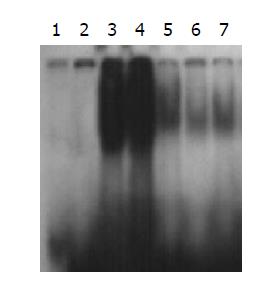
Figure 4 Effects of curcumin on NF-κB activity of colonic mucosa in rats with TNBS-induced colitis.
Lane 1: 50% ethanol group; lane 2: cold probe control group; lanes 3 and 4: TNBS group; lane 5: 0.5 % SASP group; lane 6: 2.0% curcumin preventive group; lane 7: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
Figure 5 Results are shown as effects of curcumin on IκB degradations.
Lanes 1, 2: 50% ethanol group; lane 3: TNBS group; lane 4: 0.5% SASP group; lane 5: 2.0% curcumin preventive group; lane 6: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
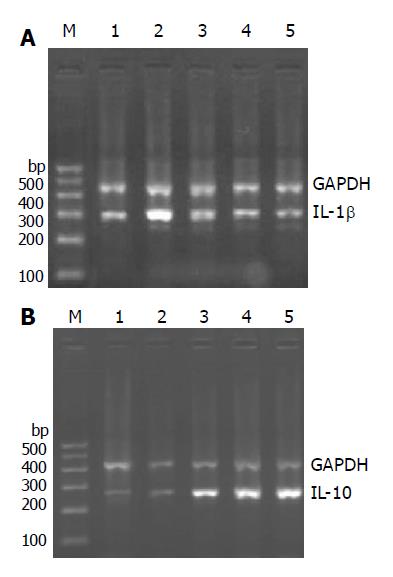
Figure 6 Effects of curcumin on expression of cytokine IL-1β mRNA(A) and IL-10 mRNA(B) in the colonic mucosa in TNBS-induced colitis.
Lane M: DNA MARKER. Lane 1: 50% ethanol group; lane 2: TNBS group; Land 3: 0.5% SASP group; lane 4: 2.0% curcumin preventive group; Land 5: 2.0% curcumin therapeutic group.
- Citation: Jian YT, Mai GF, Wang JD, Zhang YL, Luo RC, Fang YX. Preventive and therapeutic effects of NF-kappaB inhibitor curcumin in rats colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(12): 1747-1752
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i12/1747.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i12.1747